Global Population Distribution (SQA National 5 Geography): Revision Note
Exam code: X833 75
Specification checklist
This page covers what you need to know from the SQA National 5 geography specification to answer questions on:
Physical and human factors influencing global population distribution
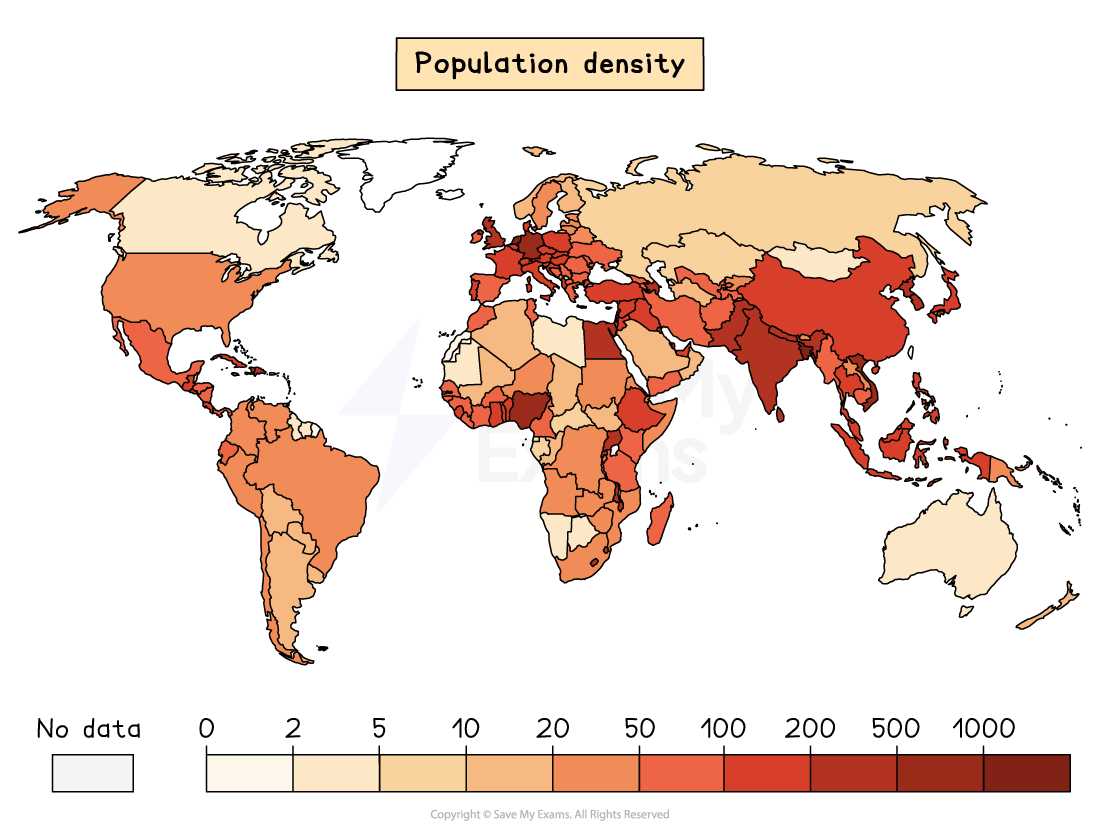
What is global population distribution?
Global population distribution is the way people are spread across the world
Population distribution is uneven
Approximately 5% of the Earth's land surface supports 75% of the population
Around 80% of the world's population lives in the northern hemisphere
Population density also varies across the world
Population density is calculated by dividing the total population by the total area
It is measured in the number of people per km2
The total area can be on different scales - region, country, continent
Population distribution refers to where people live
It is affected by both physical and human factors
Areas that have more positive characteristics (both physical and human) are more able to sustain a population and so will have higher population levels
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If asked to describe population density and distribution in the exam, remember that they do not mean the same thing
Density refers to the actual number of people living in an area per km2
Distribution refers to where people live
Physical factors affecting global population distribution
Climate and weather
Temperate climates with stable weather conditions are more attractive for settlements
Areas with consistent sunlight, temperature and precipitation are viewed as more suitable because there is enough rainfall to provide water
Very dry areas, very cold or very wet regions often have sparse populations because low rainfall and/or low temperatures make farming difficult
Relief and landforms
The shape and elevation of the land affect the accessibility, soil quality, drainage and natural hazards of an area
Volcanic areas, river deltas, lowland plains and valleys with fertile soil have higher population densities
Flat land is attractive for building settlements and is easiest for agricultural activities
Steep slopes and mountainous areas with poor-quality soil have low population densities
Soil types and quality
Volcanic areas can be highly attractive due to the fertile soil and resources and minerals (sulphur, gold, diamonds, etc.) brought to the surface for economic activity
Vegetation
Grasslands are more attractive for the development of settlements
Areas with dense forest or a lack of vegetation have sparse populations
Natural resources such as freshwater, raw materials and minerals
The presence of fresh water, minerals, fossil fuels, forests, fisheries and other resources attracts human settlement and economic activity
Natural landscapes with attractive scenery attract tourists, which creates jobs
Areas that are dry or suffer from regular drought or excessive rainfall, or are prone to flooding, are less densely populated
Areas that lack resources often have little industry, so employment opportunities are limited
Natural hazards
The frequency and intensity of earthquakes, volcanoes, floods, droughts, hurricanes and other events can deter or displace human populations
Human factors affecting global population distribution
Economic development and jobs
Areas with higher levels of income, trade, and industrialisation tend to attract more people and offer better living standards
Past industrial regions such as Glasgow, Manchester and Sheffield have continued higher densities of population
Political stability
Areas with lower levels of conflict, violence, and corruption tend to be more peaceful and secure, which encourages population growth and migration
Services
Areas with better access to education, health care, and social welfare tend to have a higher quality of life and lower mortality rates
Services such as entertainment and retail also attract people to some areas
Government aid
Some areas receive government funding, which attracts industries and creates jobs
Transport and communication
Better transport infrastructure makes some places more accessible
The central lowlands of Scotland have higher population densities because they are more accessible by road and train
Places which are more accessible attract businesses and industry, which creates jobs
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the exam, you may be asked to give reasons for the differences in population density around the world. You will be expected to be able to give both physical and human factors that affect where people live.
Worked Example
Look at Diagram Q12.
Give reasons for the differences in population density across the world.
You may refer to both physical and human factors in your answer.
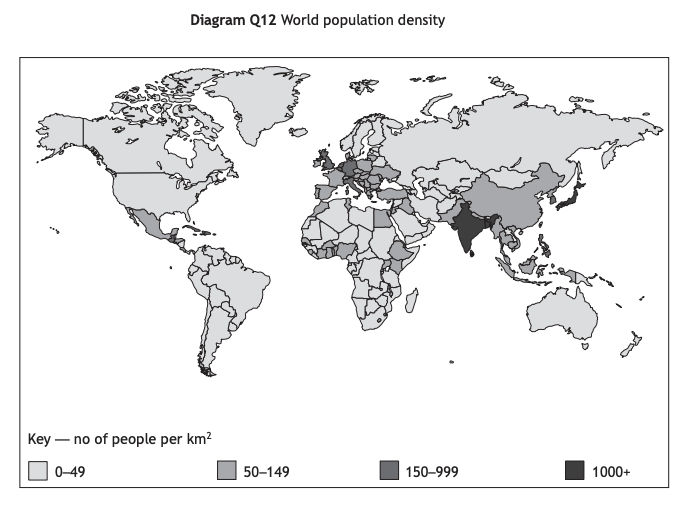
Answer
People prefer to live in a temperate climate where it is not too hot or cold [1]. Fewer people live in areas of extreme climate, such as the Sahara or the Arctic. [1]
More people tend to live in areas where there are plenty of natural resources[1] Areas with fewer natural resources tend to have less industry and so fewer jobs.[1]
Cities have higher population densities because there are more jobs available. [1] They are also more accessible because of better transport links. [1]
This is one possible response to the question; many other reasons could be given
One mark is awarded for each valid point (up to a maximum of six marks)
A valid developed point would be awarded two marks

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
