Population Increase (SQA National 5 Geography): Revision Note
Exam code: X833 75
Specification checklist
This page covers what you need to know from the SQA National 5 geography specification to answer questions on:
Factors affecting birth and death rates
Global population growth
Nearly 80 million people are added to the world's population each year
Population growth was steady and low until 1804, when the world population reached 1 billion
After 1804, it took just over 100 years for the population to double to 2 billion
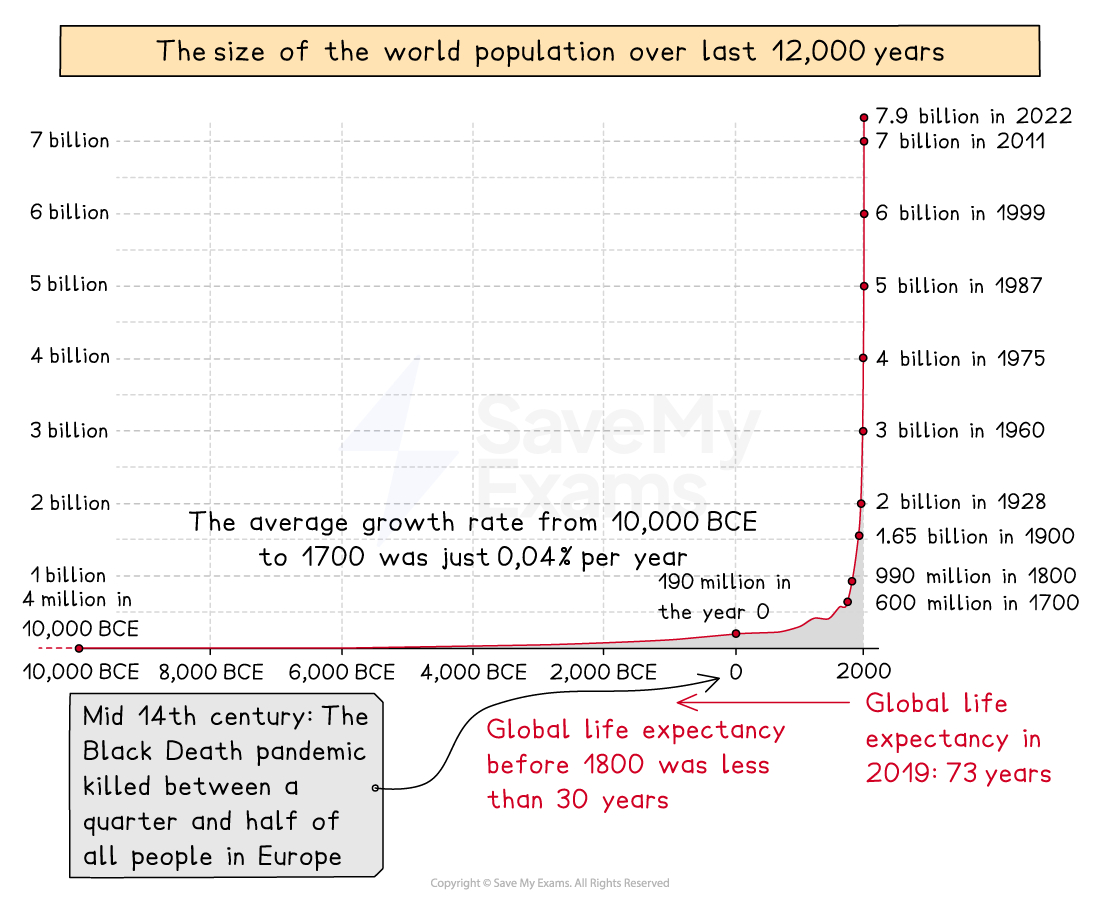
The rate of increase after 1930 was more rapid and led to a population explosion
The fastest increase in population happened during the 1980s and 1990s
Population growth rate is the average annual change of the population size during a set period of time, usually a year
The population is still increasing, but at a slower rate
In 1970, the growth rate was 2%
In 2022, the growth rate was under 1%
It is predicted by the UN that the population will stabilise at around 11 billion in 2100
Factors affecting birth and death rates
What is natural increase?
Natural change in population is calculated by subtracting the death rate from the birth rate
The combination of a decreasing death rate and a high birth rate led to a rapid natural increase and population explosion
A natural decrease happens when the birth rate is lower than the death rate
What is the birth rate?
The birth rate is the number of live babies born per 1000 people
This figure is calculated by:
dividing the total number of births by the total population and multiplying by 1000
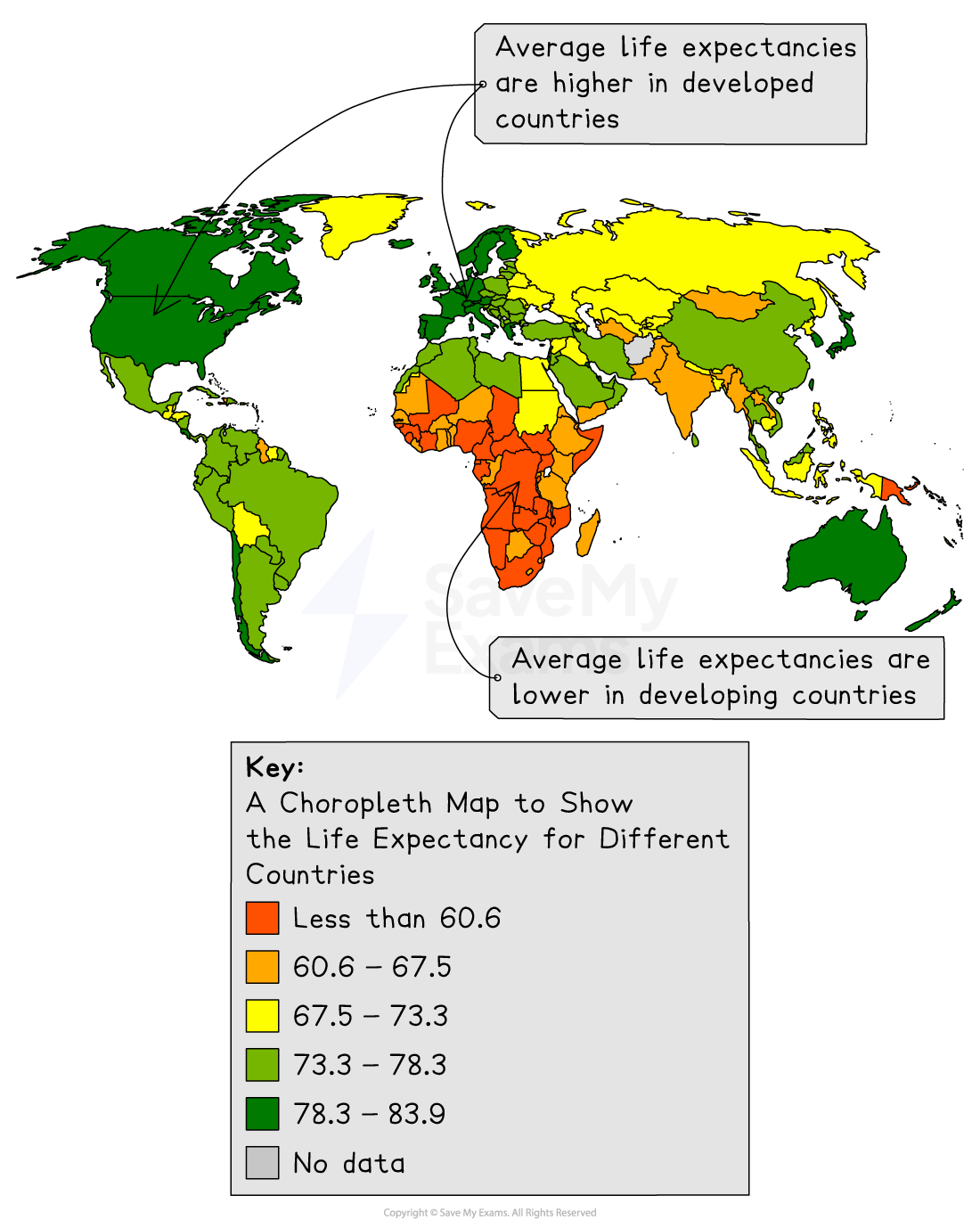
In developed countries, the birth rate tends to be low, whereas in developing countries, the birth rate tends to be high
What is the death rate?
The death rate is the number of deaths per 1000 people
This figure is calculated by:
dividing the total number of deaths by the total population and multiplying by 1000
In developed countries, the death rate tends to be low, whereas in developing countries, the death rate tends to be high
Why do death rates change?
Globally, there has been a decrease in death rates and an increase in average life expectancy
This is the result of improvements in:
Agriculture
Medicine and medical care
Water supply and sewage disposal lead to a reduction in disease
Agriculture
Improvements in agriculture and food production have led to:
Increased calorie intake
More varied diets
Less malnutrition
Medicine and medical care
Advances in medicine and medical care include:
More medicines to treat a wider variety of diseases and illnesses, for example, the development of antibiotics, vaccines and chemotherapy
Greater medical knowledge and understanding
Increases in the number of doctors and health care professionals
Improved care for the elderly
Water supply and sanitation
Clean water and improved sanitation decrease death rates because:
It reduces the spread of diseases such as cholera and typhoid
These developments have happened more rapidly in developed countries, leading to lower death rates in these countries
Why do birth rates change?
The birth rate in developed countries has decreased due to:
Increased access to contraception
More education and information regarding family planning
Greater gender equality has led more women to have careers and have children later in life, which results in fewer children being born
The cost of raising children leads to people having smaller families
The birth rate has remained high mainly in developing countries due to:
Lack of access to family planning and contraception
An increase in the number of women surviving childbirth
Families continue to have large numbers of children to look after their parents in old age and to help support the family
A culture of having larger families, which takes many years to change
Religious reasons
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Population also changes as a result of migration into and out of a country/area but this is not part of the natural increase.
Worked Example
Look at Diagram Q9B.
Give reasons for the falling worldwide death rates.
Answer
Improved diets with a variety of foods mean that people live longer [1]
Better pensions and elderly care mean that people are more cared for and so live longer [1]
Improvements in medical care mean people are less likely to die of illnesses or diseases. [1]
Vaccinations against disease have reduced death rates [1]
These are just some examples of the reasons which could be given
One mark is awarded for each valid point
A developed point may be awarded two marks
A list of reasons will gain a maximum of one mark

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
