Factors Affecting Weather in the UK (SQA National 5 Geography): Revision Note
Exam code: X833 75
Specification checklist
This page covers what you need to know from the SQA National 5 geography specification to answer questions on:
Within the context of the United Kingdom:
The effect of latitude, relief, aspect and distance from sea on local weather conditions
The impact of latitude on weather
Temperatures decrease the further an area is from the equator
This is due to the curvature of the Earth
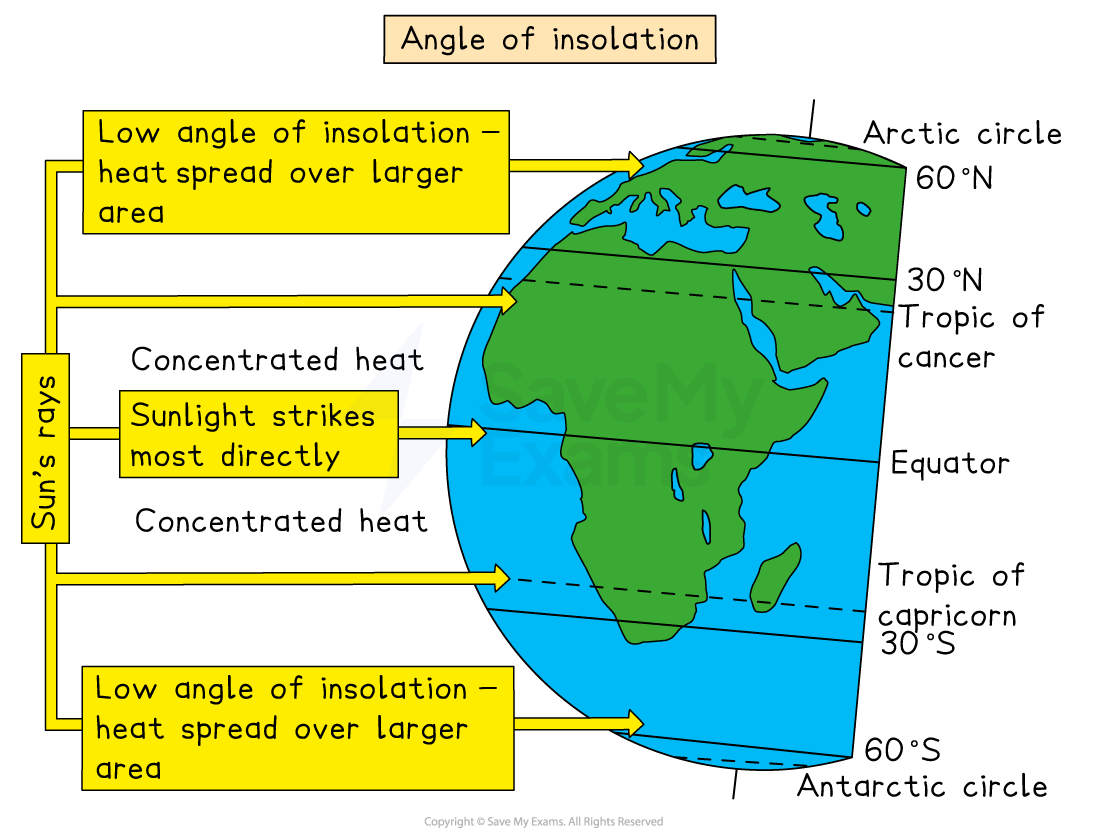
In areas closer to the poles, the amount of insolation (solar radiation) is reduced because:
It has a larger area of atmosphere to pass through
The sun is at a lower angle in the sky
The heat is spread over a larger area
As a result, more energy is lost and temperatures are cooler
In the UK, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun
This means that the sun is more intense than at other times of the year
For six months of the year, the poles receive little or no solar energy due to the Earth’s orbit and tilt
In polar regions, snow and ice cover reflect much more of the solar radiation, giving a high albedo effect
The impact of relief on weather
Altitude refers to the height above sea level
The relief of the land refers to variations in height and shape
Locations at higher altitudes have colder temperatures
Temperature usually decreases by 1°C for every 100 metres in altitude
This is because air at higher altitudes is thinner, as the gas molecules are further apart
This makes it difficult for heat to be transferred between the molecules due to the distance between them
Areas at higher altitudes are also more affected by wind chill
Wind chill is a measure of how cold the air feels on your skin because cold winds take away body heat more quickly.
Upland areas, therefore, have cooler average temperatures due to strong winds and the wind chill effect
The impact of aspect on weather
Aspect is the direction that a slope is facing
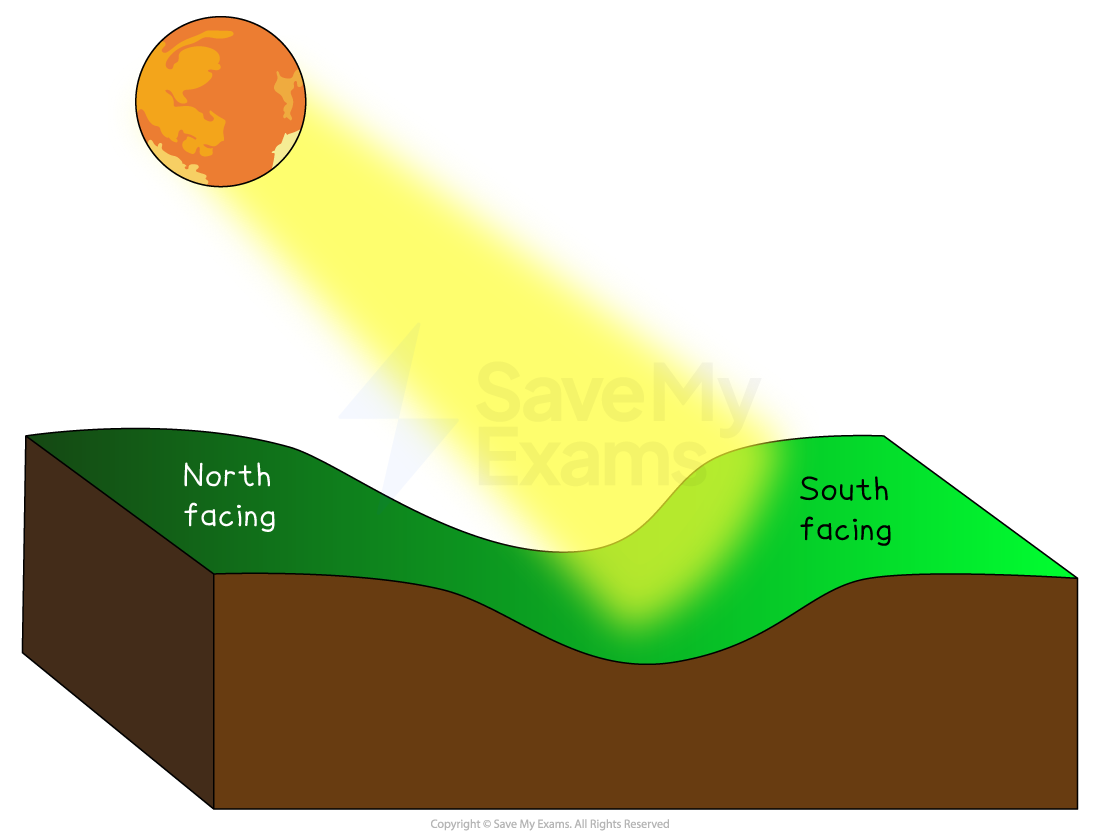
In the northern hemisphere, slopes and buildings which are south-facing are warmer and places which are north-facing are colder
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west
North-facing slopes remain shaded (e.g. northern-facing slopes of the Cairngorms)
The northern corries are used for skiing as they hold the snow, while south-facing slopes which receive more sunshine are used for:
Forestry
Grazing
Settlement
The impact of distance from the sea on weather
Oceans heat up and cool down much more slowly than land
They are ‘thermal reservoirs’
This means that their temperature stays more constant than the land
In summer, the sea is cooler than the land and in winter it is warmer
Coastal locations are affected by this more than places inland at the same latitude and altitude
They are:
Cooler in summer
Milder in winter
In Edinburgh and other coastal areas on the east coast, summer temperatures can be significantly reduced compared to places just a few miles inland because of haar (sea fog)
Worked Example
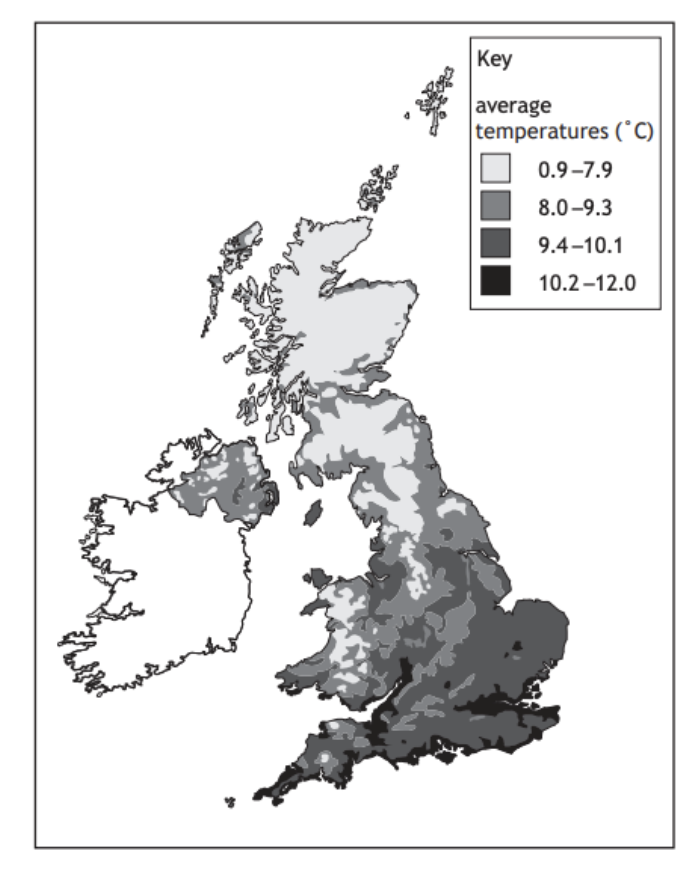
Look at Diagram Q1
Explain the factors which affect average UK temperatures.
You may refer to factors such as latitude, relief, aspect and distance from the sea in your answer.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Think about where it is colder and wetter in the UK and the reasons for this. This will help you apply this information to your answer.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
