National Socialism in Power: Treatment of Jews & other Minority Groups (SQA National 5 History): Revision Note
Exam code: X837 75
Summary
The Nazis believed only “Aryan” Germans should have rights, so they targeted Jews and others. From 1933, Jewish people lost jobs and faced boycotts. This was followed by further discrimination and violence through the Nuremberg Laws and 'Kristallnacht'.
Other groups were also attacked: People from the Roma population were killed, some Black people and people with disabilities were sterilised. Many patients with mental health illnesses were killed, and people seen as “anti-social” (including homosexuals and Jehovah’s Witnesses) were jailed in camps. The aim was to remove these groups from society using laws, fear, and violence.
Treatment of Jewish people by the Nazis
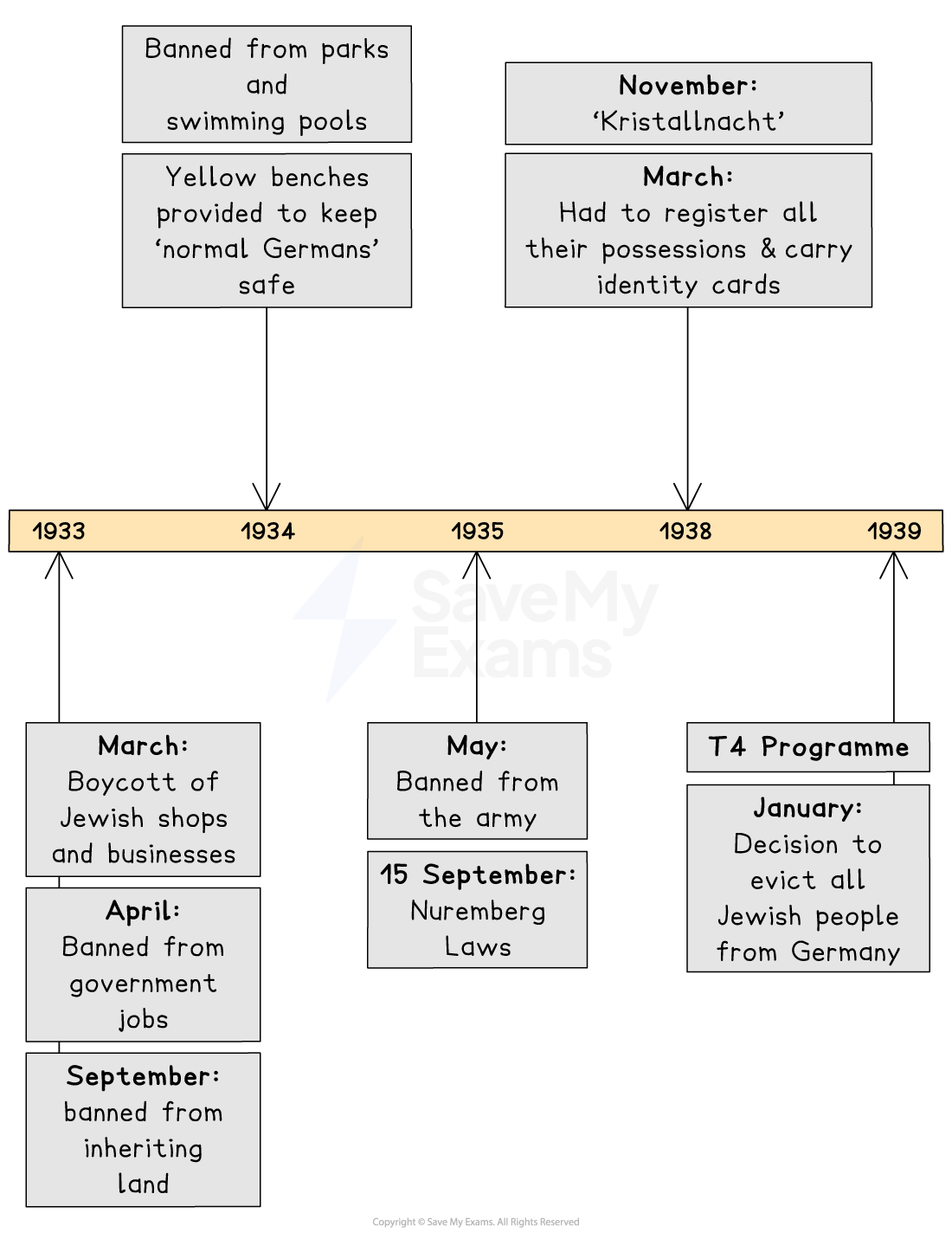
From 1933, Jewish people were sacked from public jobs and barred from many professions
The 1935 Nuremberg Laws took away German citizenship from Jewish people and banned mixed marriage or sex between Jewish people and “Aryans”
During 'Kristallnacht'(9–10 November 1938), synagogues and Jewish businesses were destroyed
Almost 100 people were killed
About 30,000 Jewish men were arrested
The men were sent to concentration camps
Persecution and discrimination continued from 1935
In 1938–39, Jewish people had to:
Carry ID cards
Add “Israel” or “Sarah” to their names
From November 1939, wear the Star of David
In 1939, many Jewish people were forced into ghettos in occupied Eastern Europe

Treatment of other minority groups by the Nazis
People from the Roma and Sinti populations were rounded up
Between 250,000 and 500,000 Roma and Sinti were killed by the Nazis
Black people and some Germans of mixed race were forcibly sterilised
Homosexuals were arrested under Paragraph 175 and sent to concentration camps
Jehovah’s Witnesses and other “asocial” groups were imprisoned for refusing to conform
The 1933 Sterilisation Law forced people with conditions judged “hereditary” to be sterilised
From 1939 the T4 programme killed thousands of people with disabilities or mental health issues gas, injections, or starvation
This was presented as “euthanasia” by the Nazis
Why did German people accept the treatment of minorities?
Propaganda was used to lie about the Jewish people and other minorities
This increased prejudice and discrimination
Many German people then accepted the violence, boycotts and sackings
People were frightened to speak out for fear of being arrested by the SS or Gestapo
Many people were arrested and sent to concentration camps without trial after speaking out
Jewish properties and businesses were given to non-Jewish Germans
This benefited some people
Worked Example
Explain the reasons why Jews and other minorities were treated so badly in Nazi Germany, 1933–1939
[6 marks]
Nazi ideology taught racism and antisemitism, so Jewish people and other minorities were seen as inferior and blamed for Germany’s problems. This belief encouraged harsh laws and violence against them. [1]
The aim of a “pure” Aryan people led to the Nuremberg Laws in 1935, which removed Jewish citizenship and banned marriages with Germans, making discrimination legal and routine. [1]
Propaganda repeated lies about Jews and other groups. Goebbels’ ministry used films, radio, and newspapers to spread hate, so many Germans accepted boycotts, sackings, and later violence like Kristallnacht in 1938. [1]
A police state enforced persecution. The Gestapo and SS arrested suspects without fair trials and sent many to concentration camps, so fear kept people silent and allowed harsher treatment. [1]
Economic gain encouraged persecution. “Aryanisation” took Jewish businesses and property and gave them to non-Jewish Germans, so some people benefited and supported tougher measures. [1]
Policies of “social hygiene” targeted other minorities. The 1933 Sterilisation Law and, from 1939, the T4 killings punished disabled people, while Roma, homosexuals, and Jehovah’s Witnesses were arrested and sent to camps. [1]

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
