Opposition to the Treaty of Versailles (SQA National 5 History): Revision Note
Exam code: X837 75
Summary
Many Germans opposed the Treaty of Versailles. The treaty created new borders which divided the German population and put foreign troops in parts of Germany.
To many people, these changes felt like a national insult. Many people refused to accept the treaty as permanent; they looked for leaders who promised to undo it. This harmed trust within the country and relations with other countries.
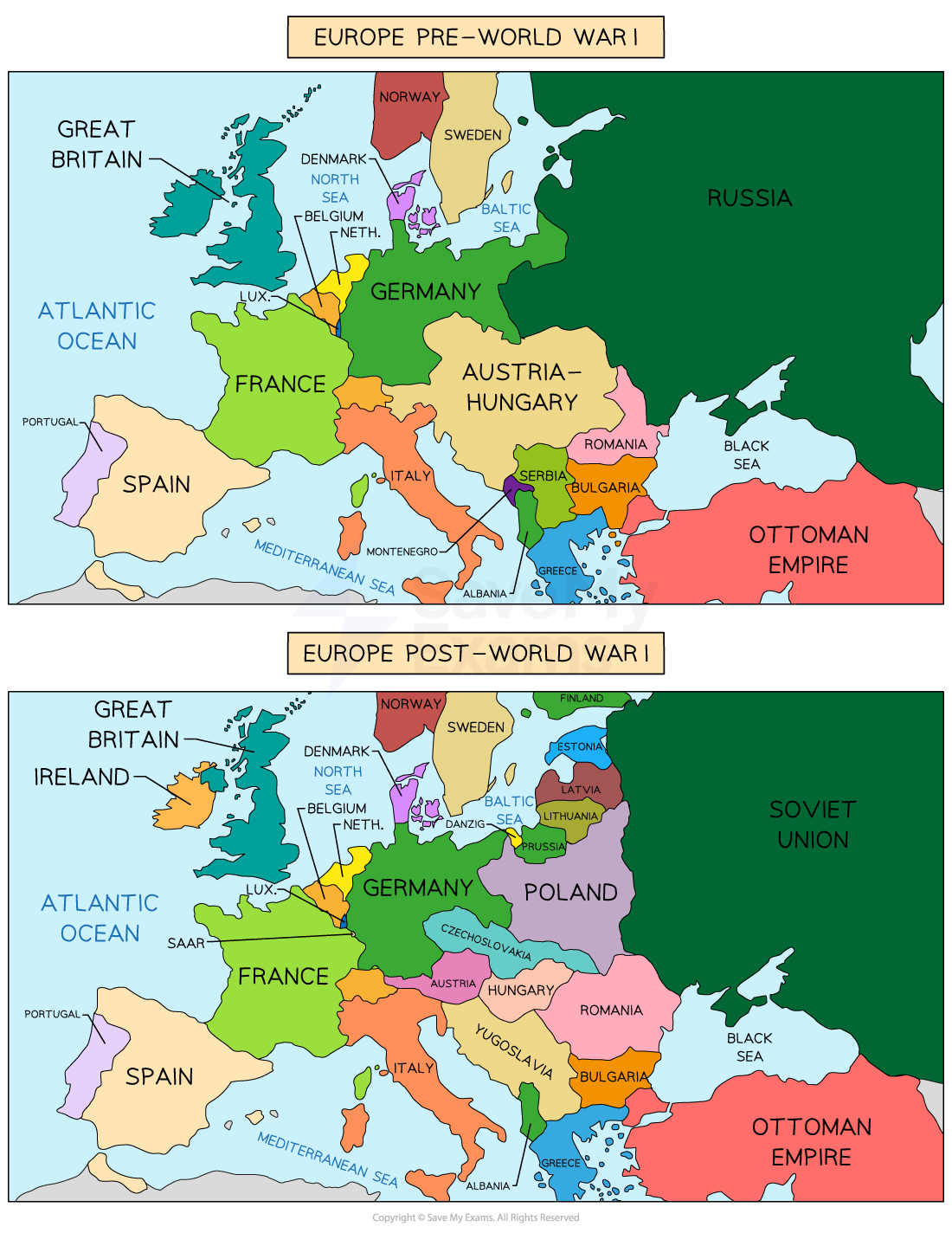
Opposition to the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was seen as unfair and humiliating
Many Germans called it a “diktat” (a deal forced on them)
Germany was not invited to the treaty talks
The war-guilt blame hurt people's pride, and losing land (like Alsace-Lorraine) angered people
Many Germans feared economic problems
Huge reparations and loss of coal and iron areas meant fewer jobs and higher prices
People were worried they would not be able to feed their families or rebuild the country
There was a huge political backlash because political parties on the right (and many army officers) swore to overturn the treaty
Protests and violence followed (for example, anger at army cuts and at reparation payments)
This weakened trust in the Weimar government
Reparations and loss of coal/iron areas hurt the economy
A crisis followed in 1923 (hyperinflation) and Germany became dependent on foreign loans in the late 1920s
Border changes meant new tensions began to build
New borders led to German minorities in countries like Poland and Czechoslovakia
Arguments over these areas led to later conflict

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
