Causes of the Great War (SQA National 5 History): Revision Note
Exam code: X837 75
Summary
European countries had formed two rival alliances: the Triple Entente (Britain, France and Russia) and the Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy). These alliances created an atmosphere of distrust and competition.
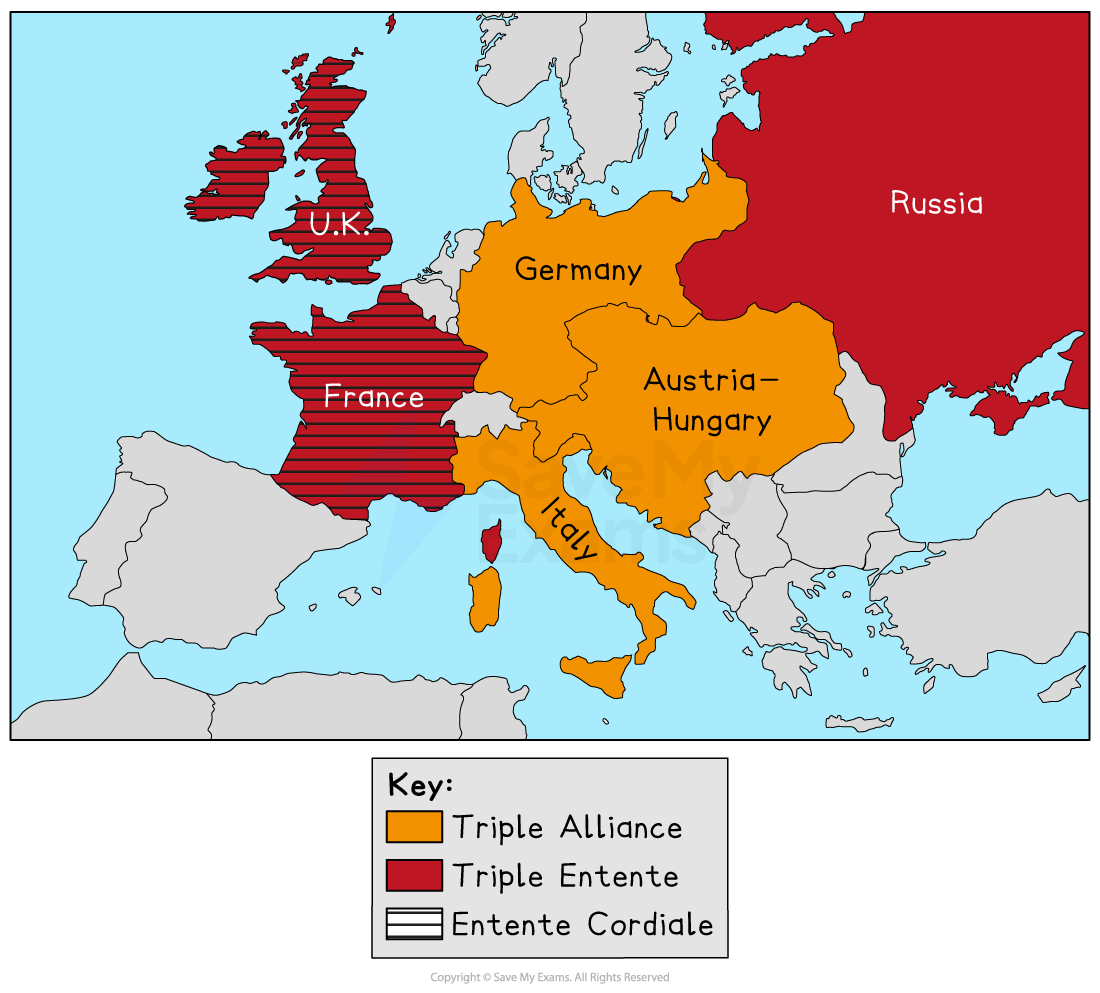
Countries raced to build powerful navies, expand their armies, and gain colonies overseas. Germany was rapidly building up its navy, aiming to become a major world power. This was a concern for Britain who had for many years dominated trade by sea.
In the years before 1914, tensions in Europe increased. France was still bitter about Alsace-Lorraine, a valuable region on the border that Germany had taken back in 1871. This meant France and Germany had a hostile relationship.
Another issue was Pan-Slavism: a movement where Slavic peoples in Eastern Europe wanted to support each other. Serbia led this movement with Russia's backing, which created conflict with Austria-Hungary, which controlled many Slavic territories.
In 1914, a Bosnian Serb assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir to the Austria-Hungarian throne. This assassination triggered the outbreak of war. As a result of the alliance system, when Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, its allies were drawn in to support it. Russia supported Serbia, Germany backed Austria-Hungary, and France and Britain joined Russia's side. What started as one seemingly isolated event quickly escalated into a war involving most of Europe.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The information on this page will not be covered in the final exam but provides the context to help you understand the content that will be examined.
Empires and trade
Empire rivalry
Britain and France both had huge empires
Germany wanted to become a dominant imperial power and acquire more colonies
This created distrust and suspicion between the countries
Germany was also building a larger navy
Britain was concerned because it depended on its control of the seas to dominate trade
Trade competition
Countries fought for markets and raw materials (coal, oil, metals)
Stronger trade meant more money for armies and navies, so economic rivalry increased military growth
Control of Alsace-Lorraine
Alsace-Lorraine is on the border between France and Germany, in north-eastern France today
Germany had taken control of Alsace-Lorraine from France in 1871, and France wanted it back
The French people wanted revenge
This created hostility between the two countries
The Balkans
The Balkans are a region in southeastern Europe
Just before the outbreak of war, the Balkans had many peoples and borders
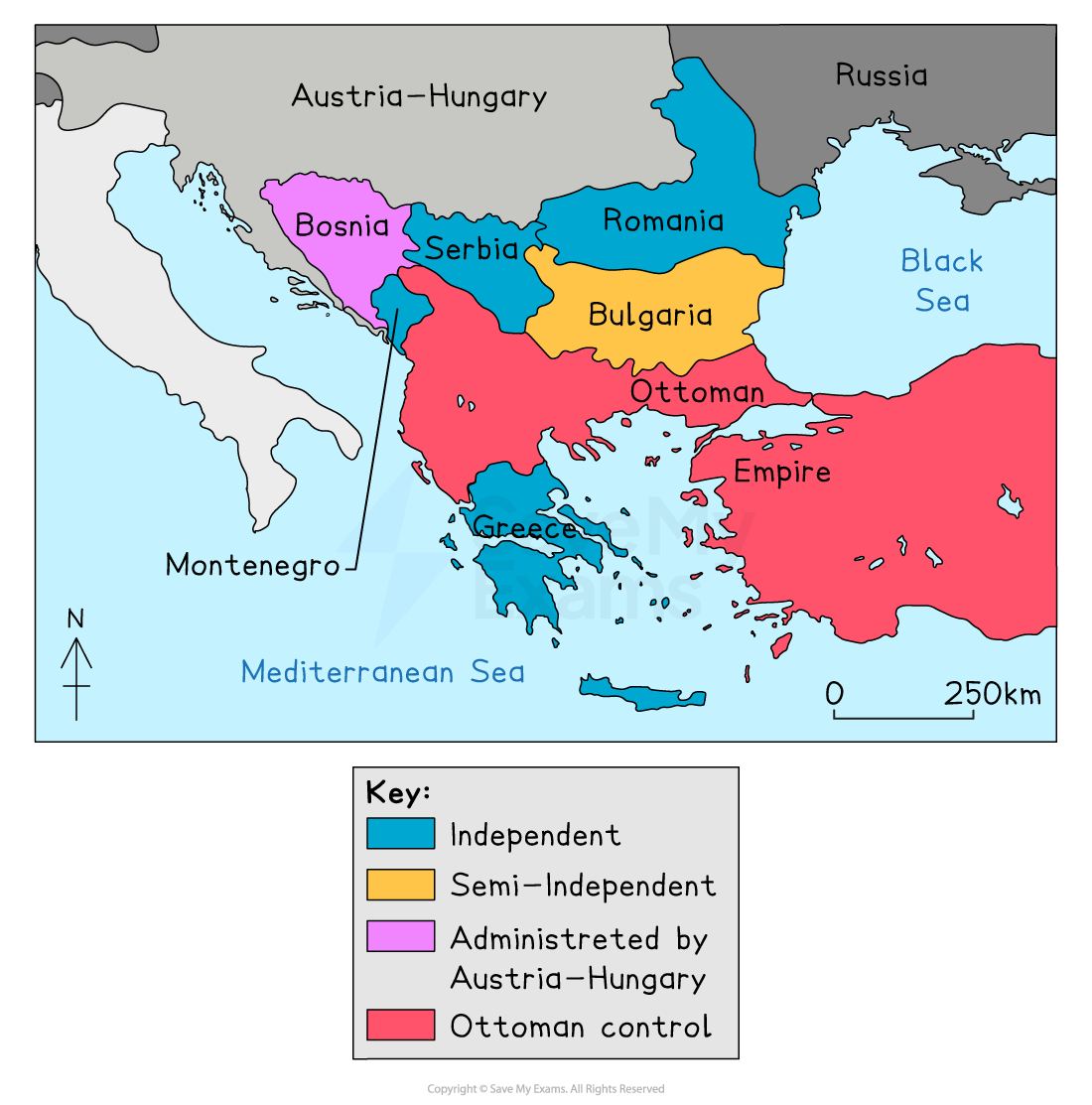
Serbia wanted to unite and lead the Slavic people
This was a problem because Austria-Hungary controlled regions where many Slavic people lived, and didn't want to lose the land
Russia supported Serbia because it was also a Slavic country
This meant that even small disagreements could quickly turn into big conflicts.
Serbia wanted to unite Slavs (Pan-Slavism)
This mix made relations in the region very tense and one of the reasons why it became known as the “powder keg” of Europe.
The impact of Pan-Slavism
Pan-Slavism was the idea that Slavic people should help each other
This gave Serbia the confidence to challenge Austria-Hungary's control over Slavic areas in the Balkans
Constant fighting (such as the Balkan Wars) created lots of anger and fear
When Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated in 1914, these tensions exploded and dragged the major powers into war
Relations between Britain and Germany
Britain and Germany entered into an arms race, each hoping to build a larger naval fleet than the other
As an island nation, Britain needed to ensure it had a larger naval fleet of Dreadnoughts to protect its sea trade and security
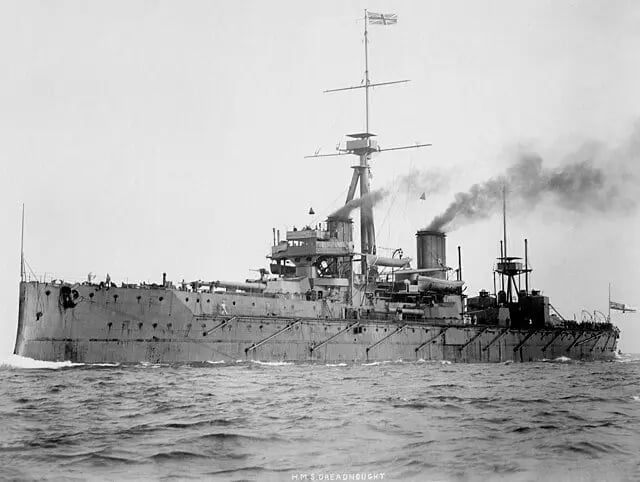

The British government realised that Germany was increasing its production of warships and the size of its navy
This affected relations between the two countries because Britain was suspicious of Germany
In 1914, Germany invaded Belgium as the first step in the plan to attack France,
Britain had to act because it had promised to protect Belgium in 1839 by signing the Treaty of London
As a result of the invasion, Britain declared war on Germany

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
