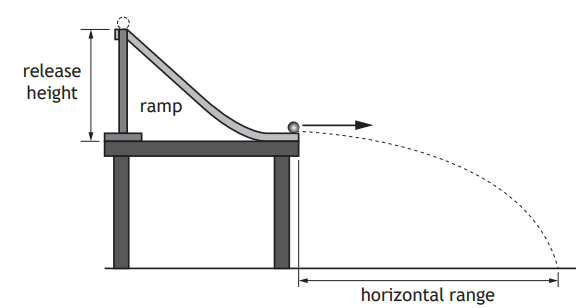
During a cycle race, a cyclist attempts to pass a water bottle to a team-mate.
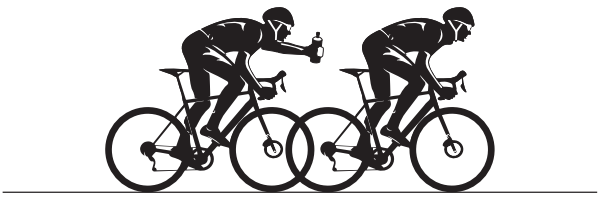
The cyclist is travelling in a straight line at 12.5 m s−1 when they drop the bottle.
The bottle hits the ground 0.53 s later.
The effects of air resistance on the bottle are negligible.
A spectator at the side of the road observes the cyclist dropping the bottle.
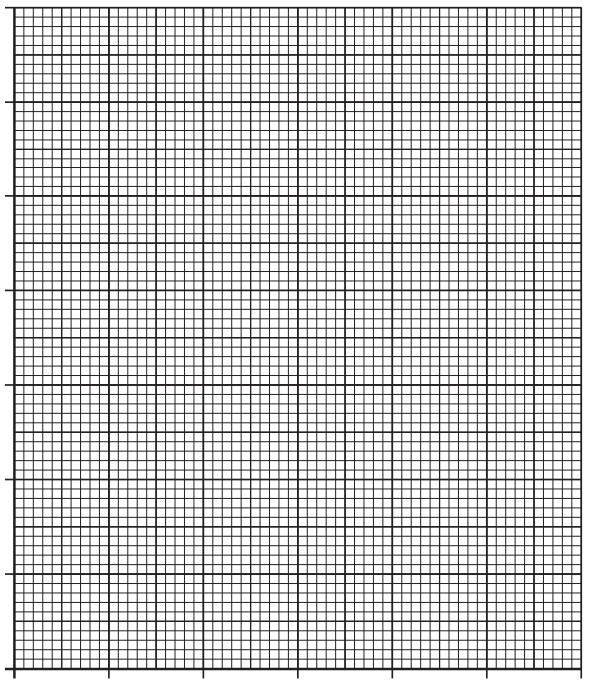
On the diagram below, sketch the path taken by the bottle from the point it is dropped, as observed by the spectator at the side of the road.
(i) Calculate the vertical velocity of the bottle as it reaches the ground.
[3]
(ii) Sketch a velocity‑time graph showing the magnitude of the vertical velocity of the bottle from the time it is released until it reaches the ground.
Numerical values are required on both axes.
[2]

(iii) Determine the height from which the bottle was dropped.
[3]
Was this exam question helpful?