A sample of uranium has an activity of Bq.
The number of nuclei decaying in 15 minutes is
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X857 75
A sample of uranium has an activity of Bq.
The number of nuclei decaying in 15 minutes is
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student makes the following statements about nuclear fusion:
I Nuclear fusion is when a large nucleus splits into smaller nuclei.
II Plasma containment is required to sustain nuclear fusion reactions in a reactor.
III Nuclear fusion takes place at low temperatures.
Which of these statements is/are correct?
I only
II only
I and II only
I and III only
II and III only
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
An aircraft is flying at high altitude.
Flying at high altitude increases the exposure of passengers and crew to radiation.
The graph shows how altitude affects the equivalent dose rate received by the passengers and crew on the aircraft.
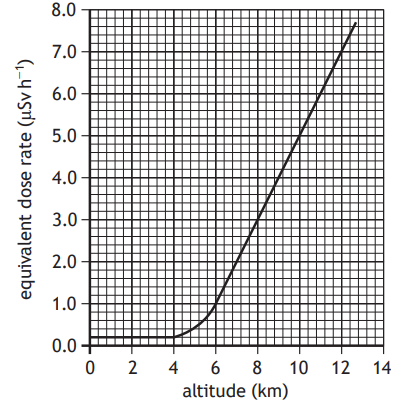
The aircraft flies at an altitude of 11 km for 3.5 hours.
Calculate the equivalent dose received by a crew member during this time.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Electromagnetic radiation has many applications in everyday life.
X‑rays are used in dental procedures to examine the condition of a patient’s teeth.
During this procedure the patient’s head is exposed to X‑rays.
The mass of the patient’s head is 4.5 kg.
The patient’s head receives an absorbed dose of 5.0 μGy from the X‑rays.
(i) Calculate the energy of the radiation absorbed by the patient’s head.
[3]
(ii) Calculate the equivalent dose received by the patient’s head.
[3]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
An experiment is carried out, using the apparatus shown, to investigate the radiation emitted from different radioactive sources.
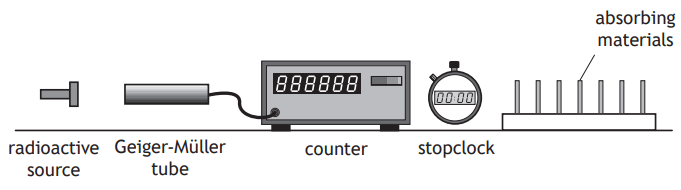
Different absorbing materials are placed, in turn, between the radioactive source and the Geiger‑Müller tube, and the count rate is determined.
This procedure is repeated for each radioactive source.
The results are shown in the table.
Radioactive source | Count rate (counts per minute) | |||
No absorbing material | Sheet of paper | 3 mm thickness of aluminium | 8 mm thickness of lead | |
X | 540 | 542 | 539 | 380 |
Y | 823 | 350 | 354 | 171 |
Z | 652 | 649 | 12 | 14 |
One of the sources emits beta radiation only, one emits gamma radiation only, and one emits both alpha and gamma radiation.
State which source, X, Y or Z, emits both alpha and gamma radiation.
Justify your answer.
How did you do?
A second experiment is carried out to investigate the ionising effect of radiation.
A radioactive source is held close to a spark counter. The spark counter consists of a metal wire connected to a microammeter and a high voltage power supply as shown.
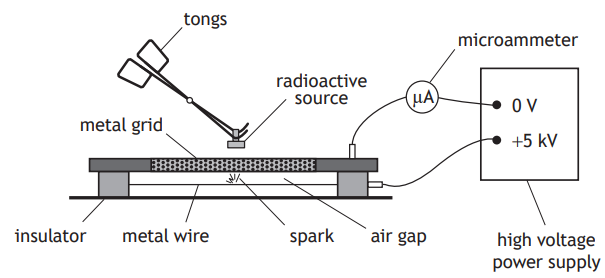
A radioactive source is placed close to the metal grid.
Radiation from the source ionises the air between the metal wire and the grid. Sparks are produced between the wire and the grid.
(i) State what is meant by the term ionisation.
[1]
(ii) The radioactive source used in this experiment emits alpha and gamma radiation.
The source is placed at different distances above the metal grid and the sparks produced are observed.
The results are shown in the table below.
Distance between the source and metal grid (mm) | Observation |
10 | continuous sparking |
30 | few sparks |
60 | no sparks |
Using information from the table, state which type of radiation emitted from the source is causing the air between the wire and metal grid to be ionised.
You must justify your answer
[2]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Iodine‑125 is a radioactive substance used to treat cancer.
A sealed capsule containing iodine‑125 is implanted inside a patient, next to the cancer cells.
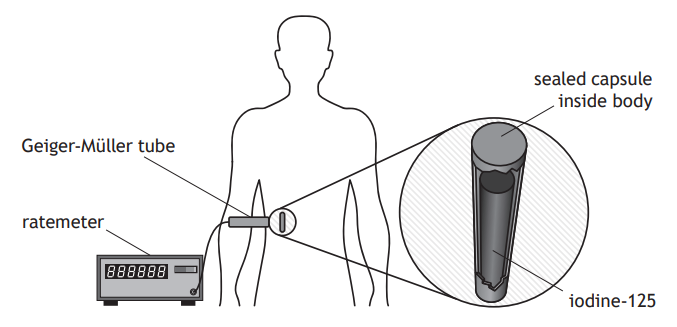
Gamma rays emitted by the iodine‑125 damage the cancer cells.
A Geiger-Müller tube and ratemeter are used to measure the count rate from the iodine‑125.
Measurements of the count rate are taken at regular time intervals.
These measurements are used to produce a graph showing how the corrected count rate varies with the number of days after implant.
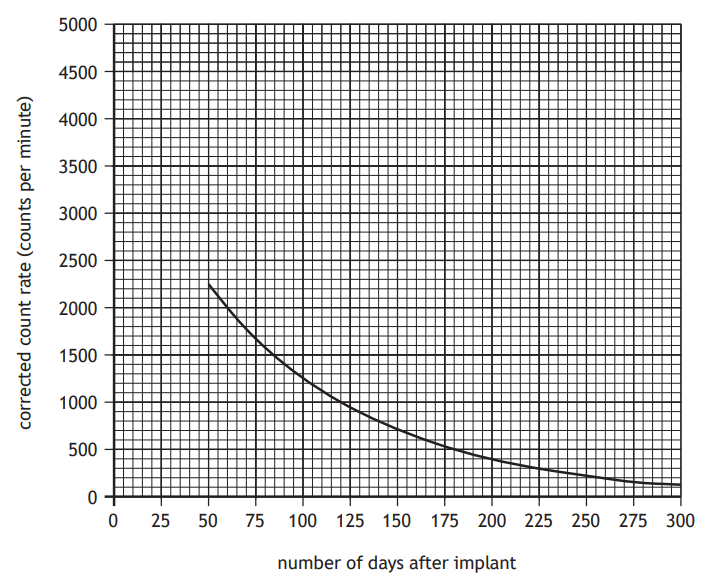
(i) State the additional measurement that must have been made in order to determine the corrected count rate.
[1]
(ii) Using the graph, determine the half‑life of iodine‑125.
[1]
(iii) Determine the time it takes for the corrected count rate to reduce to one eighth of its initial value.
[2]
(iv) Determine the initial corrected count rate of iodine‑125 at the time it was implanted inside the patient.
[1]
How did you do?
State one other use of nuclear radiation.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A radioactive source emits alpha, beta, and gamma radiations.
Sheets of aluminium and paper are placed in front of the source as shown.
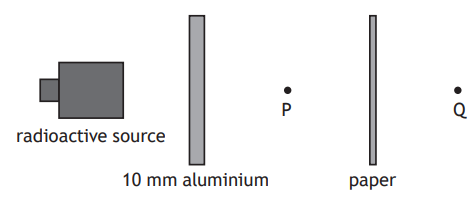
Which row in the table shows the radiation(s) from the source detected at points P and Q?
Radiation(s) detected at P | Radiation(s) detected at Q | |
A | beta and gamma | gamma |
B | beta | alpha |
C | beta and gamma | beta and gamma |
D | alpha and gamma | gamma |
E | gamma | gamma |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A radioactive sample emits 3000 alpha particles in 2 minutes.
The activity of the sample is:
25 Bq
1500 Bq
3000 Bq
6000 Bq
360 000 Bq
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A radioactive substance is to be injected into a patient so that blood flow can be monitored using a detector.
A number of different substances which emit either beta or gamma radiation are available.
The substances have different half‑lives.
Which row in the table identifies the radiation emitted and the half‑life of the most suitable substance?
Radiation emitted | Half-life | |
A | beta | 2 days |
B | beta | 2 years |
C | gamma | 2 seconds |
D | gamma | 2 days |
E | gamma | 2 years |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Rhodium‑106 has a half‑life of 30 s.
A sample of rhodium‑106 has an activity of 3200 Bq.
The activity of this sample after 120 s is:
27 Bq
107 Bq
200 Bq
400 Bq
800 Bq
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Smoke detectors are designed to automatically detect smoke and give a warning. It is recommended that smoke detectors are replaced every ten years.

Inside the smoke detector a radioactive source causes ionisation of the air between two electrically charged plates. When smoke enters the detector, the ionisation of the air is reduced.
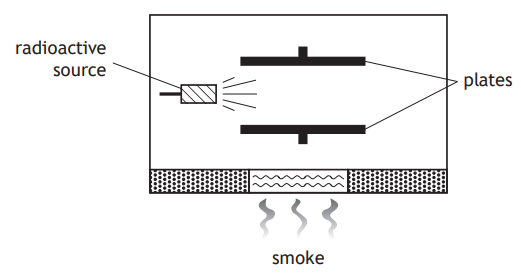
In most smoke detectors the radioactive source used is americium-241, which emits alpha particles.
Give two reasons why an alpha radiation source is used rather than a beta or gamma source.
How did you do?
The graphs show how the activity of three different alpha sources X, Y, and Z change with time.
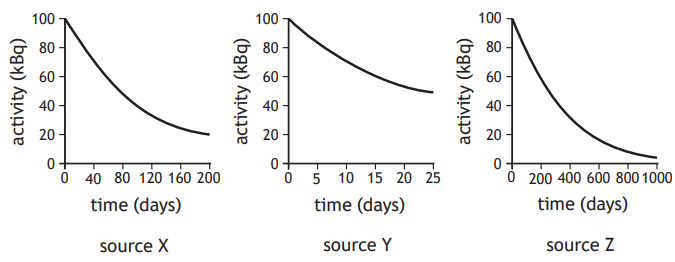
(i) State which of these three sources has the longest half‑life.
[1]
(ii) Explain why these sources would not be suitable for use in a smoke detector.
[2]
How did you do?
Manufacturers must meet health and safety standards for their radiation workers.
During an 8‑hour shift, a radiation worker receives an absorbed dose of 4.5 µGy every hour from alpha radiation.
Determine the equivalent dose received by the worker in the 8‑hour shift.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Nuclear fission is used in nuclear reactors to generate electricity.
Nuclear fusion happens naturally in stars such as the Sun.
State what is meant by the term nuclear fission.
How did you do?
Electricity generated from nuclear fission reactions is used to power the engines of an icebreaker ship.

(i) The power output of the nuclear reactor in the icebreaker ship is 150 MW.
Each nuclear fission reaction releases 2.9 10−11 J of energy.
Determine the minimum number of fission reactions that occur in the reactor each hour.
[4]
(ii) For many years, scientists have been attempting to develop nuclear fusion reactors. Current fusion reactors can only sustain reactions for a limited period of time.
Describe one difficulty in sustaining nuclear fusion reactions in a reactor.
[1]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which row in the table shows the paths taken by alpha particles and gamma radiation as they pass through a uniform electric field between two metal plates?
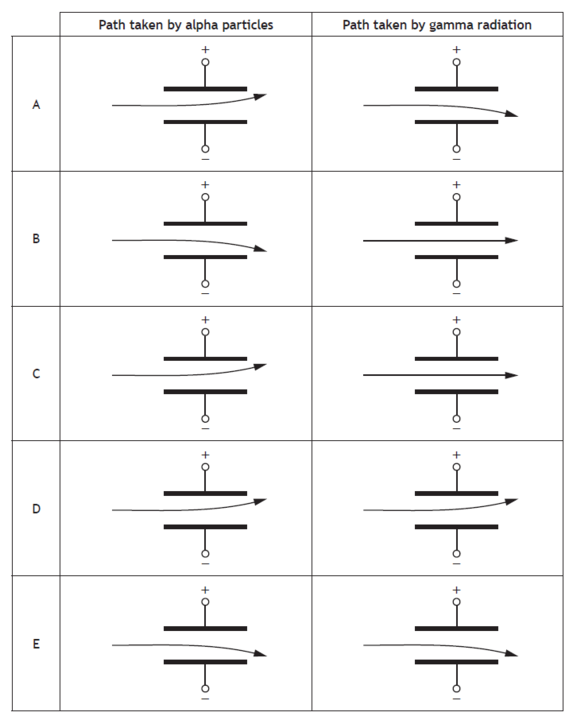
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
For a particular radioactive source, 1800 atoms decay in a time of 3 minutes.
The activity of the source is
10 Bq
600 Bq
1800 Bq
5400 Bq
324 000 Bq
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The crew on an aircraft during a transatlantic flight are exposed to cosmic radiation at an equivalent dose rate of 5·0 μSv h-1.
The crew complete 6 transatlantic flights each month. The average duration of a flight is 8 hours.
The equivalent dose received by the crew due to cosmic radiation during transatlantic flights in one year is
30 μSv
40 μSv
60 μSv
240 μSv
2880 μSv
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A radioactive tracer is injected into a patient to enable doctors to check the function of a patient’s kidneys.
Radiation from the tracer is monitored outside the patient’s body by a detector.
Which row in the table shows the most suitable type of radiation emitted and the half-life for the tracer?
Type of radiation emitted | Half-life of tracer | |
A | alpha | 6 hours |
B | beta | 6 hours |
C | beta | 6 years |
D | gamma | 6 hours |
E | gamma | 6 years |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The activity of a radioactive source is 56 MBq.
The activity of the source 40 hours later is 3·5 MBq.
The half-life of this source is
8 hours
10 hours
16 hours
20 hours
28 hours
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A technician carries out an experiment, using the apparatus shown, to determine the half-life of a radioactive source.
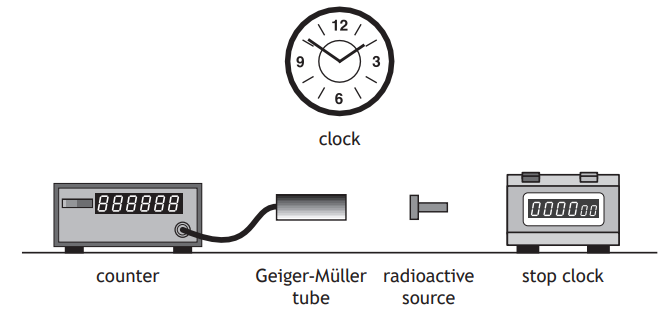
Describe how the apparatus can be used to determine the half-life of the radioactive source.
How did you do?
The technician carries out the experiment over a period of 30 minutes, and displays the data obtained in a graph as shown.
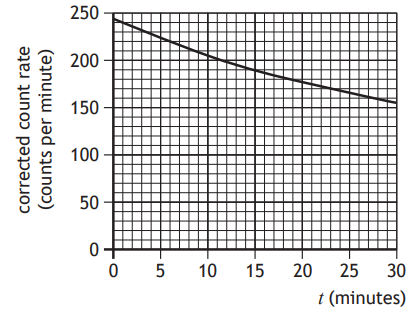
Suggest an improvement that the technician could make to the procedure to more easily determine a value for the half-life of this source.
How did you do?
In a second experiment, the technician absorbs 1·2 μJ of energy throughout their body from a radioactive source.
The mass of the technician is 80·0 kg.
(i) Calculate the absorbed dose received by the technician.
[3]
(ii) During the experiment, the technician receives an equivalent dose of 4·5 10-8 Sv.
Calculate the radiation weighting factor of this source.
[3]
How did you do?
The technician wears a film badge to monitor exposure to radiation.
The film badge contains a piece of photographic film behind windows of different materials.
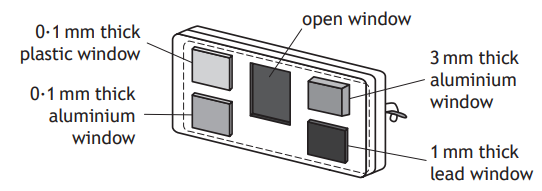
Explain how this badge is used to determine the type of radiation the technician has been exposed to.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A physics teacher makes the following statement.
‘Instead of nuclear fission, perhaps one day nuclear fusion will become a practical source of generating energy.’
Using your knowledge of physics, comment on the similarities and/or differences between using nuclear fission and nuclear fusion to generate energy.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following statements describes the term ionisation?
The removal of a proton from an atom to form a charged particle.
The removal of an electron from an atom to form a charged particle.
The removal of a neutron from an atom.
The splitting of a large nucleus into smaller nuclei.
The joining of small nuclei to form a larger nucleus.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
In a radioactive source 1.8 106 nuclei decay in 10 hours.
The activity of the source is
1.8 105 Bq
3.0 104 Bq
3.0 103 Bq
500 Bq
50 Bq
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A sample of tissue receives an absorbed dose of 0.20 µGy from a source of alpha radiation and an absorbed dose of 6.0 µGy from a source of slow neutrons.
The total equivalent dose received by the sample of tissue is
6.2 µSv
19 µSv
22 µSv
64 µSv
140 µSv
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A technician carries out an experiment, using the apparatus shown, to determine the half‑life of a radioactive source.
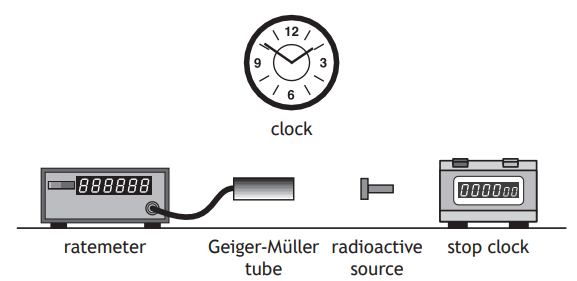
Before carrying out the experiment the technician measures the background count rate.
The technician takes readings of the count rate displayed on the ratemeter every 60 s for a period of 20 minutes.
A graph of the technician’s measurements is as shown.
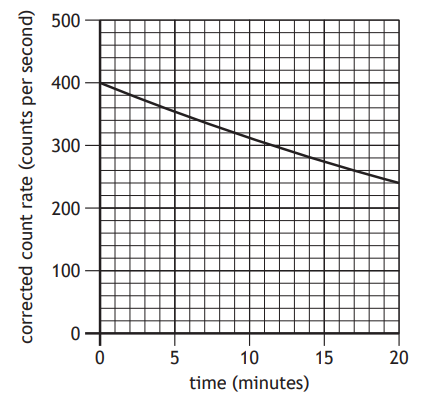
Which of the following changes would allow the technician to more easily determine the half-life of the radioactive source?
Take readings of the count rate every 30 seconds for 20 minutes.
Take readings of the count rate every 60 seconds for 40 minutes.
Place lead shielding around the radioactive source.
Move the radioactive source closer to the Geiger-Müller tube.
Move the radioactive source further away from the Geiger-Müller tube.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Two students are discussing radiation.
The first student states: ‘All radiation is dangerous, so we should never allow ourselves to be exposed to it.’
The second student states: ‘No, it’s only nuclear radiation that we need to worry about.’
Using your knowledge of physics, comment on the students’ statements.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Medical face masks can be sterilised using gamma radiation to kill bacteria.
The masks are placed into sealed plastic packages. These packages are then placed in a steriliser where they are exposed to gamma radiation.
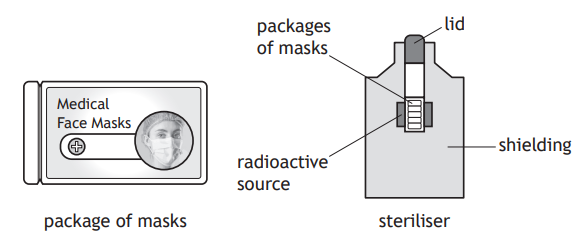
The gamma radiation is produced by a cobalt-60 source.
The source has an initial activity of 848 000 GBq.
The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.3 years.
Determine the activity of the source 21.2 years later.
How did you do?
The face masks receive an absorbed dose of 25 kGy to ensure that they are safe for use.
The mass of each face mask is 2.2 10-3 kg.
(i) The masks receive an absorbed dose of 0.50 Gy each second.
Determine the length of time, in seconds, that the masks remain in the steriliser.
[1]
(ii) Calculate the energy absorbed by each face mask.
[3]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A sample of tissue receives an equivalent dose rate of 0·40 mSv h−1 from a source of alpha radiation.
The equivalent dose received by the sample in 30 minutes is
0·20 mSv
0·80 mSv
4·0 mSv
12 mSv
720 mSv
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A radioactive source has an initial activity of 200 kBq. After 12 days the activity of the source is 25 kBq.
The half-life of the source is
3 days
4 days
8 days
36 days
48 days
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
In the following passage some words have been replaced by the letters X, Y and Z.
During a nuclear X reaction two nuclei of smaller mass number combine to produce a nucleus of larger mass number. These reactions take place at very Y temperatures and are important because they can release Z
Which row in the table shows the missing words?
X | Y | Z | |
A | fusion | low | electrons |
B | fusion | high | energy |
C | fission | high | protons |
D | fission | low | energy |
E | fusion | high | electrons |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A tritium torch includes a sealed glass capsule containing radioactive tritium gas.
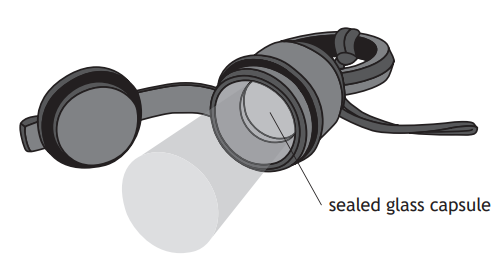
Beta particles emitted by the tritium gas are absorbed by a coating on the inside of the glass capsule.
The coating then emits visible light.
State what is meant by a beta particle.
How did you do?
The half-life of tritium gas is 12·3 years.
The manufacturer states that the torch will work effectively for 15 years.
Explain why the torch will be less effective after this time.
How did you do?
During the manufacturing process a glass capsule cracks and a worker receives an absorbed dose of 0·40 mGy throughout their body from the tritium gas.
The mass of the worker is 85 kg.
(i) Calculate the energy of the radiation absorbed by the worker.
[3]
(ii) Calculate the equivalent dose received by the worker.
[3]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A technician carries out an experiment, using the apparatus shown, to determine the half-life of a gamma radiation source.
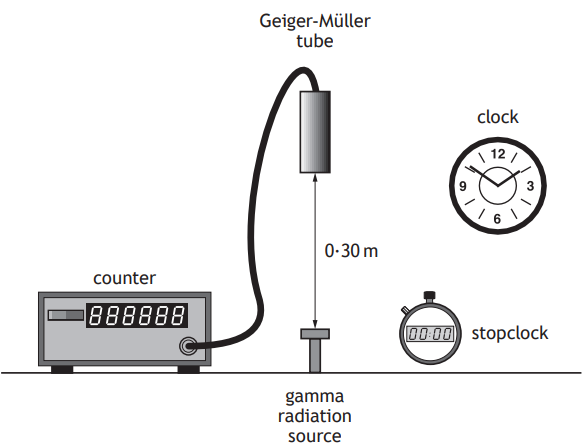
Before carrying out the experiment the technician measures the background count rate.
(i) Explain why this measurement is made.
[1]
(ii) State a source of background radiation.
[1]
How did you do?
The technician’s results are shown in the table.
Time (minutes) | Corrected count rate (counts per minute) |
0 | 680 |
20 | 428 |
40 | 270 |
60 | 170 |
80 | 107 |
100 | 68 |
(i) Using the graph paper below, draw a graph of these results.
[3]
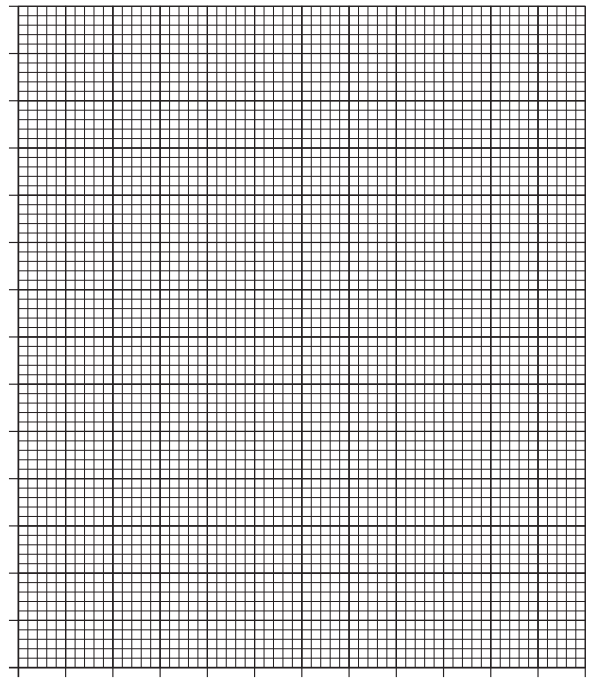
(ii) Use your graph to determine the half-life of the gamma radiation source.
[1]
How did you do?
The technician repeats the experiment with an alpha radiation source.
(i) Suggest a change the technician must make to the experimental set-up to determine the half-life of the alpha radiation source.
Justify your answer.
[2]
(ii) During the first 15 s of the experiment the alpha radiation source has an average activity of 520 Bq.
Calculate the number of nuclear disintegrations that occur in the source in the first 15 s of the experiment.
[3]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Read the passage and answer the questions that follow.
Spacecraft travelling to distant parts of the Solar System need to have a source of power to operate their electrical systems.
Many spacecraft use solar cells to generate electricity, but this is not always suitable.
Some spacecraft, such as Voyager 2, are powered using energy generated by Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs). The RTGs in Voyager 2 use plutonium-238 as a fuel. The half-life of plutonium-238 is 88 years. The plutonium decays to uranium in a nuclear fission reaction. The heat generated by this radioactive decay is then converted into electrical energy.
In the future, NASA plans to equip spacecraft with miniature nuclear reactors, which use nuclear fission chain reactions to generate power.
Explain why the decay of plutonium to uranium is described as a nuclear fission reaction.
How did you do?
Describe the role of neutrons in a nuclear fission chain reac
How did you do?
Voyager 2 has been travelling through space for nearly 50 years.
Explain why the power output of the RTGs on Voyager 2 have decreased over this time.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?