Doris is a small, rocky, irregular shaped object that orbits the Sun between Mars and Jupiter.
Doris is an example of
an asteroid
a dwarf planet
an exoplanet
a planet
a star
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X857 75
Doris is a small, rocky, irregular shaped object that orbits the Sun between Mars and Jupiter.
Doris is an example of
an asteroid
a dwarf planet
an exoplanet
a planet
a star
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A space vehicle of mass 350 kg is free falling vertically towards the surface of Mars.
Rocket engines are now fired, which apply a combined upwards force of 2200 N on the vehicle.
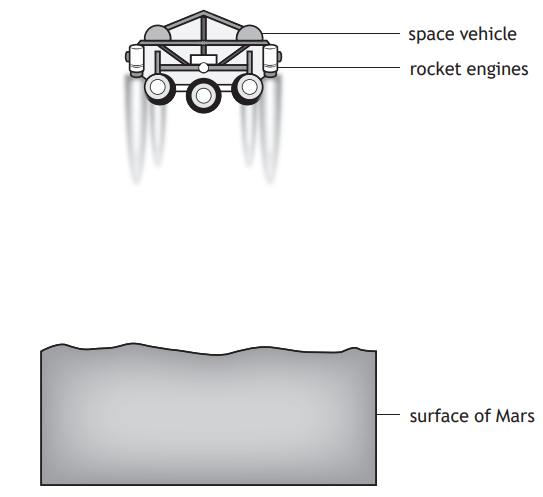
Just after the rocket engines are fired, the vehicle will
move away from the surface of Mars at a constant speed
move away from the surface of Mars with an increasing speed
move towards the surface of Mars at a constant speed
move towards the surface of Mars with a decreasing speed
move towards the surface of Mars with an increasing speed
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Information about some satellites is shown in the table.
Name of satellite | Date launched | Orbital altitude h (km) | Orbital period T |
UKube-1 | 8 July 2014 | 825 | 101 minutes |
Kosmos 2460 | 1 March 2010 | 19 100 | 676 minutes |
Magellan | 22 August 2019 | 20 200 | 718 minutes |
Astra 1KR | 20 April 2006 | 36 000 | 24 hours |
Vela 4B | 28 April 1967 | 111 000 | 111 hours |
Television signals are transmitted from satellites that remain above the same point on Earth’s surface at all times.
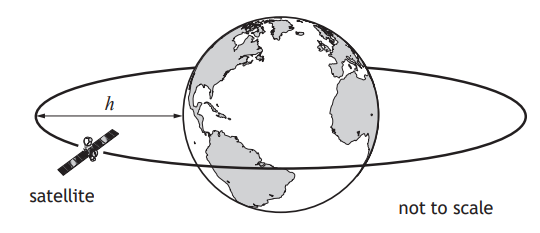
State which of the satellites in the table is used to transmit these television signals.
You must justify your answer.
How did you do?
UKube‑1 has a mass of 3.5 kg.
At an orbital altitude of 825 km the gravitational field strength of Earth is 7.7 N kg−1.
Calculate the weight of UKube‑1 at this orbital altitude.
How did you do?
Another satellite is in orbit at an altitude of 1200 km.
Predict the orbital period of this satellite.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A space scientist makes the following statement.
‘Before we can have human space exploration of the solar system and beyond, we need to build a base on the Moon.’
Using your knowledge of physics, comment on the benefits and/or challenges of using a base on the Moon from which humans could explore the solar system and beyond.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
An astronomer is using a space‑based telescope to observe a star.
Suggest an advantage of using a space‑based telescope compared to using a ground‑based telescope to observe the star.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following lists the distances from longest to shortest?
radius of Earth; radius of orbit of Moon; diameter of galaxy
radius of orbit of Moon; radius of Earth; diameter of galaxy
diameter of galaxy; radius of orbit of Moon; radius of Earth
diameter of galaxy; radius of Earth; radius of orbit of Moon
radius of orbit of Moon; diameter of galaxy; radius of Earth
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Three satellites X, Y, and Z are orbiting the Earth as shown.
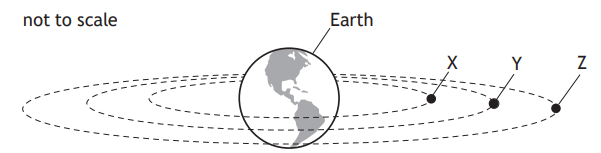
Satellite Z is a geostationary satellite.
Which row in the table shows possible periods for the orbits of satellites X, Y, and Z?
Period of orbit of satellite X (hours) | Period of orbit of satellite Y (hours) | Period of orbit of satellite Z (hours) | |
A | 12 | 18 | 24 |
B | 24 | 18 | 12 |
C | 24 | 24 | 24 |
D | 40 | 36 | 24 |
E | 4 | 6 | 12 |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
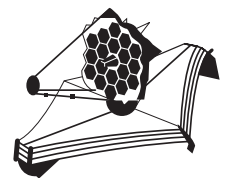
A spacecraft has four rocket engines P, Q, R, and S and is travelling to the right as shown.
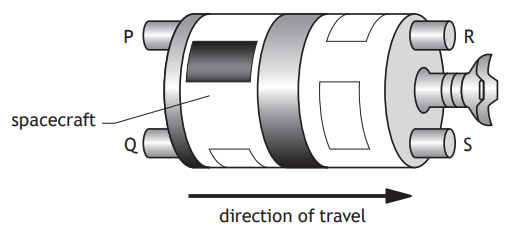
When switched on, each rocket engine produces the same amount of force.
Which rocket engines are switched on to reduce the speed of the spacecraft?
R and S
Q and S
P and Q
P and R
P, Q, R, and S
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The weights of three masses on the surface of a planet are shown in the table.
Mass (kg) | Weight (N) |
0.50 | 4.4 |
2.5 | 22 |
4.0 | 35 |
The weight of a 6.0 kg mass on the surface of the planet is:
0.68 N
1.5 N
8.8 N
53 N
59 N
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A spaceship on Mars is being prepared for the return journey to Earth.

The mass of the spaceship including fuel and crew is 1.3 106 kg.
The rocket engines on the spaceship produce a constant upward thrust of 1.2 107 N.
State what happens to the acceleration of the spaceship as its altitude increases.
Justify your answer.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Space exploration is often in the news, yet we have only explored about 5% of the oceans on Earth.

Using your knowledge of physics, comment on the similarities and/or differences between space exploration and underwater exploration.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A geostationary satellite orbits the Earth.
Which row in the table shows the altitude above the surface of the Earth and orbital period of the geostationary satellite?
Altitude above the surface of the Earth (km) | Orbital period (hours) | |
A | 36 000 | 12 |
B | 36 000 | 24 |
C | 36 000 | 48 |
D | 18 000 | 12 |
E | 18 000 | 24 |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The weight of a robot on Earth is 240 N.
The weight of the robot on Mars is
3·7 N
65 N
91 N
240 N
890 N
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
In 1971, the astronaut Alan Shepard hit a golf ball on the surface of the Moon.

Using your knowledge of physics, comment on the similarities and/or differences between this event and hitting an identical ball on the surface of the Earth.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Astronomers use satellite-based telescopes to collect information about objects in space.
(i) Suggest an advantage of using satellite-based telescopes such as the Hubble Space Telescope.
[1]
(ii) State one other use of satellites.
[1]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The table shows the altitude and period of four satellites.
Satellite | Altitude (km) | Period (minutes) |
International Space Station | 408 | 93 |
AprizeSat-3 | 686 | |
Intelsat-18 | 35 800 | 1440 |
Hubble Space Telescope | 537 | 95 |
The period of the AprizeSat-3 satellite is
85 minutes
94 minutes
98 minutes
1440 minutes
1600 minutes
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Read the passage and answer the questions that follow.
Spacecraft travelling to distant parts of the Solar System need to have a source of power to operate their electrical systems.
Many spacecraft use solar cells to generate electricity, but this is not always suitable.
Some spacecraft, such as Voyager 2, are powered using energy generated by Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs). The RTGs in Voyager 2 use plutonium-238 as a fuel. The half-life of plutonium-238 is 88 years. The plutonium decays to uranium in a nuclear fission reaction. The heat generated by this radioactive decay is then converted into electrical energy.
In the future, NASA plans to equip spacecraft with miniature nuclear reactors, which use nuclear fission chain reactions to generate power.
Explain why solar cells may not be a suitable source of power when exploring distant parts of the Solar System.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
NASA is planning a crewed mission to the Moon. Part of the mission includes placing a spacecraft in orbit at an altitude of 140 km above the surface of the Moon.
Once the spacecraft is in orbit, some of the astronauts will travel to the surface of the Moon in a transportation module.
These astronauts will remain on the surface of the Moon for approximately one week.
Describe one physics-related challenge these astronauts will face while on the surface of the Moon.
How did you do?
After spending time on the Moon, the astronauts will return to the orbiting spacecraft using the transportation module.
During the first part of this return journey, the rockets on the transportation module will exert a constant upward force.
State what will happen to the acceleration of the transportation module during this part of the journey.
You must justify your answer.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Around 500 years ago Nicolaus Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, proposed a model of the Universe with the Sun motionless at its centre and the stars fixed in position in the night sky.
Using your knowledge of physics, comment on this model.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Launched in 2022, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is the world’s premier space-based science observatory.
The NASA website states that the JWST will solve mysteries in our Solar System and probe the mysterious structures and origins of our Universe.
State an advantage of using a space-based telescope compared to ground‑based telescopes.
How did you do?
In 2023, the JWST was used to study the exoplanet LHS 475 b.
State what is meant by the term exoplanet.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A galaxy is a collection of
stars
satellites
moons
planets
asteroids
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The communications satellite Iridium-124 has a period of 97 minutes and an orbital height of 630 km.
The geostationary satellite Astra-5B has a period of 1440 minutes and an orbital height of 36 000 km.
A satellite with an orbital height of 23 000 km has a period of
62 minutes
97 minutes
835 minutes
1440 minutes
2250 minutes
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Far out in space, the rocket engine of a space probe is switched on for a short time causing it to accelerate.
When the engine is then switched off, the probe will
slow down until it stops
follow a curved path
continue to accelerate
move at a constant speed
change direction
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A spacecraft lands on a distant planet.
The gravitational field strength on this planet is 14 N kg−1.
Which row in the table shows how the mass and weight of the spacecraft on this planet compares with the mass and weight of the spacecraft on Earth?
Mass on planet | Weight on planet | |
A | same as on Earth | greater than on Earth |
B | greater than on Earth | greater than on Earth |
C | same as on Earth | same as on Earth |
D | greater than on Earth | same as on Earth |
E | same as on Earth | less than on Earth |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Within our solar system distances are often measured in astronomical units (AU).
1 AU = 1·501011 m.
Mars orbits the Sun at an average distance of 1·52 AU.
(i) Determine the average distance, in metres, at which Mars orbits the Sun.
[1]
(ii) Calculate the average time for light from the Sun to reach Mars.
[3]
How did you do?
In the future it is hoped that humans will be able to travel to Mars. One challenge of space travel to Mars is maintaining sufficient energy to operate life support systems.
(i) Suggest one solution to this challenge.
[1]
(ii) State another challenge of space travel to Mars.
[1]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?