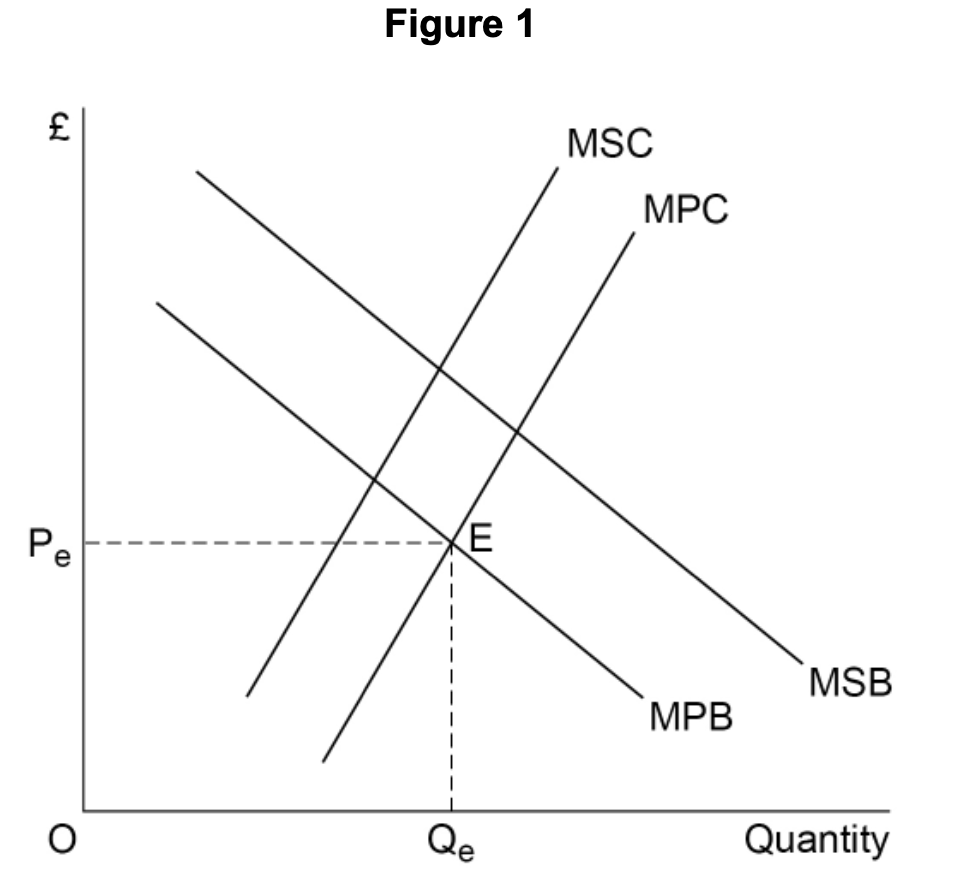
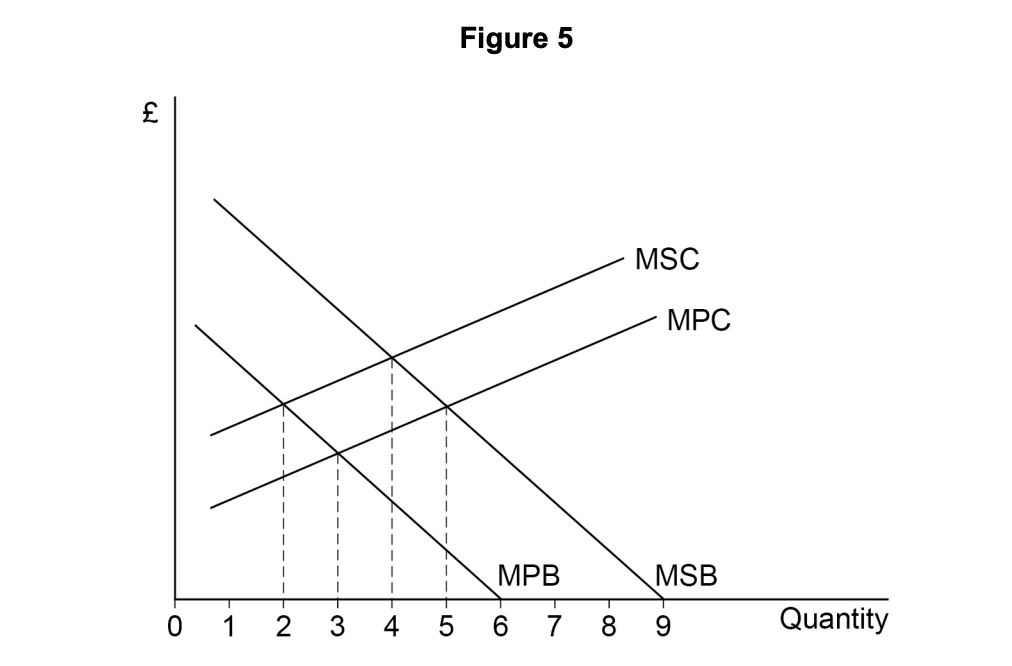
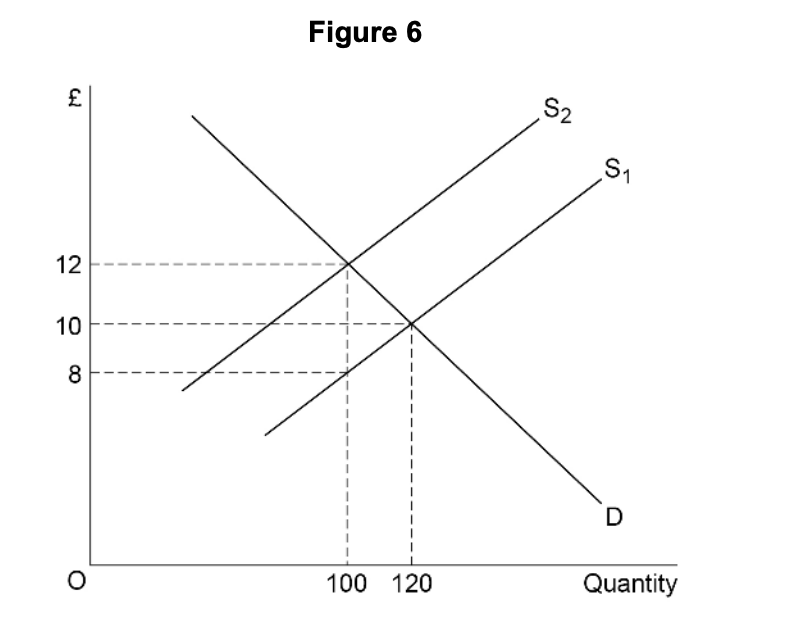
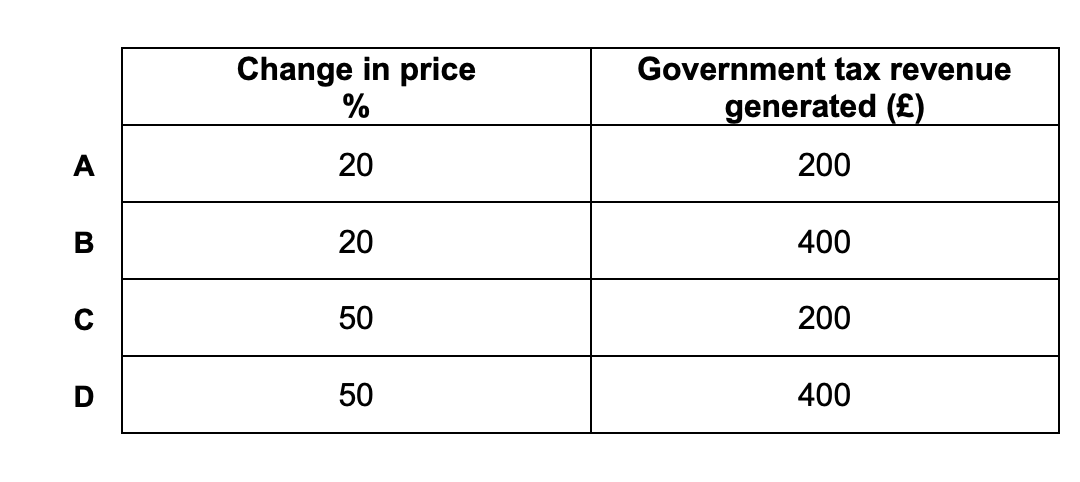
Which one of the following distinguishes a private good from a pure public good?
A private good can only be provided by private firms and not the government
Consumption of a private good creates negative externalities for other consumers
Consumers of a private good have full knowledge of any externalities in its production
One person’s consumption of a private good reduces the amount available for other consumers
Was this exam question helpful?