Conservatism: Core Ideas & Principles (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Introduction
Conservatism is based on a sceptical view of human nature, a preference for stability, and a belief in gradual change
Its core ideas relate to views about human nature, the state, society and the economy
Although conservatives share common assumptions, different strands (Traditional, One Nation, New Right) interpret these ideas in different ways
Core principle: pragmatism
Core idea
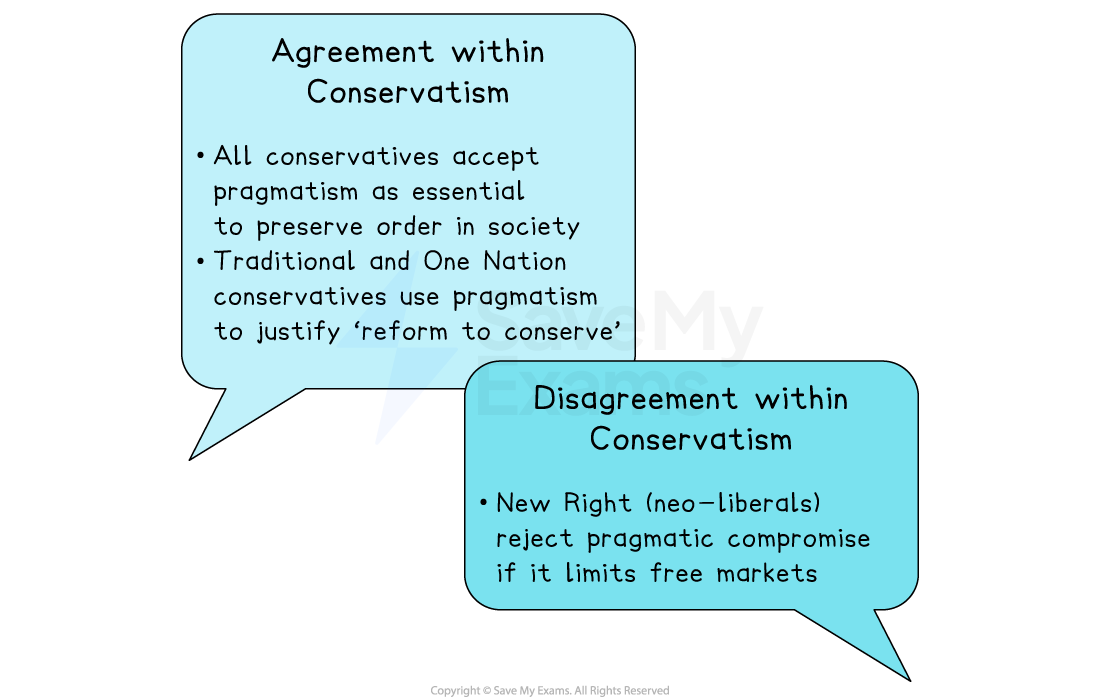
Conservatives prefer practical, cautious solutions based on experience, rather than risky “grand plans” or abstract theories
Preference for practical solutions over abstract theory
Politics should evolve through experience
Society should change gradually to avoid instability or revolution
Values empirical evidence - politicians should act on “what works”
Supports incremental reform rather than radical change
Links to conservative view of human nature as flawed → need for simple, cautious decision-making
Key thinker
Michael Oakeshott, Rationalism in Politics (1962)
Political decisions must reflect historical experience, not theory
Links to the four concepts
Human nature: flawed → need for cautious, practical decision-making
State: should govern cautiously; reform to conserve
Society: gradual, organic change
Economy: avoid sudden economic upheaval; pragmatic adjustments
Do Conservatives agree on this principle?
Core principle: tradition
Core idea
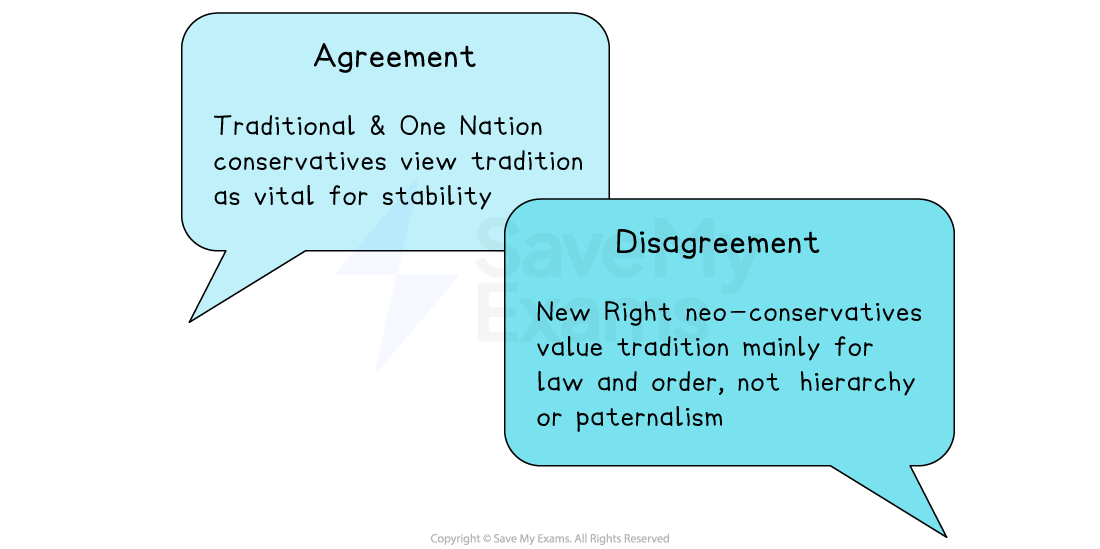
Tradition is the “accumulated wisdom” of past generations. Conservatives believe we should respect it, not discard it
“Accumulated wisdom of generations” (Burke)
Provides stability, shared identity and social cohesion
Respect for long-standing institutions (monarchy, Parliament, family)
Change should be slow and respect continuity
Linked to pragmatism — what worked in the past should not be changed rapidly
Key thinker
Edmund Burke, Reflections on the Revolution in France (1790)
Society is a partnership “between those who are living, those who are dead, and those who are to be born”
Links to the four concepts
Human nature: people seek security and familiarity
State: institutions embody accumulated wisdom
Society: organic, stable, rooted in continuity
Economy: cautious economic reform; preserve inherited frameworks
Do Conservatives agree on this principle?
Core principle: human imperfection
Core idea
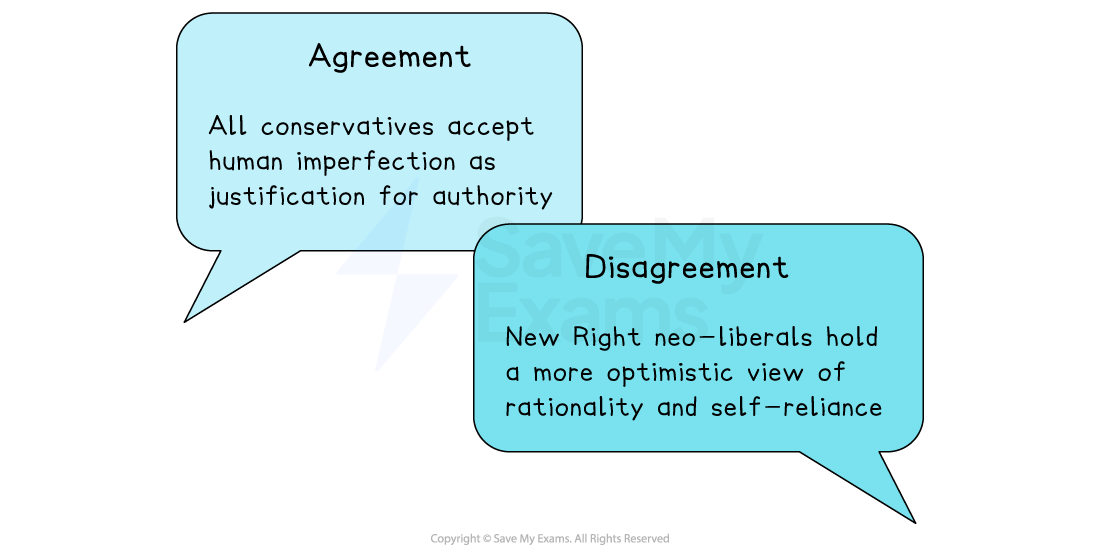
Conservatives believe humans are flawed and cannot be perfected
Humans are flawed psychologically, morally and intellectually
People require strong authority, law and order and stable institutions
Society should prioritise order over liberty
Rejects optimistic or rationalist views of human nature
Three types of imperfection
Psychological: humans desire security, not freedom
Moral: people are selfish and need guidance
Intellectual: humans are limited and cannot understand complex change
Key thinker
Thomas Hobbes, Leviathan (1651)
Life without authority is “nasty, brutish and short”
Links to the four concepts
Human nature: inherently flawed
State: needs strong, authoritative government
Society: requires hierarchy and order
Economy: scepticism towards radical economic change
Do Conservatives agree on this principle?
Core principle: organic state
Core idea
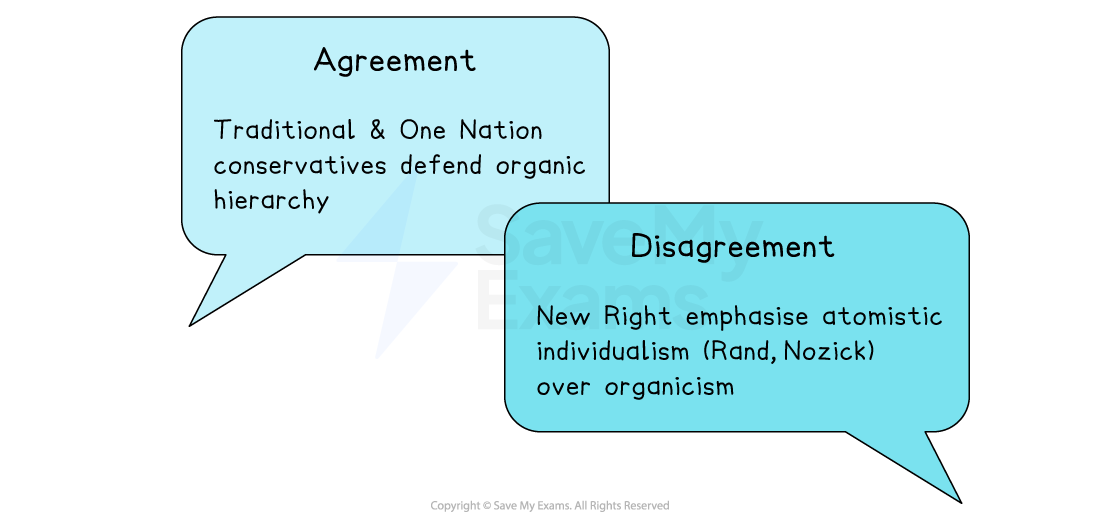
Society is like a living organism – it grows and changes naturally over time, rather than being built from a blueprint
Society evolves naturally like a living organism
Individuals are interdependent
Social hierarchy is natural, beneficial and based on merit
‘Noblesse oblige’: those at the top have obligations to those below
Stability depends on shared values and traditions
Key thinker
Edmund Burke — society is a “partnership in all art and science”
(implying organic growth rather than designed systems)
Links to the four concepts
Human nature: people rely on structured communities
State: natural hierarchy supports authority
Society: cohesion based on shared values and gradual evolution
Economy: preference for ordered, stable economic relationships
Do Conservatives agree on this principle?
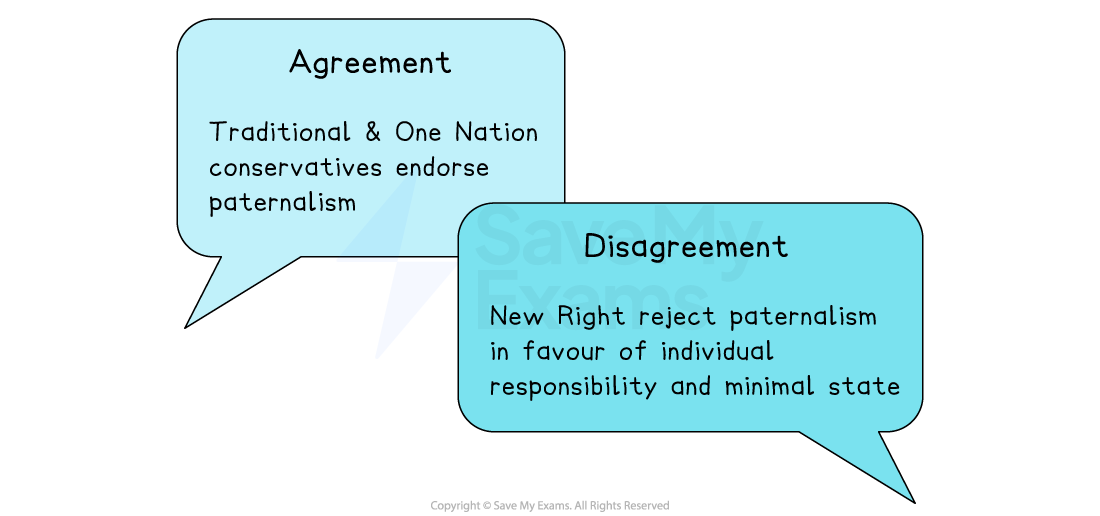
Core principle: paternalism
Core idea
The powerful have a duty (“noblesse oblige”) to care for the less fortunate
The state should intervene to maintain stability and harmony
Supports welfare and gradual reform within a natural hierarchy
Inequality is natural but creates moral obligations
Key thinker
Michael Oakeshott, On Being Conservative (1956)
Government should maintain peace, not impose radical change
Links to the four concepts
Human nature: people need guidance
State: authority acts benignly for public good
Society: hierarchy with mutual obligations
Economy: cautious support for welfare to maintain order
Do Conservatives agree on this principle?
Core principle: libertarianism (neo-liberalism)
Core idea
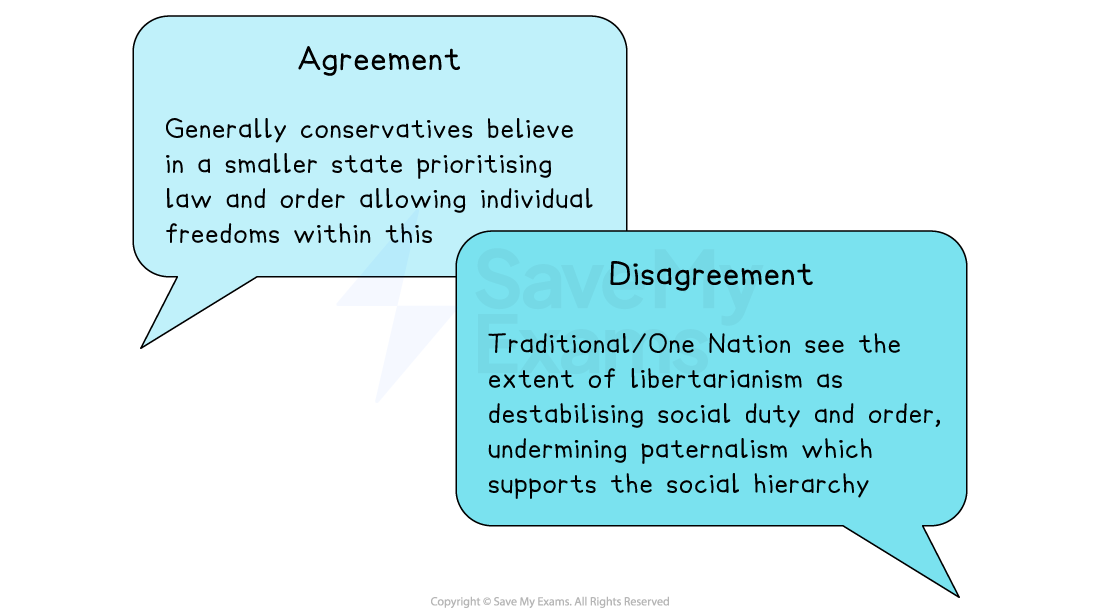
Libertarianism prioritises individual freedom, especially in the economy, and wants the smallest possible state
Prioritises individual freedom and minimal state intervention
Markets allocate resources more efficiently than governments
Taxes restrict liberty — Nozick compared taxation to forced labour
Emphasises personal responsibility
Supports strong law and order to protect freedom
Key thinker
Ayn Rand, Atlas Shrugged (1957)
Defended laissez-faire capitalism and “the virtue of selfishness”
Links to the four concepts
Human nature: individuals are rational and self-interested
State: should be minimal (“night-watchman state”)
Society: focus on individuals rather than organic unity
Economy: free markets, low taxes, deregulation
Do Conservatives agree on this principle?

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
