Differing Views & Tensions in Conservatism (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Introduction to the strands of Conservatism
Conservatism contains several different strands that have developed over time in response to major social and economic changes
They share core assumptions such as respect for tradition, scepticism about human nature and a preference for order and stability
They differ on how much change is acceptable, the role of the state, and the balance between freedom and authority
The three main strands you need to know are:
Traditional Conservatism which emphasises hierarchy, order, and paternalism
One-Nation Conservatism – an adaptation of traditional ideas to reduce social division caused by capitalism
The New Right – a late 20th-century development combining neo-liberal free-market ideas with neo-conservative commitments to authority and public morality
Summary of views on social order and economic freedom
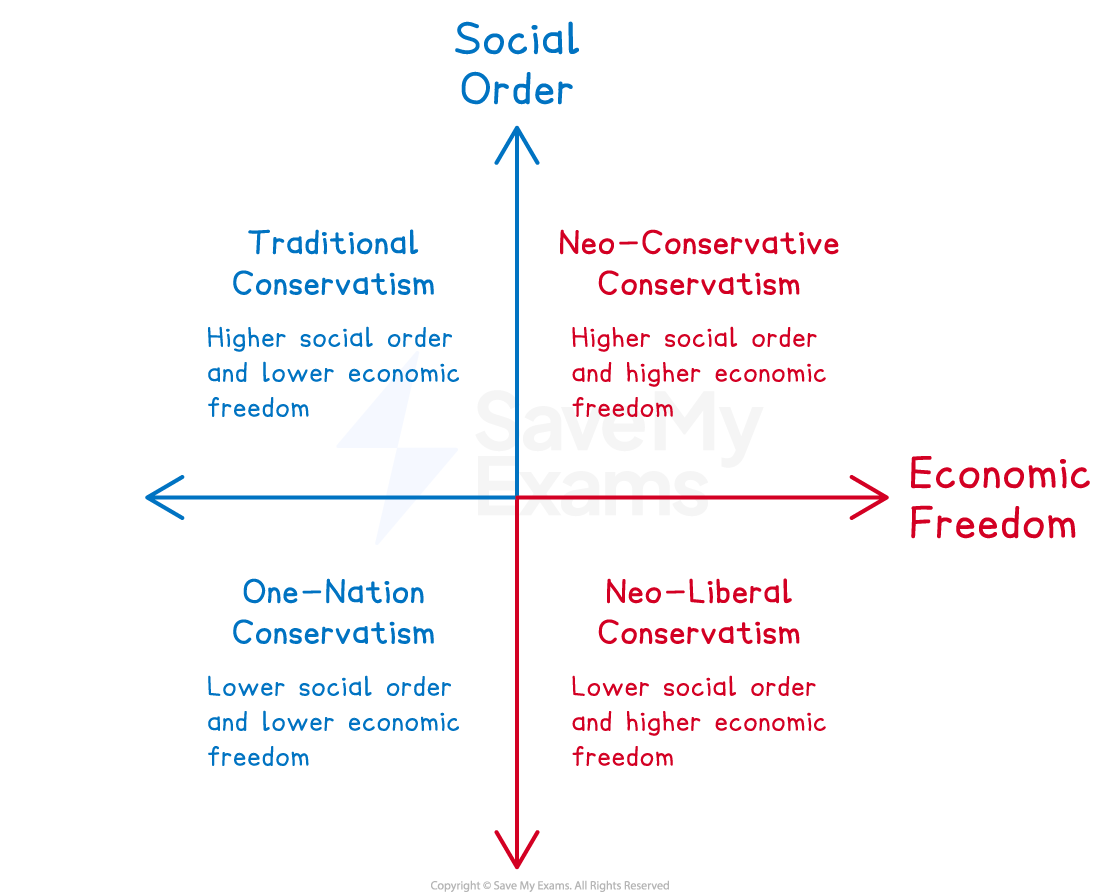
'Higher social order' is an ideology that believes strongly in:
authority; clear hierarchy; strong policing; strict moral and social rules; maintaining order over individual freedom; traditional values
E.g., Traditional Conservatism, Neo-Conservatism
'Lower social order' is an ideology that places less emphasis on:
strict hierarchy, heavy policing, strong authority, rigid social/moral rules
E.g., One-Nation Conservatism, Neo-Liberalism
Traditional Conservatism
Traditional Conservatism emerged after the French Revolution as a defence of social hierarchy and order
Conservatives feared that radical change would undermine social cohesion
The monarchy, the Church and other traditional institutions should, in the view of traditional conservatives, be preserved
Reforms should be introduced gradually
According to traditional conservatives, society is shaped by a natural hierarchy of governance, making inequality inevitable
However, it is paired with a paternalistic duty to support and protect those in need
An organic society based on paternalism, shared obligations and moral order is central to traditional conservative thinking
Key thinkers
Burke – “reform to conserve”; society as a contract between generations
Hobbes – strong authority needed for stability; subjects offer loyalty for protection
Oakeshott – politics is a “conversation”; change should be gradual and evolutionary
One-Nation Conservatism
One Nation conservatism emerged as a response to the intense industrial poverty that developed during the Industrial Revolution
Its supporters sought to promote the unity of the whole nation, encouraging all classes to feel a shared identity while preserving the existing social hierarchy
The tradition also advocated limited reforms, such as widening the franchise and introducing basic welfare measures, to maintain social stability and prevent social unrest
Economically, One Nation conservatives argued for pragmatic, centrist policies, favouring a mixed economy and accepting limited state intervention where necessary
Above all, this strand of conservatism places strong emphasis on national unity, rather than focusing solely on the maintenance of social hierarchy
Key thinkers
Disraeli (Sybil, 1845) – warned of “two nations”; supported limited reform to prevent class conflict
Macmillan (The Middle Way, 1938) – proposed a middle ground between socialism and laissez-faire
New Right Conservatism
There are two strands within new right conservatism
1. Neo-liberals
Concerned with the economy and individual freedom
Support free-market economics, deregulation, low tax, individual responsibility
Favour minimal state intervention in the economy
Argue for an atomistic view of society
More positive view of human rationality
2. Neo-conservatives
Concerned with society, cohesion and traditional values
Emphasise law, order and moral authority
Seek to restore importance of social hierarchy
Support moral guidance and patriotism
Oppose permissiveness; return to traditional values
Key thinkers
Rand – freedom through capitalism and laissez-faire economics
Nozick (Anarchy, State and Utopia, 1974) – only a minimal state is justified
Summary of Conservatism and the four themes
What do conservatives think about the four themes?
Theme | General agreement between strands | Disagreements between strands |
|---|---|---|
Human nature |
|
|
Society |
|
|
State |
|
|
Economy |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
