Liberalism: Core Ideas & Principles (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Introduction to Liberalism
Liberalism emerged in the 17th and 18th centuries as thinkers began challenging absolute monarchy, religious authority and rigid social hierarchies
Early liberals such as John Locke argued that individuals possess natural rights and that government should only exist with the consent of the governed
Over time, liberalism has centred on protecting individual freedom and limiting state power
Although classical and modern liberals disagree on how far the state should intervene, all liberals share a commitment to core principles about the individual, society and government
Key principles of Liberalism
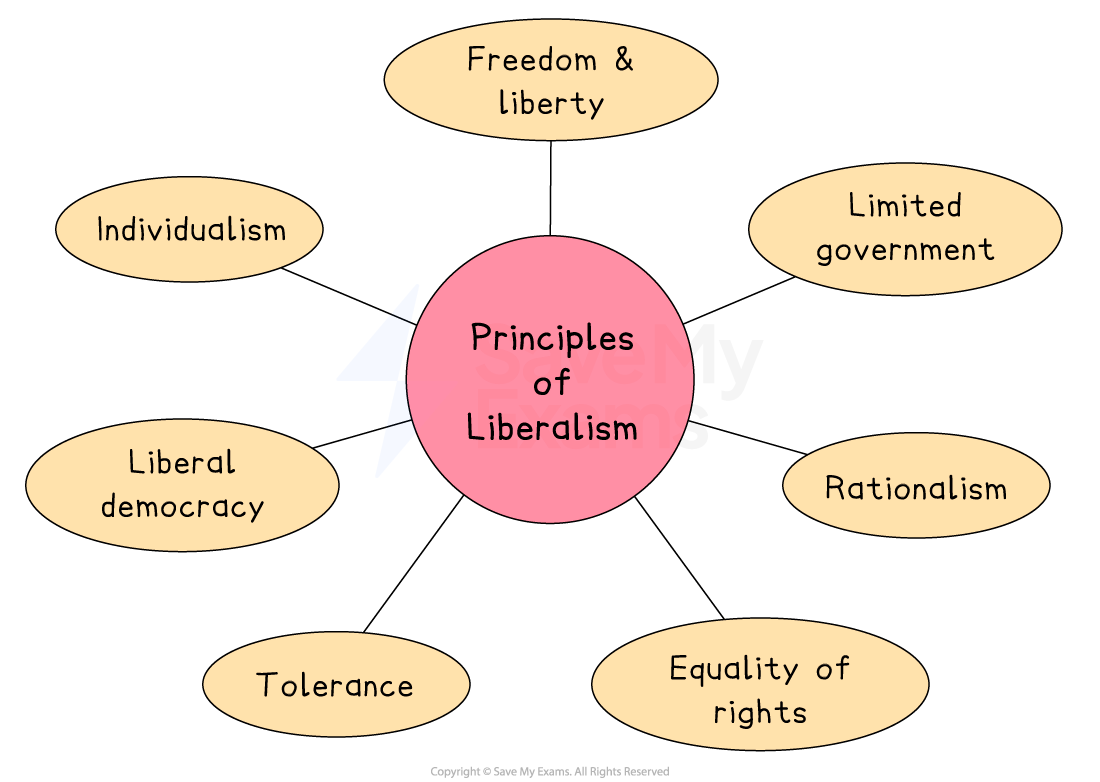
Core principle: individualism
Core idea
Liberals believe individuals have inherent worth
They therefore possess rights that should be respected and protected
Individuals are seen as rational beings
They are capable of making their own decisions and taking responsibility for their actions
Liberalism supports freedom of conscience
Each person should be free to follow their own beliefs without unnecessary state interference
Key thinkers
John Locke
Individuals have natural rights of life, liberty, and property ownership
These existed before the formation of a government
Mary Wollstonecraft
Women’s rationality means they deserved education to develop their individual potential
Different strands of individualism
Egoistical individualism | Developmental individualism |
|---|---|
|
|
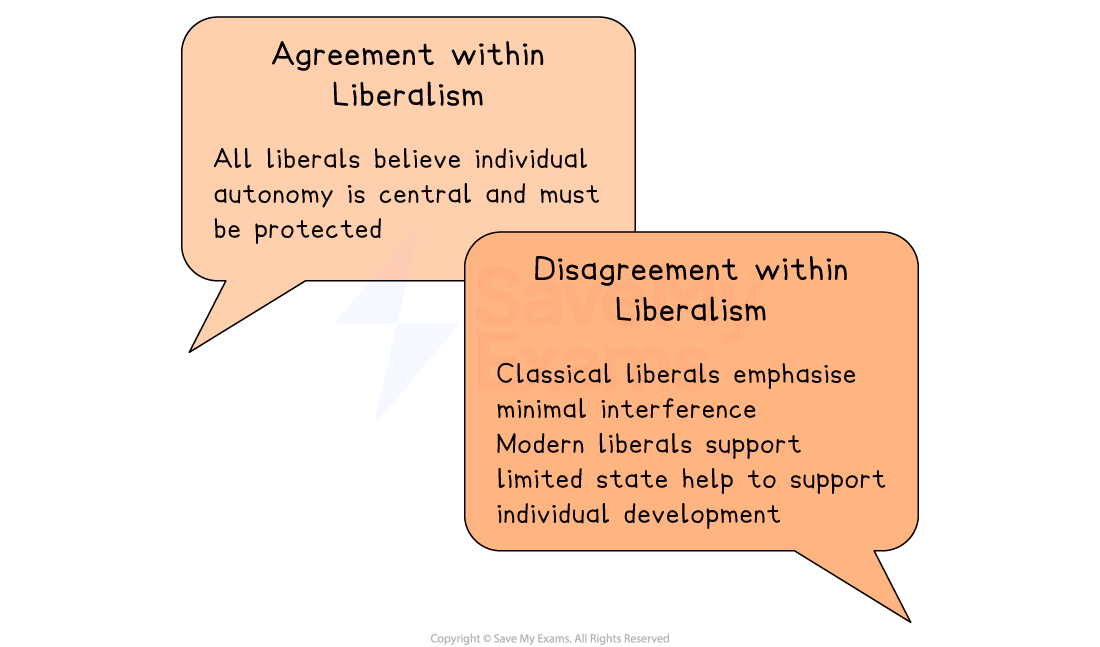
Tolerance is essential to individualism
If individuals want their freedoms protected, they must also allow others to live according to their own beliefs
Do Liberals agree on this principle?
Core principle: freedom and liberty
Core idea
Freedom is essential to liberalism
Individuals should be free to make their own decisions as long as they do not harm others
Key thinkers
John Stuart Mill
The Harm Principle - defends individual freedom unless behaviour harms others
John Rawls
Argued for basic liberties and equality of opportunity to allow individuals to flourish
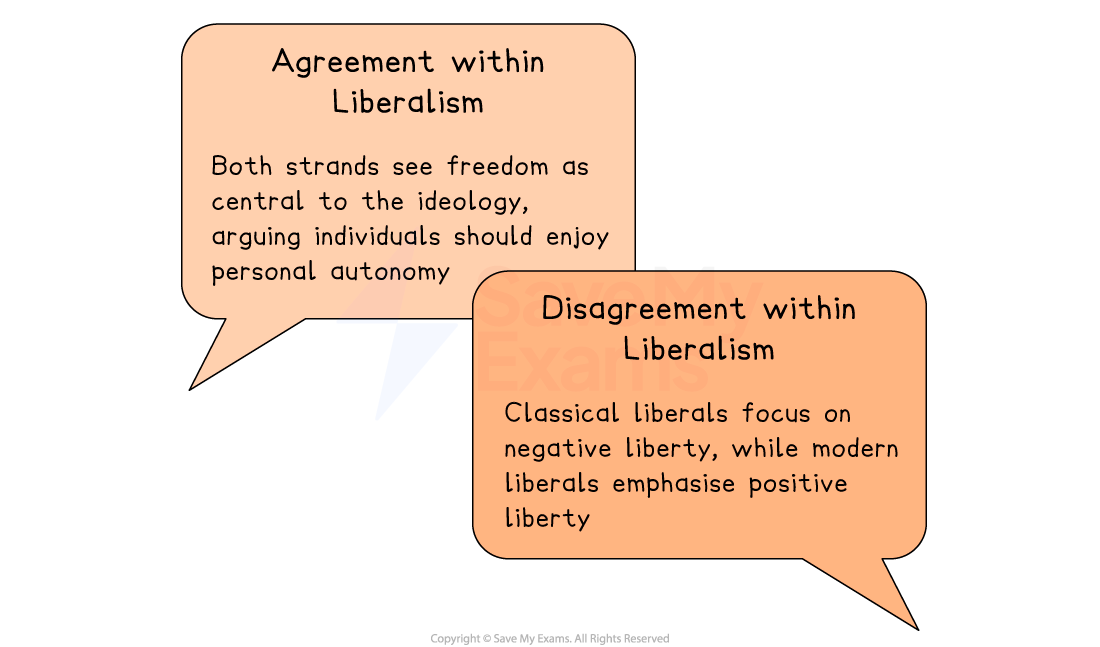
Negative vs positive liberty
Negative liberty | Positive liberty |
|---|---|
|
|
Do Liberals agree on this principle?
Core principle: the state
Core idea
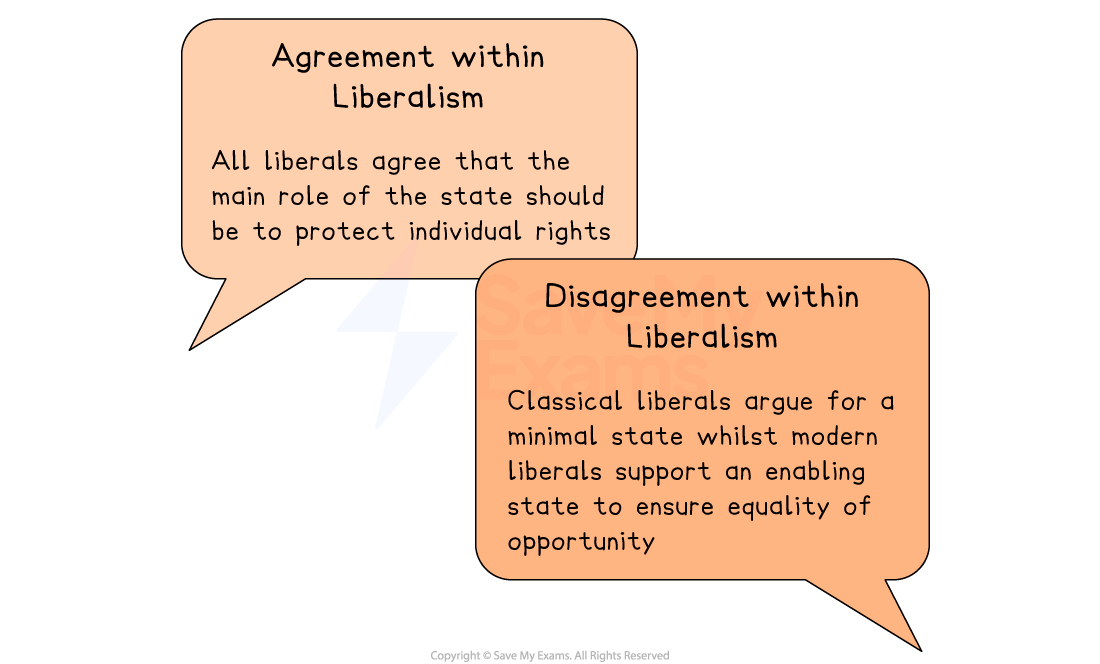
Liberals support a limited government with checks and balances to prevent tyranny
The main purpose of the state is to protect individual rights
The state exists only due to the consent of the governed, expressed through democratic participation
The state is viewed as a necessary evil
It is necessary to protect rights but potentially dangerous if it becomes too powerful
Key thinkers
John Locke
Argued for the social contract
Governments only have authority because citizens consent in return for rights protection
John Rawls
Supported state involvement to prevent individuals succeeding at the expense of others
Do Liberals agree on this principle?
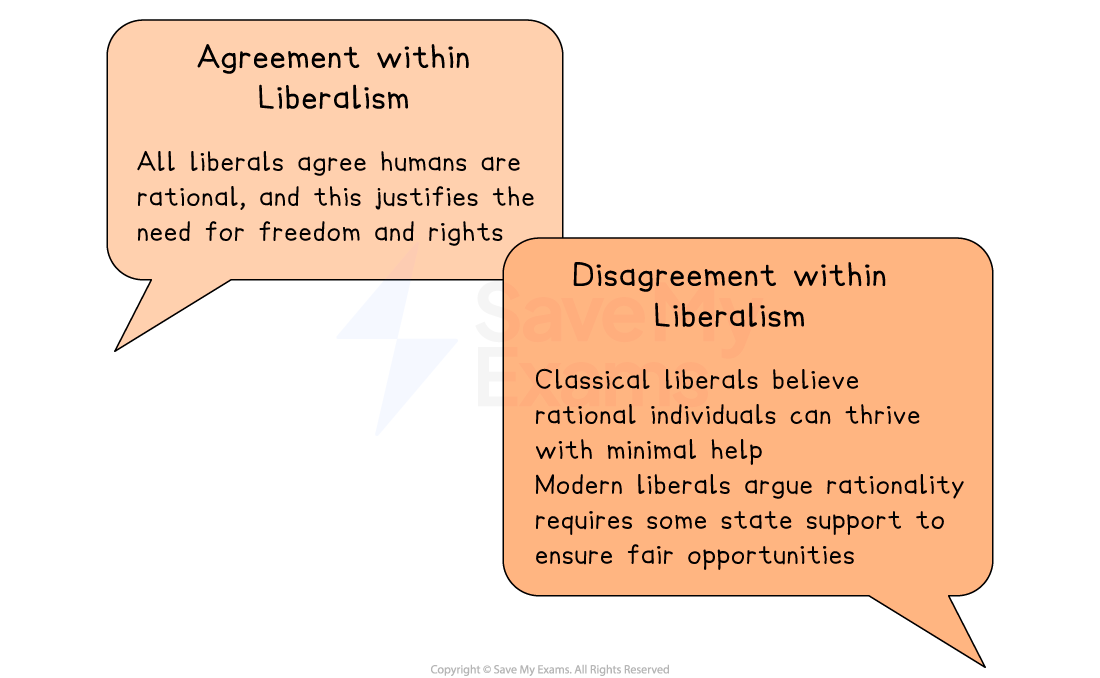
Core principle: rationalism
Core idea
Liberals believe humans are rational, capable of reasoning and making informed decisions
Rationalism supports freedom
Because individuals can think for themselves, they should be allowed to choose their own path
Rational discussion and debate can lead to peaceful reform, rather than relying on tradition or authority
Key thinkers
John Locke
Challenged traditional authority such as the monarchy
Mary Wollstonecraft
Argued that women are rational and should have equal rights
Do Liberals agree on this principle?
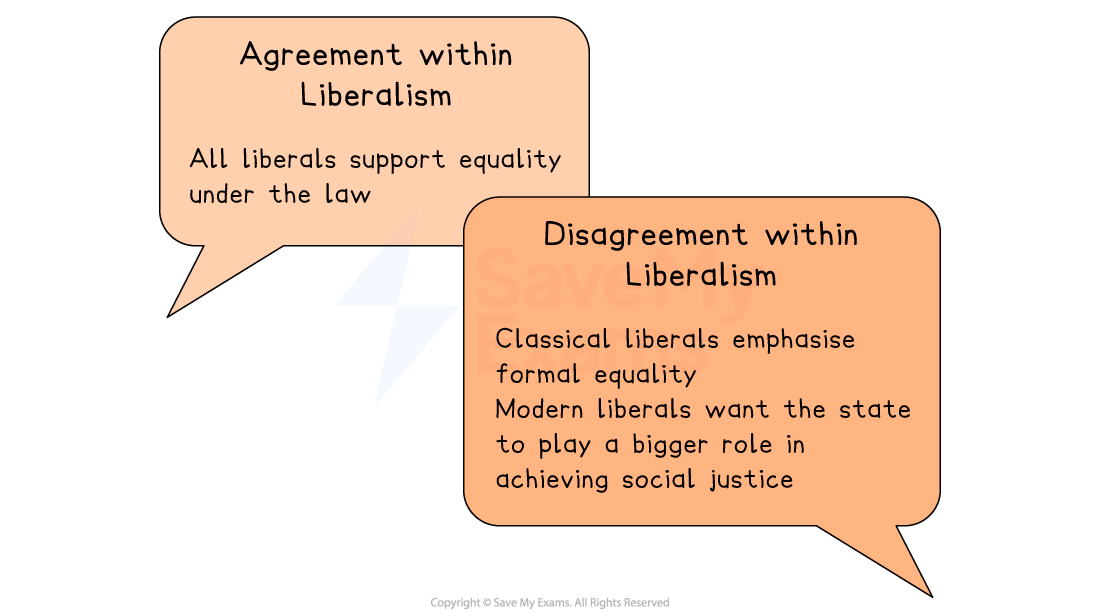
Core principle: equality and social justice
Core idea
Liberals support formal equality, meaning all individuals have the same legal rights
They also believe in equality of opportunity, allowing individuals the chance to develop their abilities and talents
Key thinkers
John Rawls
The ‘theory of justice’ argued for state-led redistribution to improve opportunities for the least advantaged
Betty Friedan
Argued for personal and professional gender equality, supported by formal equality but also changing societal attitudes towards women
Types of equality
Foundational equality | Formal equality |
|---|---|
|
|
Equality of opportunity | Social justice |
|
|
Do Liberals agree on this principle?
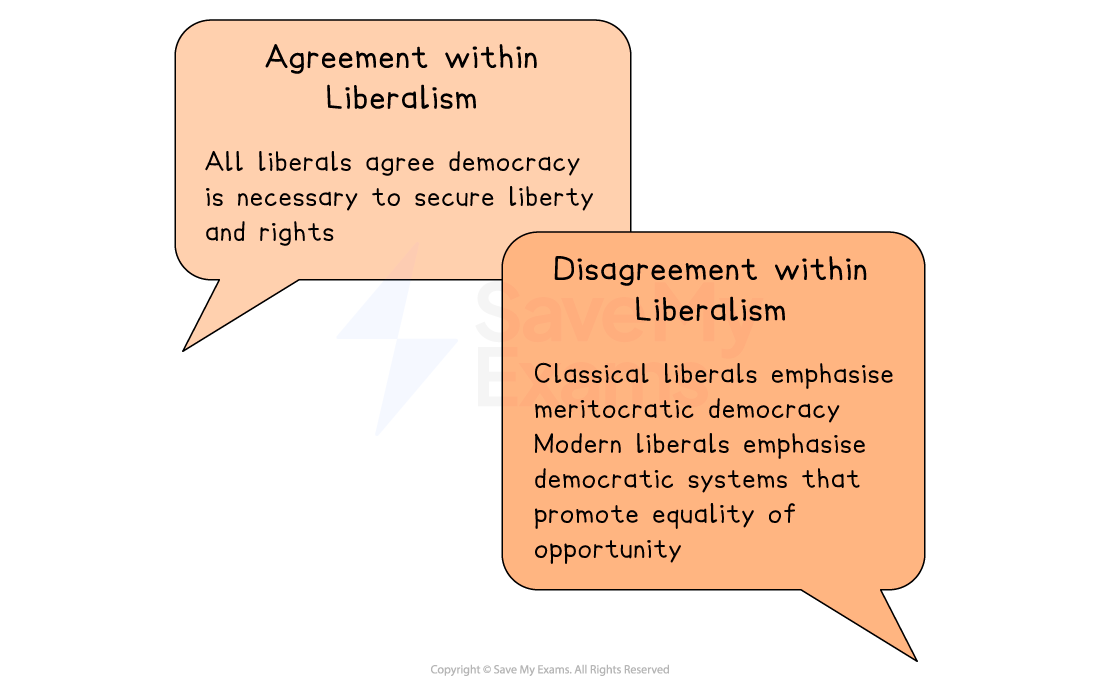
Core principle: liberal democracy
Liberal democracy combines democratic participation with liberal values such as rights, tolerance and the rule of law
Features include free and fair elections, government accountability, constitutionalism, protected rights and political tolerance
Liberal democracy protects freedom and ensures government power is limited
However, democracy can risk tyranny of the majority, where popular opinion undermines individual rights
All liberals agree democracy is necessary to secure liberty and rights
Classical liberals emphasise meritocratic democracy
Modern liberals emphasise democratic systems that promote equality of opportunity
Key thinkers
John Locke
Argued for the social contract and government by consent
Mary Wollstonecraft
Argued for women’s equal rights so they could participate fully in politics
Do Liberals agree on this principle?

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
