Socialism: Core Ideas & Principles (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Introduction to socialism
Socialism developed in the 19th century as a reaction to the inequality and exploitation caused by industrialisation and capitalism
Early socialists argued that rapid economic change created unfair class divisions and harmed workers
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels claimed that society was shaped by class conflict and that capitalism allowed the ruling class to exploit the working class
They believed wealth and resources should be organised collectively to create a fairer society
Over time, socialism has developed into different strands
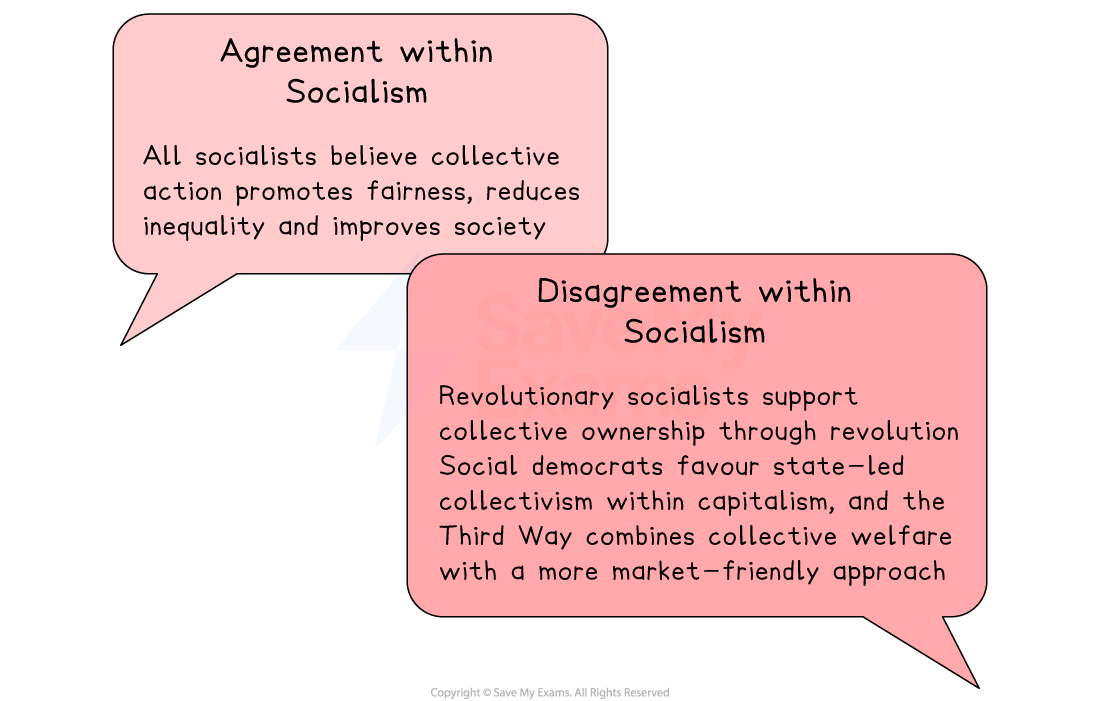
Revolutionary socialists want to replace capitalism
Social democrats and Third Way thinkers believe it can be reformed to achieve social justice
However, all socialists agree on reducing inequality, promoting cooperation and ensuring society works for the many rather than the few
Key principles of socialism

Core principle: collectivism
Core idea
Society is more important than the individual
The needs of the community should take priority over individual interests
Political and social goals should be pursued collectively rather than through individual action
The state should organise collective provision (e.g. healthcare, education) to ensure fair access and a more equal distribution of wealth
Collective effort produces better outcomes than individualism, creating fairness and reducing inequality
Humans are naturally social and co-operative - working together leads to social progress
Collectivism is closely linked to the idea of fraternity
This is a sense of brotherhood and mutual responsibility between individuals
Social solidarity gives people a sense of belonging, reducing exploitation and inequality
Capitalism can undermine collectivism as it encourages competition, which can create conflict
Key thinkers
Karl Marx & Friedrich Engels, The Communist Manifesto
Advocated collectivism through common ownership and class solidarity
Anthony Crosland
Supported extensive state intervention (e.g. progressive taxation) to deliver social justice within a regulated capitalist system
Anthony Giddens
Proposed a Third Way combining individual initiative with social responsibility inside a market economy
Do socialists agree on this principle?
Core principle: common humanity
Core idea
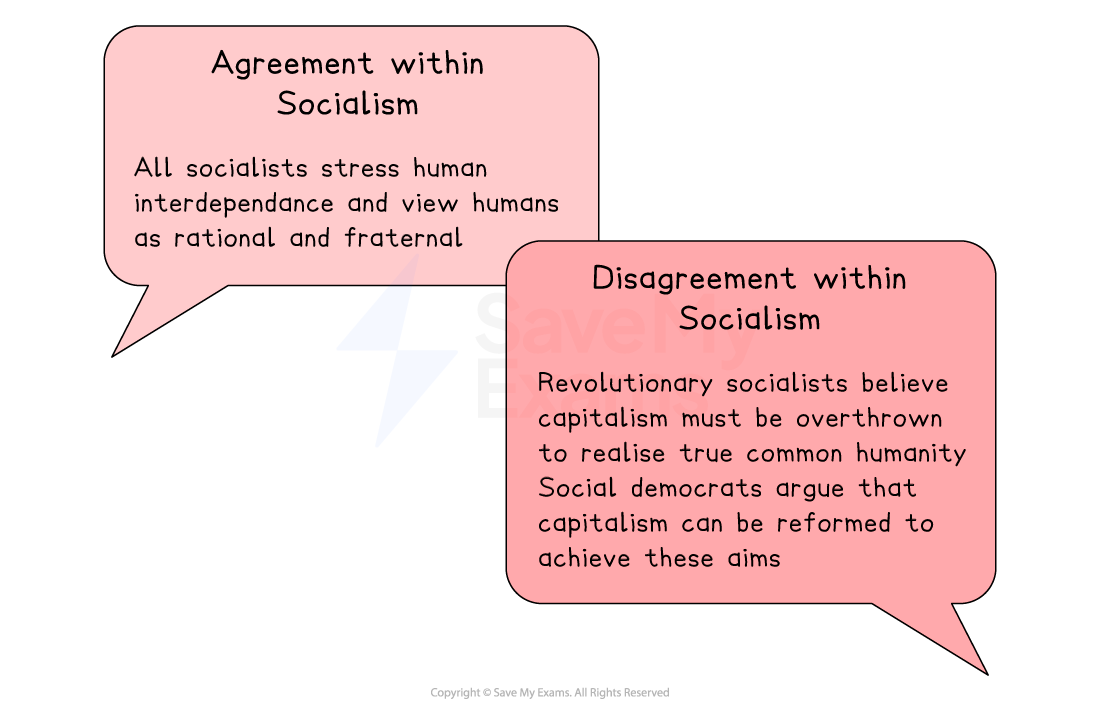
Humans share a common nature and naturally prefer co-operation over competition
They are moral, empathetic and capable of supporting each other
They are rational and able to make decisions that benefit both themselves and the wider community
Individuals develop within social structures
Human behaviour can only be understood in relation to society
Social progress comes from recognising mutual dependence
Society flourishes when individual strengths contribute to collective wellbeing
Capitalism can undermine common humanity by encouraging competition and creating social divisions
Key thinkers
Karl Marx & Friedrich Engels
Argued that capitalism produces alienation, which prevents individuals from understanding their role in society and damaging common humanity
Beatrice Webb
Advocated a national minimum of civilised life, where the state guarantees basic welfare to ensure fairness and support human development
Do socialists agree on this principle?
Core principle: equality
Core idea
Equality is the principle that everyone should be treated fairly and have the same opportunities in life
Most socialists seek social equality, where all individuals enjoy the same rights and access to opportunities and resources
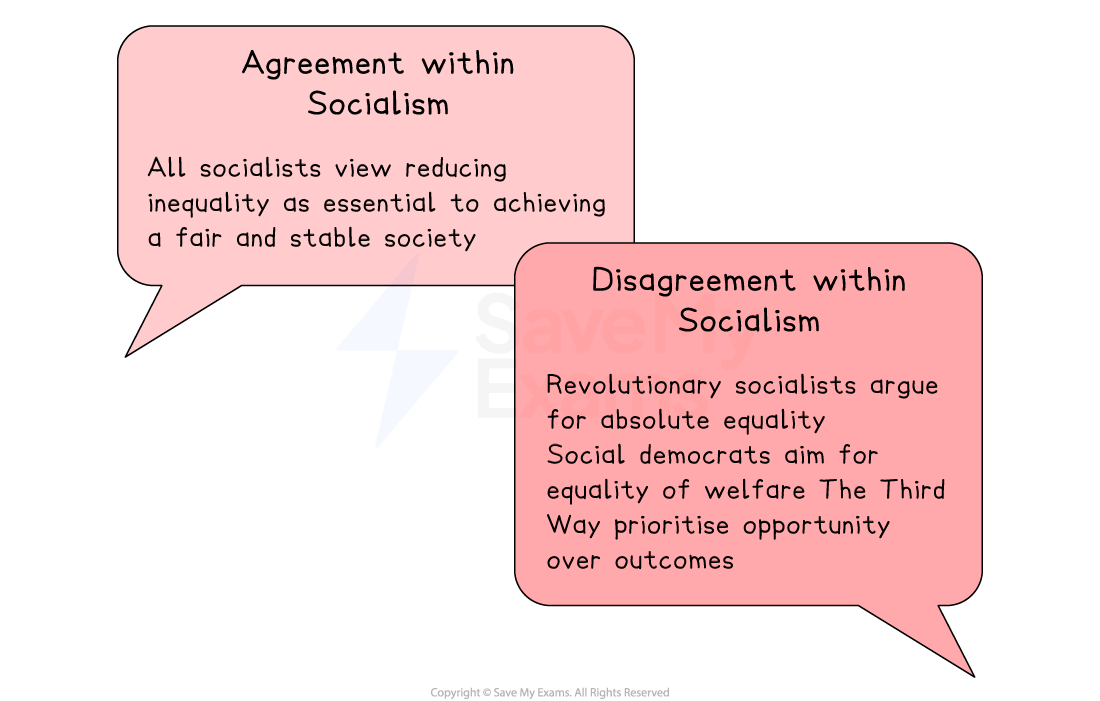
Reducing inequality is seen as both morally necessary and essential for maintaining social cohesion
Forms of equality
Socialists identify several forms of equality
Equality of outcome | Economic equality |
|---|---|
|
|
Equality of opportunity | Absolute equality |
|
|
Key thinkers
Karl Marx & Friedrich Engels
Called for the abolition of private property to deliver full economic equality
Rosa Luxemburg
Argued that genuine equality requires revolutionary transformation, not gradual reform
Anthony Giddens
Promoted equality of opportunity, enabling individuals to help themselves within a reformed market system
Do socialists agree on this principle?
Core principle: social class
Core idea
Social class refers to divisions in society based on people’s relationship to production and wealth
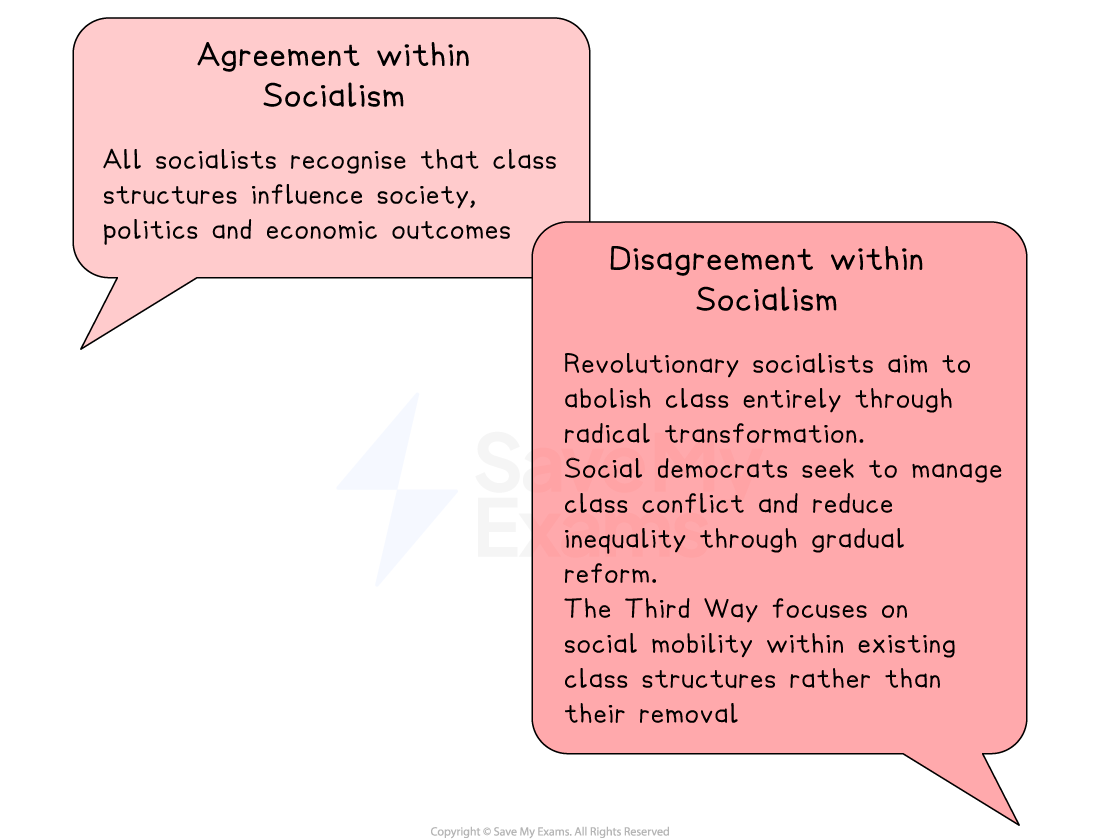
Socialists see class solidarity as a powerful force for social and political change, especially in advancing the interests of the working class.
Collective action enables the working class to challenge elite power and push for fairer political and economic structures.
Class consciousness is the awareness of one’s class position and the wider class struggle
It is essential for challenging inequality and transforming society.
Key thinkers
Karl Marx & Friedrich Engels
Argued that history is driven by class conflict, with the bourgeoisie maintaining power over the proletariat
Predicted a working-class revolution to overthrow capitalism
Beatrice Webb
Highlighted the importance of trade unions in securing political representation and democracy for working people
Anthony Crosland
Believed class inequality could be reduced through education, welfare and social reform rather than revolution
Do socialists agree on this principle?
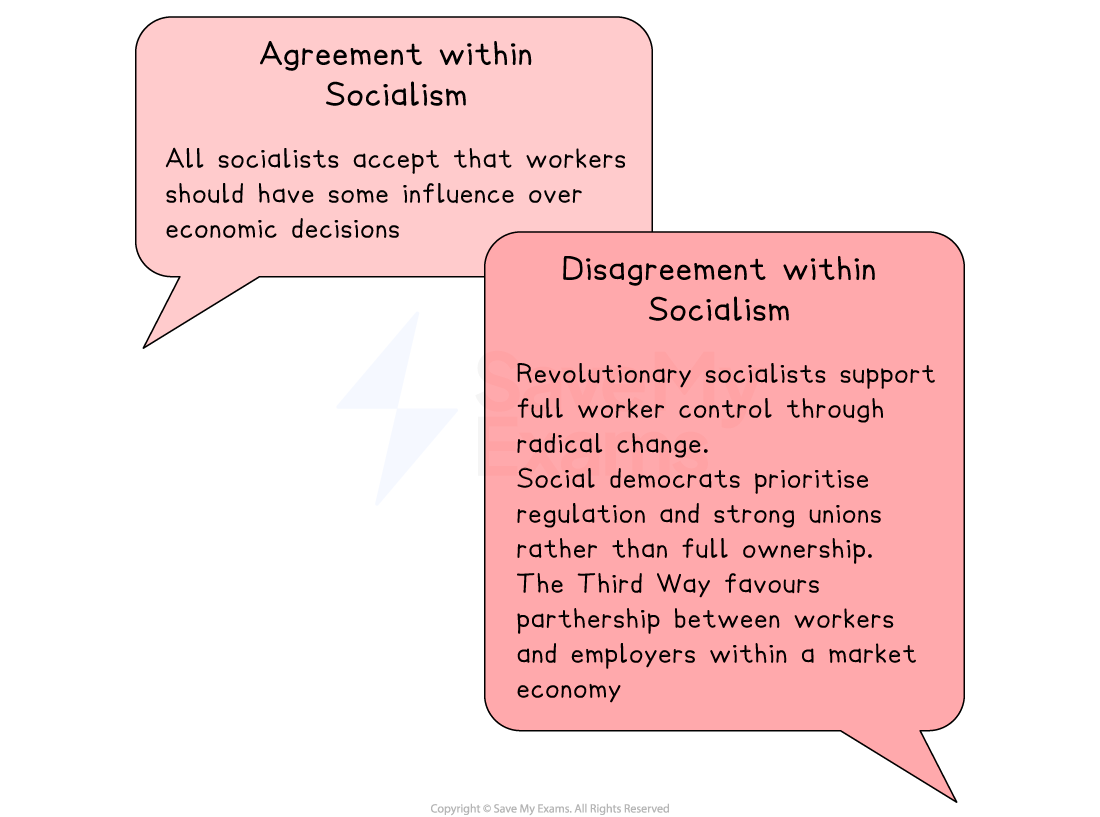
Core principle: workers' control
Core idea
Workplaces should be collectively managed for the benefit of those who work in them
Workers should participate in decision-making
They should be able to influence organisational choices to improve motivation, dignity and fairness at work
Collective control allows the rewards from labour to be more equally shared among workers
The idea can be extended to the wider state, with workers’ control achieved through revolution, gradual evolution or reform
Capitalism enables exploitation
Owners of the means of production profit from workers’ labour
Key thinkers
Karl Marx & Friedrich Engels
Supported workers’ councils and collective control over production as central to overcoming capitalist exploitation
Rosa Luxemburg
Argued that capitalism inevitably exploits workers and will eventually produce conditions for revolutionary worker control
Anthony Giddens
Promoted active individualism, suggesting that class and fixed economic roles matter less than individuals shaping their own identities within a modern economy
Do socialists agree on this principle?

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
