The Legislative Process (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
What is the legislative process?
The legislative process is the series of stages a bill must pass through in Parliament before it becomes law
Most legislation is introduced by the government, although some bills are proposed by backbench MPs or the House of Lords
Types of bill
Type of bill | Description |
|---|---|
Public bills |
|
Private bills |
|
Private Members’ Bills |
|
Stages of the legislative process
Most bills begin in the House of Commons, although some begin in the House of Lords
Once a bill has completed these stages in one House, it goes through the same process in the other House
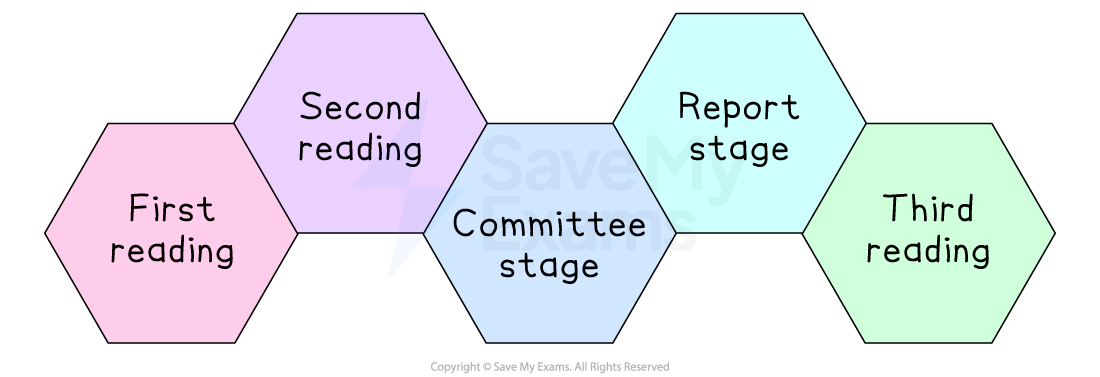
Explaining the steps in the legislative process
Stage | What happens |
|---|---|
First reading |
|
Second reading |
|
Committee stage |
|
Report stage |
|
Third reading |
|
Consideration of amendments (‘ping-pong’)
If the second House amends the bill, it returns to the first House for consideration
This process is known as parliamentary ping-pong
The bill may pass back and forth several times until agreement is reached
If agreement cannot be reached, the government may use the Parliament Acts to force the bill through the House of Lords
Royal assent
Once both Houses agree on the final text, the bill is sent for royal assent
Royal assent is a formality and has not been refused since 1708
Once granted, the bill becomes an Act of Parliament
Evaluating the legislative process
Strengths of the legislative process
Multiple stages allow detailed scrutiny of legislation
The Committee stage enables line-by-line examination and amendment
The House of Lords can improve legislation through expertise and independence
The process allows compromise between the government and Parliament
Weaknesses of the legislative process
Weakness | Explanation |
|---|---|
Executive dominance |
|
Limited scrutiny |
|
Use of Parliament Acts |
|
Ineffectiveness of Private Members’ Bills |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The legislative process is thorough in theory, with multiple opportunities for scrutiny and amendment
However, in practice, its effectiveness is often limited by Executive dominance and time pressures, meaning that Parliament does not always fully scrutinise legislation

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
