Comparative Approaches: UK and US Legislative Branches (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Comparing the UK and US Legislative Branches
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In each of the similarities and differences below, a suggestion is given as to which theory might explain this
This does not mean this is the ‘right’ answer – in most cases, multiple theories can be used to explain a similarity or difference
For Question 1a and 1b, no theories are required – they are only required in Question 2
More information on the three theories – structural, rational and cultural – can be found on the page 'Introduction to Comparative Approaches'
Comparing the nature of the UK and US legislative branches
Both the UK and the US have legislatures responsible for:
Making laws
Scrutinising the executive
Debating policy and representing citizens
However, the way each legislature is structured and how effectively it can operate differ significantly
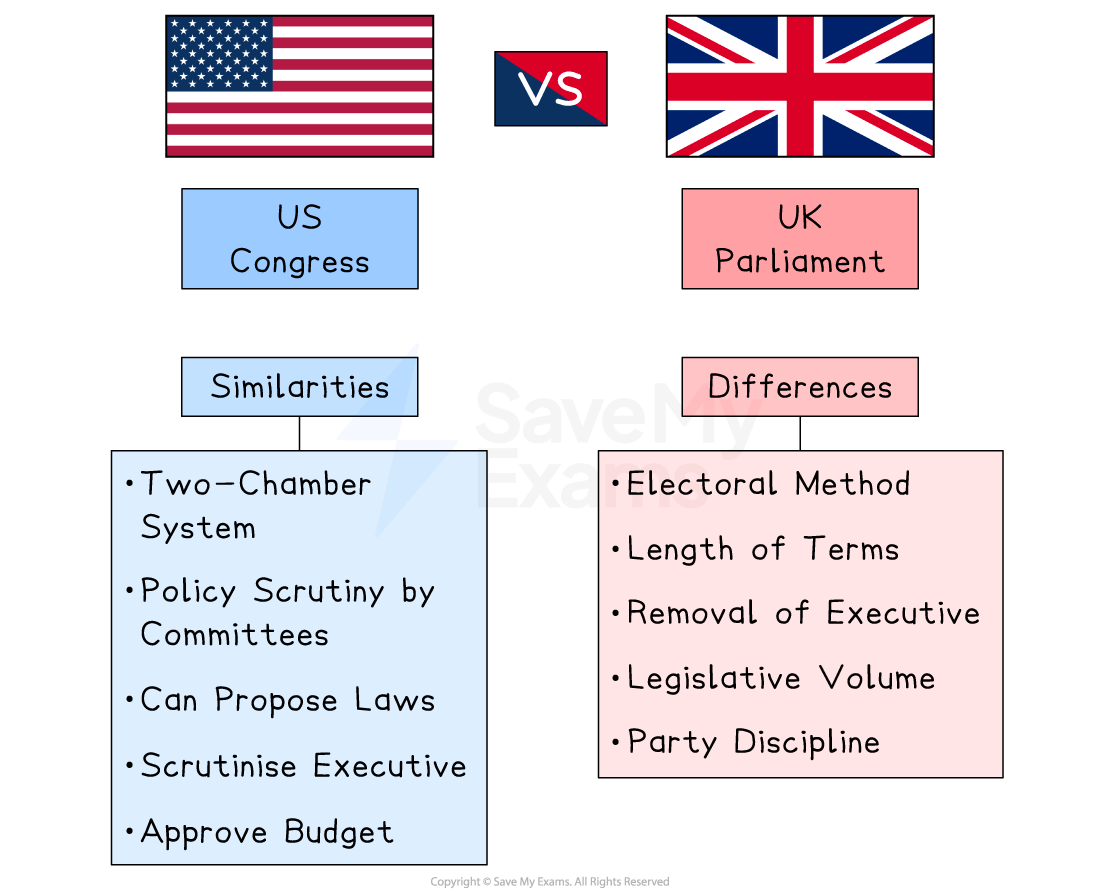
Similarities
Both legislatures have two chambers
US: Congress (Senate and House of Representatives)
UK: Parliament (House of Lords and House of Commons)
Both rely on committees to scrutinise policy
US committees investigate legislation and oversee the executive
UK select committees run inquiries and publish reports
Both can propose laws
In the UK, most bills come from the government
Both scrutinise the executive
US Congress uses hearings
UK Parliament uses mechanisms like PMQs
Both approve budgets
But the Commons is dominant in UK finance bills
Differences
Difference | Explanation + example | Theory explanation |
|---|---|---|
Electoral method |
|
|
Length of terms |
|
|
Removal of executive |
|
|
Legislative volume |
|
|
Party discipline |
|
|
Comparing the extent to which each of the Houses are equal
This comparison allows you to weigh up how far bicameralism is meaningful in both systems
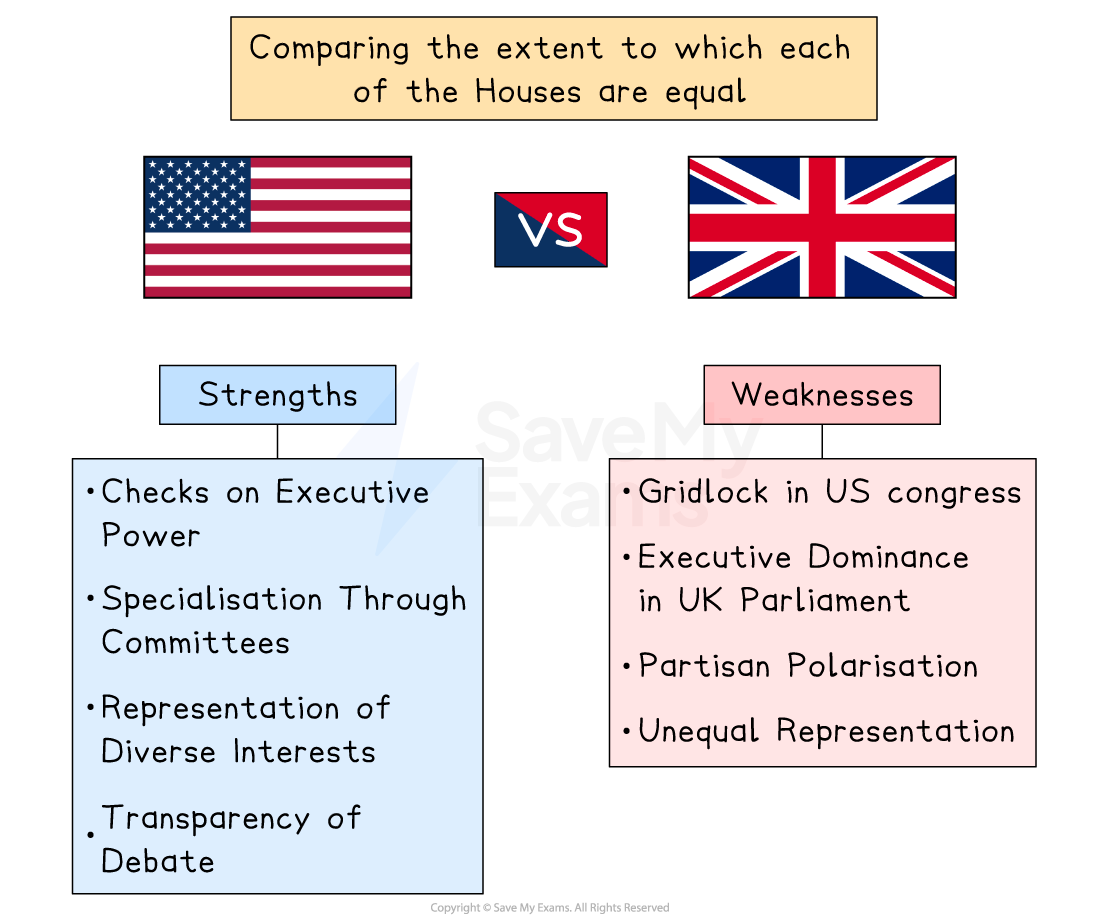
Strengths (ways the houses are meaningfully powerful)
Strength | Explanation + example | Theory explanation |
|---|---|---|
Checks on executive power |
|
|
Specialisation through committees |
|
|
Representation of diverse interests |
|
|
Transparency of debate |
|
|
Emergency flexibility |
|
|
Weaknesses (ways equality is limited)
Weakness | Explanation + example | Theory explanation |
|---|---|---|
Gridlock in US Congress |
|
|
Executive dominance in UK Parliament |
|
|
Partisan polarisation |
|
|
Unequal representation |
|
|
Limited power of some chambers |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
