Protection of Civil Liberties & Rights (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Protection methods used
Groups have used multiple methods to protect civil rights, voting rights and affirmative action, with varying levels of success
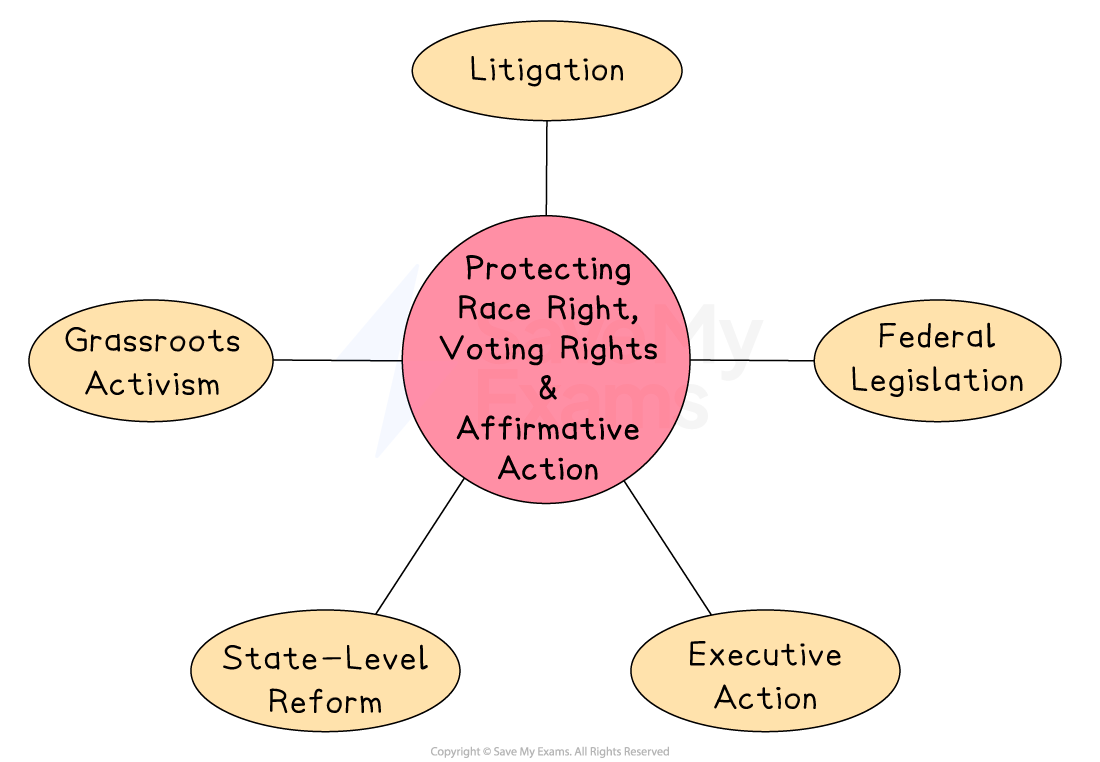
Litigation through the US court system
Grutter v Bollinger (2003) allowed race to be used as one factor in university admissions (not in isolation)
Students for Fair Admissions v Harvard (2023) removed race as a factor that could be considered
Federal legislation
The Civil Rights Act (1964) and the Voting Rights Act (1965) offered protection
Shelby County v Holder (2013) reduced federal enforcement powers, weakening protections in states such as Alabama and Georgia
Grassroots activism and social movements
Black Lives Matter (BLM), particularly after the killing of George Floyd (2020), led to widespread protests
Some local reforms followed, including police oversight and body camera policies
Congressional action following these movements has been limited despite public outcry
Executive action
The Obama administration supported affirmative action in federal programmes
DACA (2012) protected immigrant rights
However, executive-led protections were vulnerable to rollback under later administrations
Some were overturned by the Supreme Court
State-level reform
States such as California strengthened voting protections and maintained affirmative action in university admissions despite federal challenges
However, Shelby County v Holder (2013) reduced federal enforcement powers, weakening protections in states such as Alabama and Georgia
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Overall, protecting race rights in the US requires legal, political and social strategies
Litigation and legislation can be powerful but are limited when court decisions constrain enforcement
Grassroots activism and state policies can provide additional protection and momentum
How effective has the protection been?
The protection of race rights has had both successes and failures in recent decades, particularly from 2000 onwards
Reasons for success | Reasons for limitations |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Overall, protection of race rights is mixed
Legal and legislative frameworks exist, but structural, political and judicial challenges limit effectiveness
Impact of rights campaigns on current domestic policy
Campaigns by interest groups have had both successes and failures in influencing current domestic policy
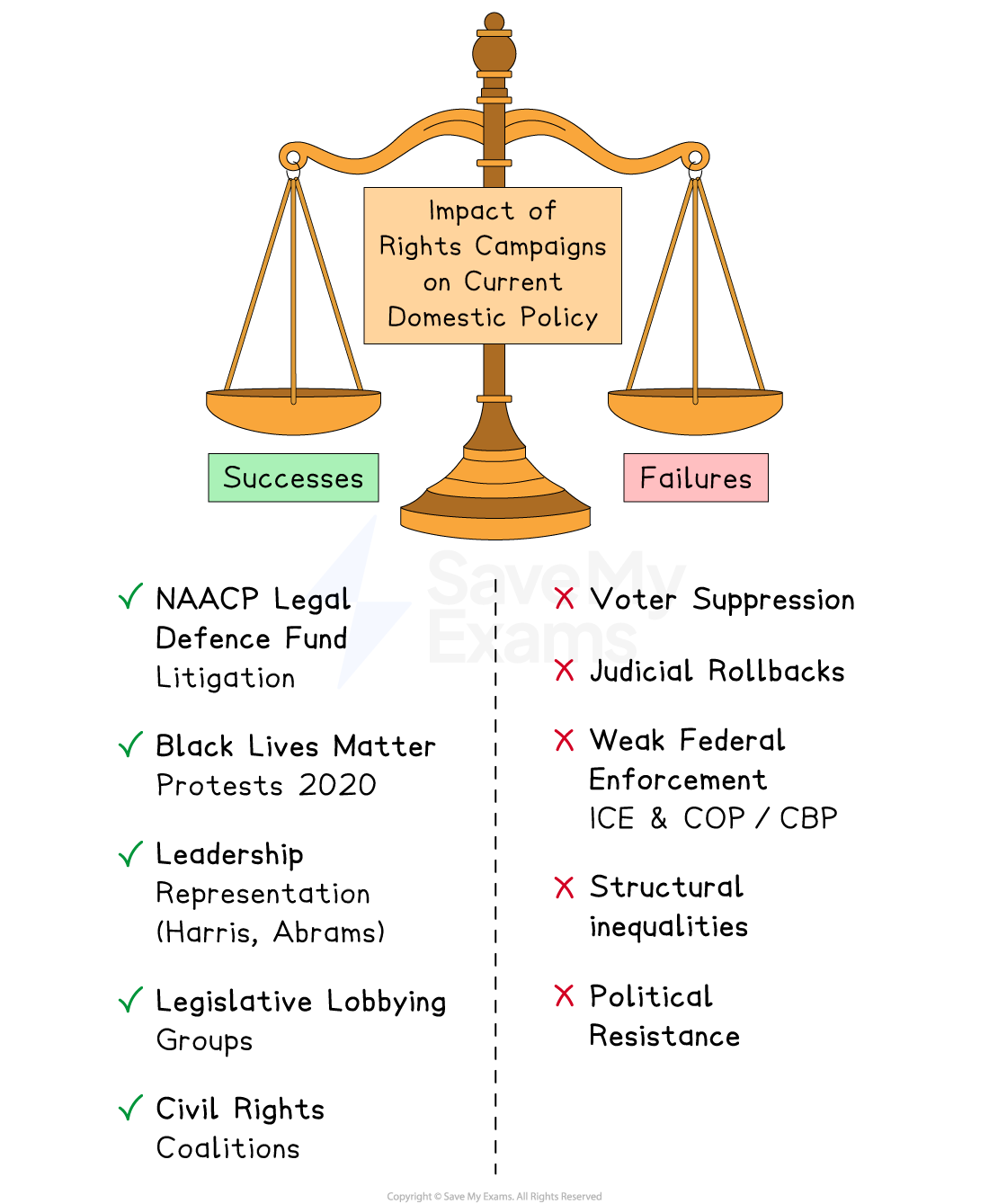
Examples of successes | Examples of failures |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Overall, protecting race and voting rights remains a multi-layered struggle requiring continuous legal, political and social strategies
Progress has been made through Supreme Court rulings, federal legislation and activism, but state resistance, judicial rollback and structural inequality continue to pose obstacles

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
