Interest Groups in the USA (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Different interest groups in the USA
Interest groups in the US can be categorised by their purpose, membership and methods of influence
Type | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
Single-issue groups |
|
|
Professional interest groups |
|
|
Policy or cause groups |
|
|
Membership size and engagement vary across group types
Single-issue groups often mobilise highly motivated supporters
Professional groups rely more on elite lobbying
Different group types use different strategies
Professional groups focusing on insider access
Cause groups rely more on litigation and public campaigns
These distinctions begin to explain why some groups are more influential than others in shaping US policy and legislation
Resources and tactics of interest groups
Interest groups use a range of methods to influence political decision-making, with varying degrees of success
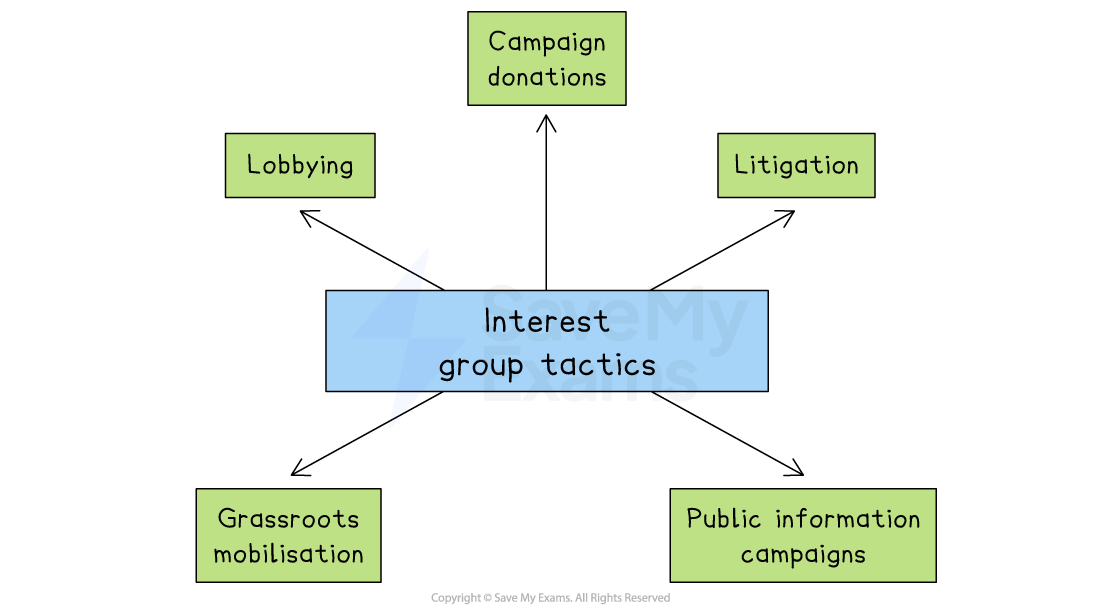
Lobbying is the most direct method, involving contact with lawmakers and officials
E.g. Pharmaceutical companies lobbied heavily during negotiations over Medicare drug pricing in 2021–22, successfully limiting the scope of price controls
Campaign donations help groups gain access
E.g. Super PAC donations from groups like AIPAC to pro-Israel candidates during the 2022 and 2024 election cycles
Litigation allows groups to challenge laws through the courts
E.g. The ACLU successfully contested parts of the Trump administration’s travel ban before the Supreme Court
Grassroots mobilisation pressures lawmakers
E.g. The March for Our Lives movement influenced passage of the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act (2022)
Public information campaigns shape opinion
E.g. NRA advertising opposing gun control after mass shootings help shape public support for Second Amendment rights
The influence, methods and power of interest groups
Interest groups' influence and success depends on resources, public support and alignment with government priorities
Case Study
National Rifle Association (NRA)

The National Rifle Association (NRA) is a powerful single-issue interest group
Its core aim is to defend Second Amendment gun rights
It has traditionally been closely aligned with conservative and Republican politicians
While the NRA remains influential within the Republican Party, its ability to veto all gun legislation has declined
Methods of influence
The NRA exerts influence through lobbying, campaign donations and grassroots mobilisation.
It grades political candidates based on their voting record on gun rights.
These ratings influence voter behaviour, particularly among conservative and rural voters
Political impact
The NRA endorsed Donald Trump in both 2016 and 2020.
This endorsement helped strengthen Trump’s support among gun owners and pro-gun voters.
For many years, the NRA was effective at blocking federal gun control legislation
Declining influence
The NRA’s influence has weakened in recent years.
Following mass shootings such as Uvalde (2022), public support for gun reform increased.
In 2022, Congress passed the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act despite NRA opposition
Internal challenges
The organisation has been damaged by financial mismanagement scandals.
A 2020 lawsuit by New York’s Attorney General further undermined its credibility and resources
Case Study
AIPAC

The American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC) is one of the most influential foreign policy interest groups in the United States
Its primary aim is to promote and maintain strong US–Israel relations
AIPAC works to ensure continued US political, diplomatic and military support for Israel
AIPAC remains highly effective due to its financial resources, strong organisation and direct access to elected officials
Methods of influence
AIPAC exerts influence through intensive lobbying, policy advocacy and campaign funding
AIPAC-backed Political Action Committees (PACs) spent millions of dollars supporting pro-Israel candidates in the 2022 and 2024 elections
These funds were used to support candidates aligned with AIPAC’s views and to challenge lawmakers critical of Israeli government actions
Influence in Congress
AIPAC’s influence is strongest within Congress, where support for Israel remains largely bipartisan
In 2024, Congress approved continued US military aid to Israel, despite growing divisions within the Democratic Party
This demonstrates AIPAC’s ability to shape foreign policy outcomes
Criticism and debate
Critics argue that AIPAC limits open debate on US Middle East policy
Supporters claim AIPAC reflects mainstream US foreign policy priorities and democratic advocacy
Case Study
The American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations

The American Federation of Labor and Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL-CIO) is the largest federation of trade unions in the United States
It represents over 12 million workers across a wide range of industries
Its main aim is to promote workers’ rights, fair pay and strong labour protections
While still influential within the Democratic Party, the AFL-CIO’s power is constrained by long-term declines in union membership
Methods of influence
The AFL-CIO influences politics through candidate endorsements, campaign funding and mobilising union members to vote and campaign.
It plays a key role in grassroots organising, particularly in industrial and unionised regions
Political impact
The AFL-CIO strongly supports Democratic candidates.
It endorsed Joe Biden in both the 2020 and 2024 presidential elections, reflecting his pro-union stance.
In 2023, Biden became the first sitting president to join a picket line, during the United Auto Workers strike in Michigan, reinforcing union support
Influence at different levels
The AFL-CIO’s influence is most visible at the state and congressional level.
Union-backed candidates often perform well in industrial regions with strong labour traditions
Limitations and challenges
The organisation faces declining union membership, which fell below 11% in 2023
Reduced membership limits financial resources and political leverage
The AFL-CIO also struggles to compete with corporate-funded interest groups

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
