Characteristics of a Nation-State & National Sovereignty (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Optional unit
Examiner Tips and Tricks
For Component 3, students only study ONE route: USA Politics (3A) or Global Politics (3B)
The nation-state
A nation-state is a clearly defined geographical area with internationally recognised borders
The nation-state is often seen as the most powerful actor in global politics
Some ethnically- or culturally-unified groups refer to themselves as nation-states, even though they do not have a clearly defined geographical area with internationally recognised borders
E.g The Kurdish and Palestinians
Case Study
The case of Palestine
Background
Palestine refers mainly to the West Bank and Gaza Strip
Palestinian leaders declared independence in 1988, but recognition as a nation-state is not universal
Current recognition status
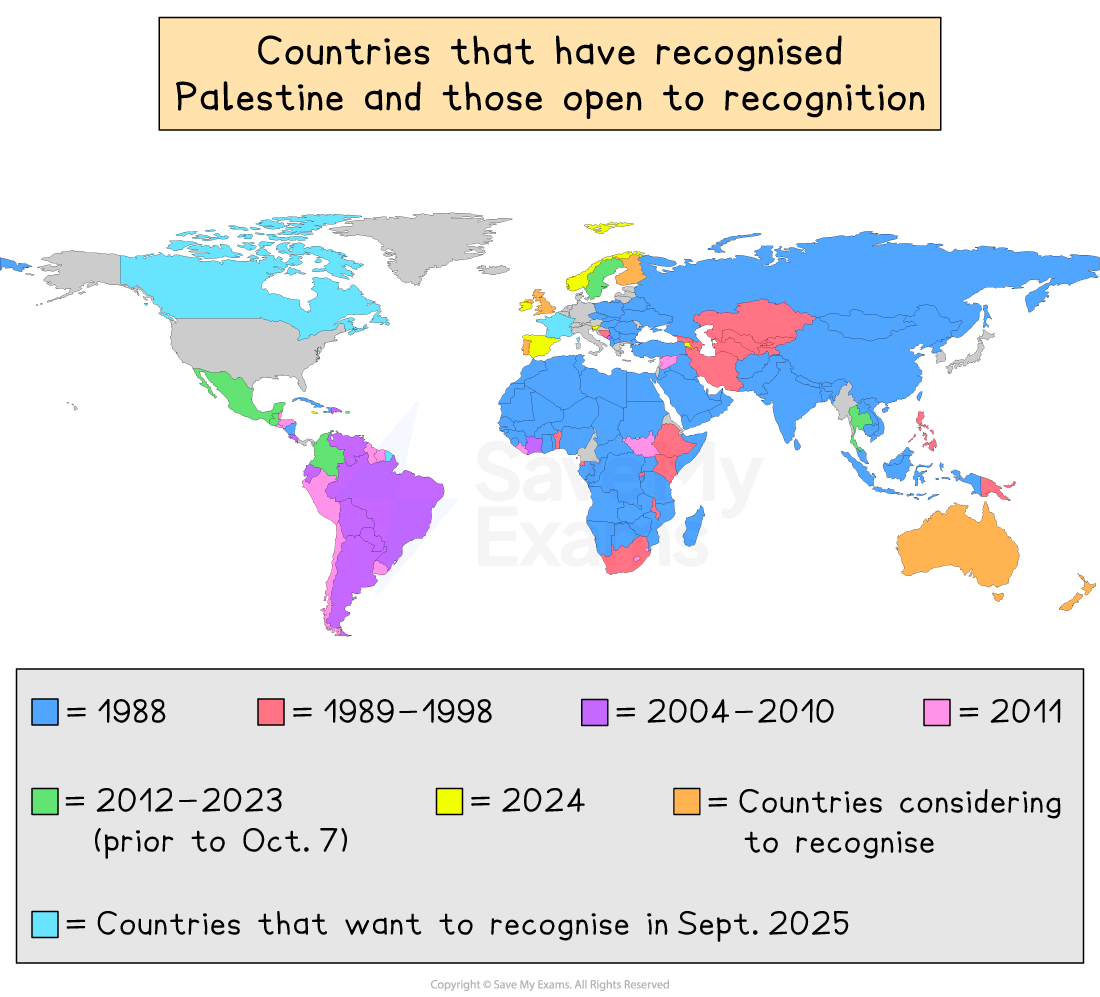
Why some states recognise Palestine
Some countries recognise Palestine as a nation state because:
Self-determination: International law supports the idea that peoples should be able to govern themselves
Elements of statehood: Palestine has a population, claimed territory, and governing bodies such as the Palestinian Authority
International support: Over 130 UN member states recognise Palestine, and it has non-member observer state status at the UN
Support for a two-state solution: Recognition is seen as encouraging peace through two states existing side by side
Why some states do not recognise Palestine
Other states choose not to recognise Palestine because:
Unclear borders: Palestine does not have fully agreed or controlled borders
Limited governance: Control of territory and government is divided, which some argue weakens statehood
Negotiation-first approach: Some states believe recognition should come only after a final peace agreement
Foreign policy reasons: Decisions are influenced by wider diplomatic relationships
National sovereignty
National sovereignty is the principle that a state has ultimate authority to govern itself and make decisions within its own borders without interference from other states or external organisations
Characteristics of national sovereignty
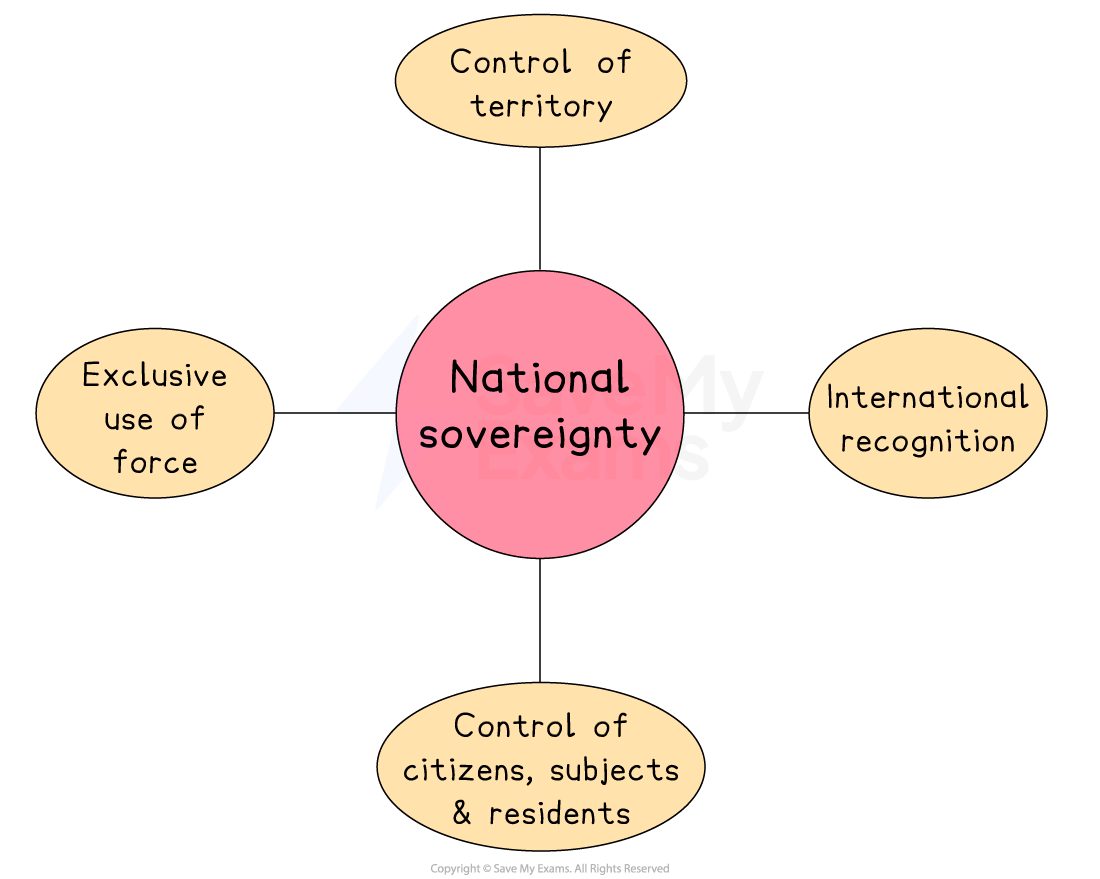
Control of territory
National sovereignty refers to the idea that the nation-state has control over its geographical area
Having control over its borders means the state has the power to limit any outside interference
Control of citizens, subjects and residents
A sovereign nation-state should have a well-functioning government which makes decisions impacting all aspects of the lives of people
In a representative democracy, this power to make decisions is granted by the citizens
Exclusive use of force
Only the government of the state has the authority to use force, usually through military and police action
International recognition
All nation states must recognise the authority of national sovereignty for other states and in return their own national sovereignty will be respected
Consequences of weak national sovereignty
Warning signs | Consequences | Example |
|---|---|---|
Borders are not controlled |
|
|
The government is ineffective or possibly corrupt |
|
|
Non-state actors are using violence |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
