Political: NATO (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
The significance of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, like the UN, originated shortly after World War 2 in 1949
This was near the beginning of the Cold War which saw the USA and Soviet Union as rivals for global dominance
NATO’s aim is collective security, which means that nation states united together are more secure than individual nation states on their own
As protection against aggressive actions, Article 5 of NATO states that an attack against one member is an attack against all
NATO began with twelve European and North American states who felt threatened by Soviet Russia
NATO's founding member states
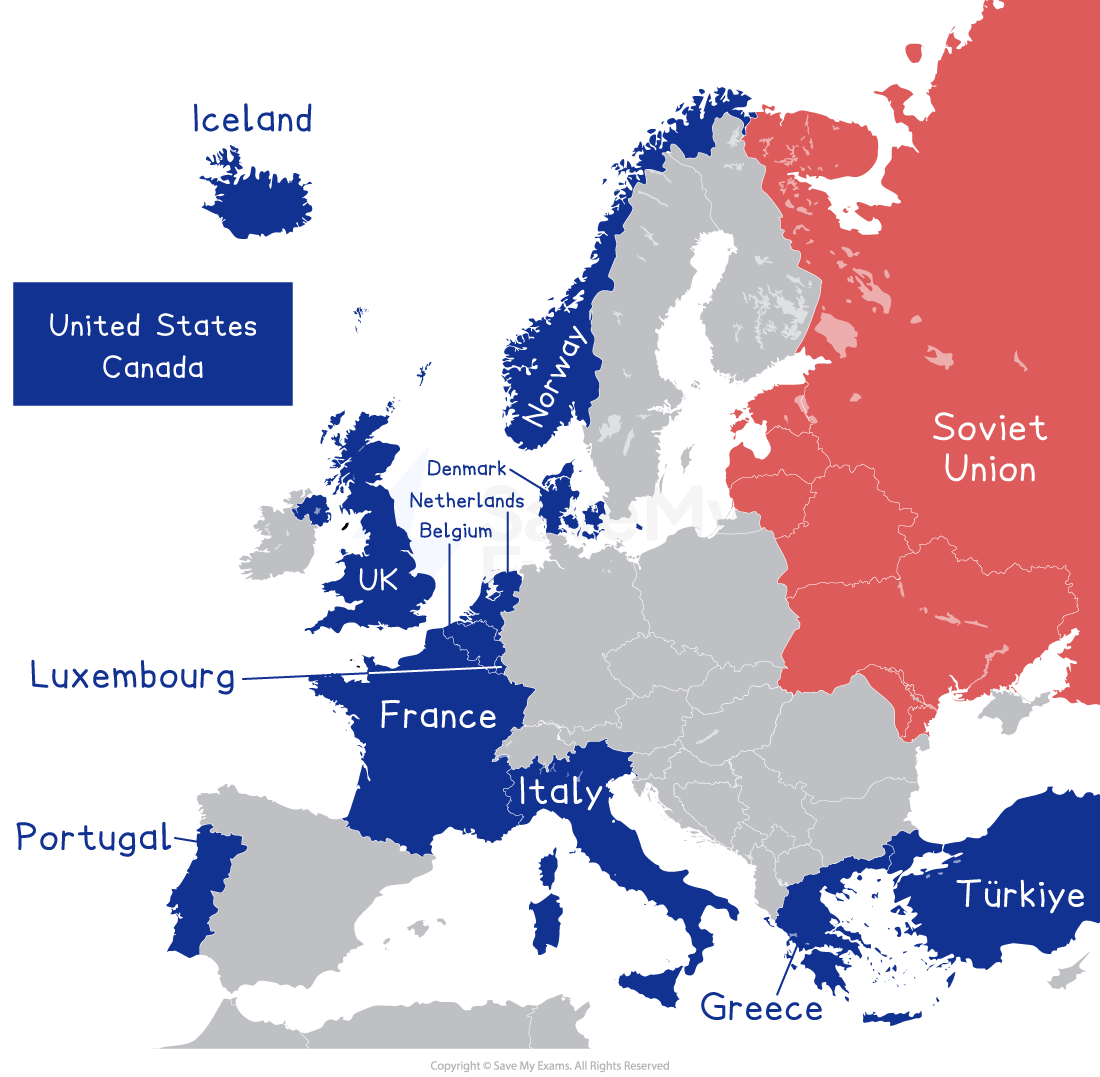
The significance of NATO
NATO, like the UN, is an intergovernmental organisation which sees power in numbers and aims to preserve peace
NATO’s original emphasis is on using the threat of a collective force as a deterrent to attack
NATO's changing role
Over the years NATO has expanded and now has a membership of 32 nations
Its purpose has also changed, particularly after the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991
"Essentially, NATO not only helps to defend the territory of its members, but also engages – where possible and when necessary – to project its values further afield, prevent and manage crises, stabilise post-conflict situations, and support reconstruction." (Source: Nato website (opens in a new tab))
NATO post-1991
The collapse of the Soviet Union, the rise of non-state actors, and Russia’s actions in Ukraine since 2014 have significantly changed the global security environment
These developments have led to new security threats, including terrorism and increased state-based conflict
NATO responds by strengthening deterrence and defence, managing crises and promoting cooperative security among states
It is involved in conflicts and crises, such as natural disasters, even when these do not directly threaten its member states
It is also involved in conflict prevention, conflict management and conflict resolution
It is no longer confined to the North Atlantic region
NATO does not have its own standing army because member states voluntarily contribute soldiers and equipment when required
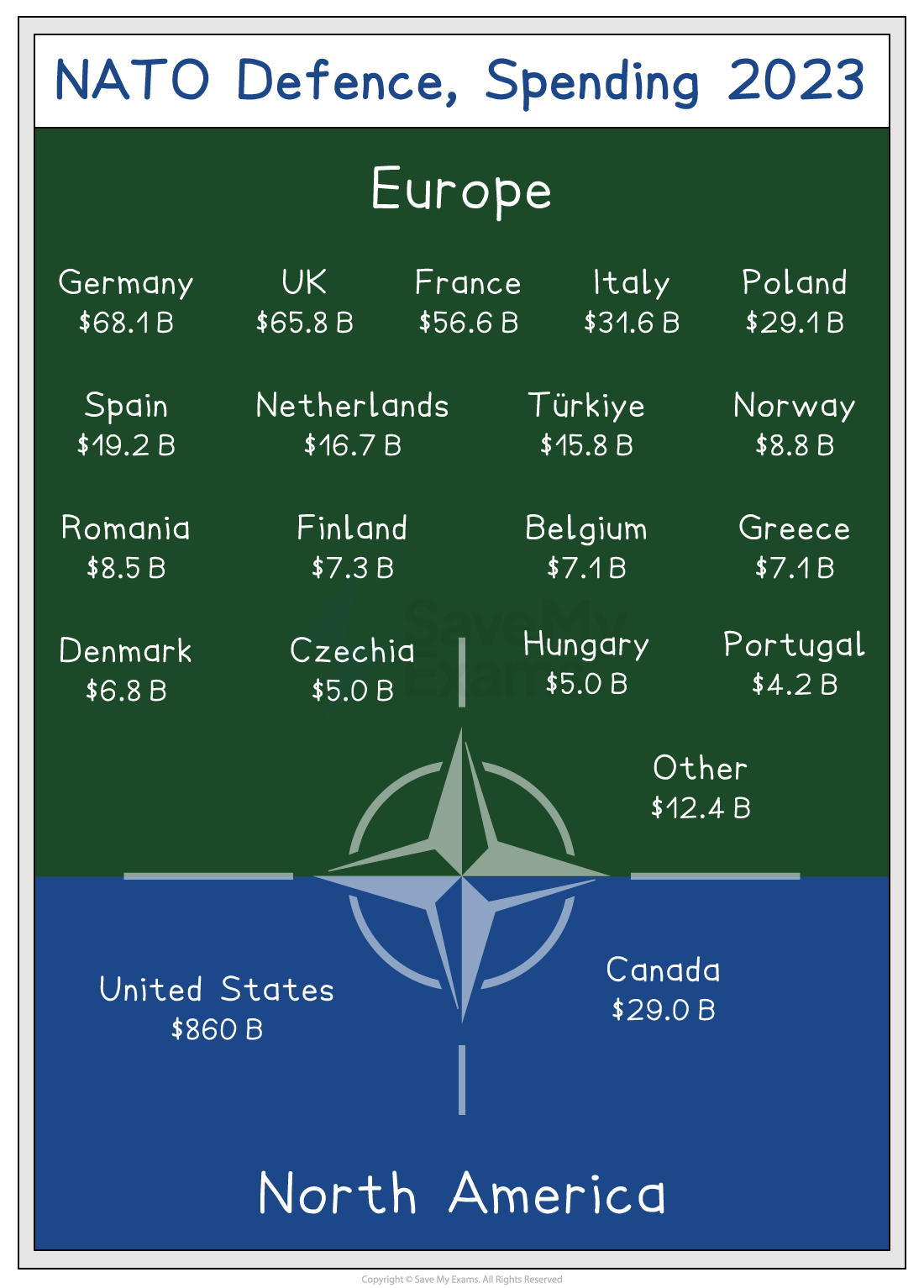
All NATO member states are expected to contribute 2% of their GDP to support NATO operations
The United States dominates in terms of financial support
This dominance is of concern to some who argue that the USA is really in control of NATO
NATO funding
Case Study
NATO in Libya

In 2011 the UN Security Council approved resolution 1970, which expressed grave concern over extreme violence and oppression taking place in Libya
As the UN has no armed forces, several state actors and NATO became involved
NATO actions
NATO prevented arms from being supplied by sea and took over Libyan airspace
They also were responsible for airstrikes which targeted Libyan military but also killed many civilians
Later that year, after the leadership of Libya had been defeated, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 2009
This established a UN support mission to Libya and supported NATOs action to protect civilians
The outcome
Most would agree that the 2011 humanitarian intervention failed the people of Libya
It was left without any form of effective leadership and has experienced extreme political instability and lack of security since 2011
An Evaluation of NATO
Strengths of NATO | Weaknesses of NATO |
|---|---|
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
