Development of Regional Organisations (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
The development of USMCA
States involved

NAFTA (1992–2020)
NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) was created in 1992
It aimed to remove most tariffs and other trade barriers between the USA, Canada and Mexico
The agreement created the world’s largest free trade zone at the time
The impact of NAFTA
Most economists agree that NAFTA benefited all three states overall
It increased trade and economic interdependence across North America
However, some citizens, particularly in the USA, were suspicious of its benefits
Critics argued it led to job losses and factory relocation, especially in US manufacturing
The Move Away from NAFTA
US concerns and power imbalance
The USA dominates the region as a global superpower
This power imbalance influenced how the agreement developed over time
President Trump argued NAFTA was unfair to the USA and harmed American workers
These concerns reflected growing US scepticism about globalisation and regionalism
USMCA (2020–Present)
Creation of USMCA
NAFTA was replaced by the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA) in 2020
USMCA has often been described as NAFTA 2.0
It updated rules on labour, trade and manufacturing while keeping free trade in place
Recent developments and uncertainty
From 2025 onwards, the USA’s renewed America First approach has threatened USMCA
The USA has imposed tariffs on Canada and Mexico and threatened further action
This shows a more unilateral US approach to trade
Significance
The potential collapse of USMCA highlights the risks of economic interdependence
Less powerful states, such as Canada and Mexico, are more vulnerable to US decisions
This shows how regionalism can be shaped – and destabilised – by power imbalances
The African Union (AU)
All African states are members (55 in total)
The African Union is headquartered in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Historical context
African regionalism developed as a response to colonial exploitation and injustice
Many African states sought greater self-determination after independence
Cooperation was seen as a way to protect sovereignty and promote collective development
Organisation of African Unity (OAU) (1963–2002)
The OAU was established in 1963
Its main aim was to protect the sovereignty of newly independent African states
It focused on resisting neo-colonialism and external interference
However, it was criticised for being too reluctant to intervene in internal conflicts and human rights abuses
Development of the AU (2002–Present)
The African Union replaced the OAU in 2002
It was designed to build on the original aims of the OAU and was partly modelled on the European Union
Its purpose expanded to include economic, social and political cooperation across the continent
Aims and objectives
To defend the sovereignty of all African states
To promote and protect human rights through the African Charter
To encourage democracy, good governance and reduced corruption
To promote economic and social development across Africa
Impact of the African Union
Achievements | Limitations and challenges |
|---|---|
|
|
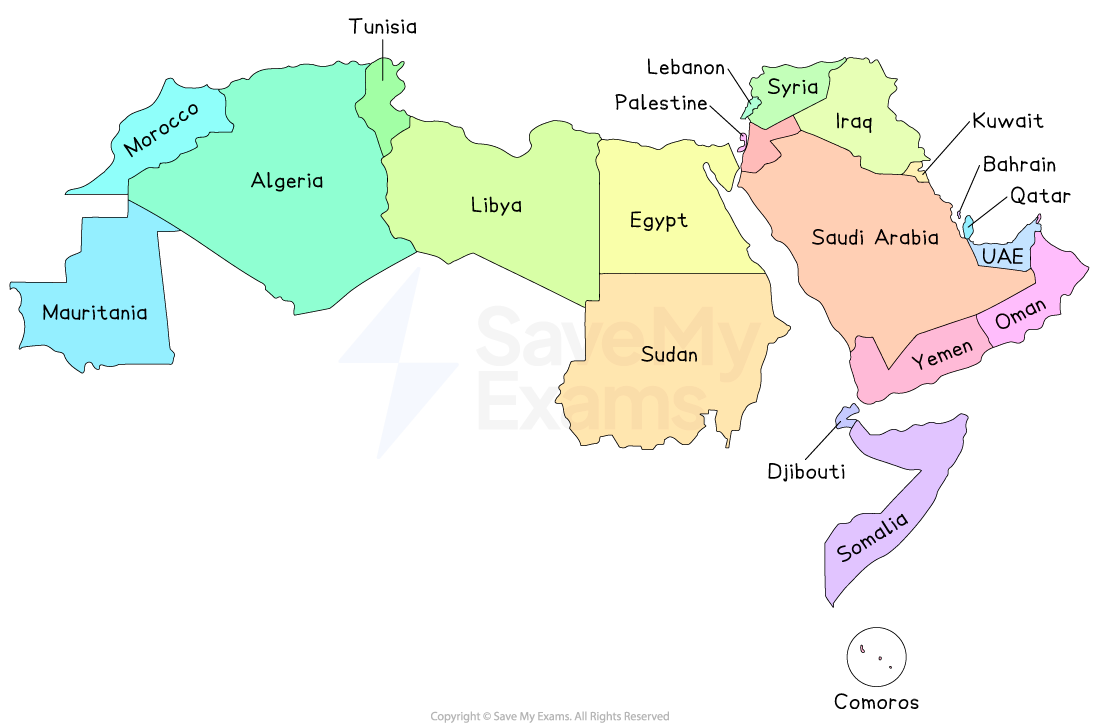
The Arab League
The Arab League was formed at the end of the Second World War in 1945 in Cairo, Egypt
The organisation aimed to address immediate post-war regional concerns
Purpose of the Arab League
To strengthen solidarity between Arab states with shared political, linguistic and cultural ties
To provide a platform for cooperation between member states
To promote economic development and regional security
To defend the sovereignty of all member states and resist external interference
The impact of the Arab League
Achievements | Limitations and challenges |
|---|---|
|
|
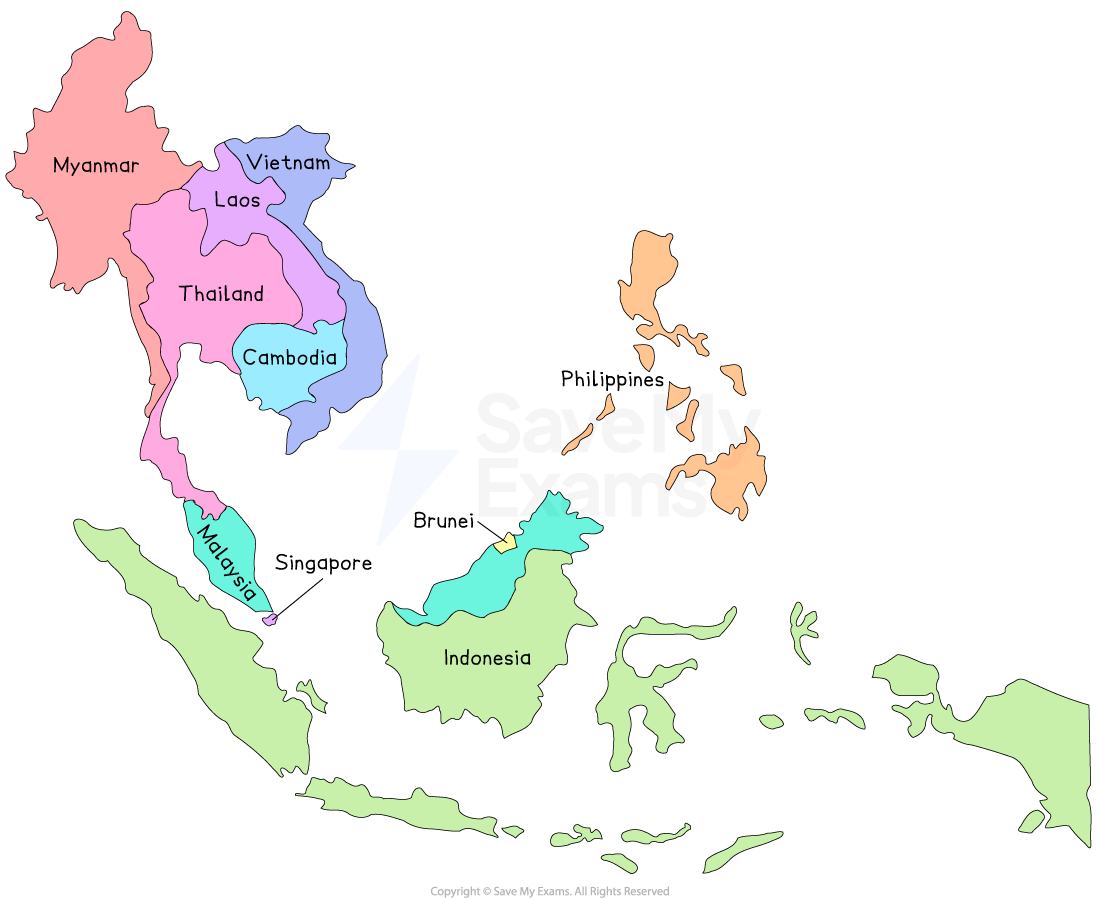
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
ASEAN was established in 1967 to encourage cooperation and stability in Southeast Asia
From the outset, ASEAN emphasised respect for state sovereignty and non-interference
Original aims
To promote economic, social, cultural, technical and educational cooperation
To encourage regional peace and stability
To uphold justice, the rule of law and the principles of the United Nations Charter
Strategic goals announced in 2025
ASEAN introduced new goals with a stronger focus on economic growth.
These included:
reducing trade barriers between member states
prioritising environmentally sustainable development
increasing innovation, adaptability and economic resilience
The impact of ASEAN
Achievements | Limitations and challenges |
|---|---|
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
