Forms of Regionalism (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Optional unit
Examiner Tips and Tricks
For Component 3, students only study ONE route: USA Politics (3A) or Global Politics (3B)
The growth of regionalism
Regionalism refers to the interconnected relationships that have formed between groups of states for multiple reasons
Geographical proximity to each other
Share similar geographical conditions
Share a common language, culture, religion or history
Similar goals and interests
Similar levels of economic development or types of resources
Similar system of government
A growth in regionalism is often thought to be a response to global governance and to globalisation in general
With regionalism states strengthen their position and power in the global arena
Smaller group of states with characteristics in common are better able to address specific needs and policies
Perceptions that global governance institutions favour powerful states
For example, the UN Security Council
Frustrations with global intergovernmental development organisations such as the World Trade Organisation, International Monetary Fund and World Bank
Globalisation is perceived to bring proportionally more benefits to powerful actors and states
Economic regionalism
Economic regionalism is the process by which states in a specific region form agreements to cooperate economically so that all will benefit
Many regional IGOs, though dealing with multiple challenges, prioritise the economic development of member states
Mutually beneficial trade agreements made between states in a specific region are the most well known examples of economic regionalism
Economic regionalism ordinarily involves states that are in the same geographic region
The Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is an exception but they do share a valuable natural resource - oil
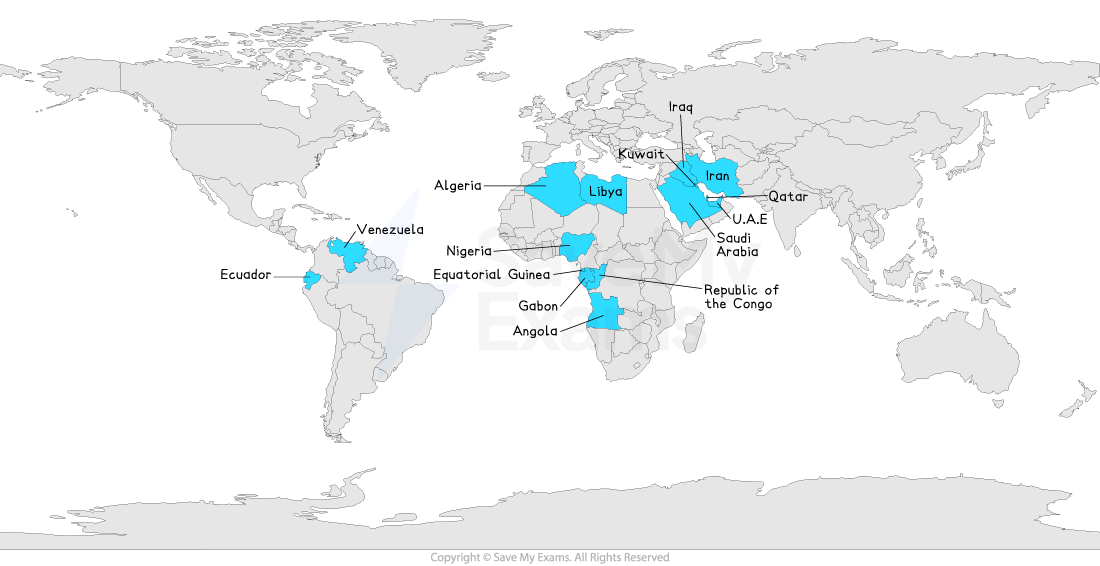
Security regionalism
Security regionalism is when countries in the same region work together to prevent and combat shared threats to security
Terrorism and/or violent resistance groups
Cyber-attacks
Resource scarcity
Conflict
Security regionalism maintains peace and security with member states, participating in:
Multilateral agreements
Arms control treaties
Assessing military capabilities
Intelligence gathering
Examples of regional security organisations include
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation NATO
Organisation for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE)
Many regional intergovernmental organisations deal with multiple political issues but also focus on maintaining peace and security
Political regionalism
At the international level amongst states
Political regionalism is based less on geographical location, and more on shared political values
However, due to historical and cultural factors shaping political values, states are often in close proximity
They cooperate to find solutions to political issues and strengthen their power globally
Non-state actors and political regionalism
This usually occurs because of historical divisions which resulted in groups being absorbed into larger states
These groups share some or all of the following:
A strong sense of shared cultural identity which differs from the majority
A dissatisfaction with their treatment or position as a group within the state
A desire for more power
Either autonomy within the state or complete separation from the state
Examples include:
Catalonia in Spain
Scotland in the UK
Quebec in Canada

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
