Regionalism & Contemporary Global Issues (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Regionalism, conflict and poverty
Conflict and poverty are two of the most concerning political issues in contemporary politics
They threaten the stability of states and, because of the interconnectivity of states, entire regions are frequently impacted
Conflict and poverty are not confined by borders
Poverty makes likelihood of conflict greater
Instability and violence often spreads throughout regions
People in conflict zones or suffering from extreme poverty often flee to neighboring countries in hope of safety or a better life
Case Study
Conflict in Central Africa
Ongoing conflict in Central Africa has led to severe humanitarian consequences
One of the most significant impacts has been the large-scale displacement of people
Across Africa, over 45 million people have been forcibly displaced by conflict
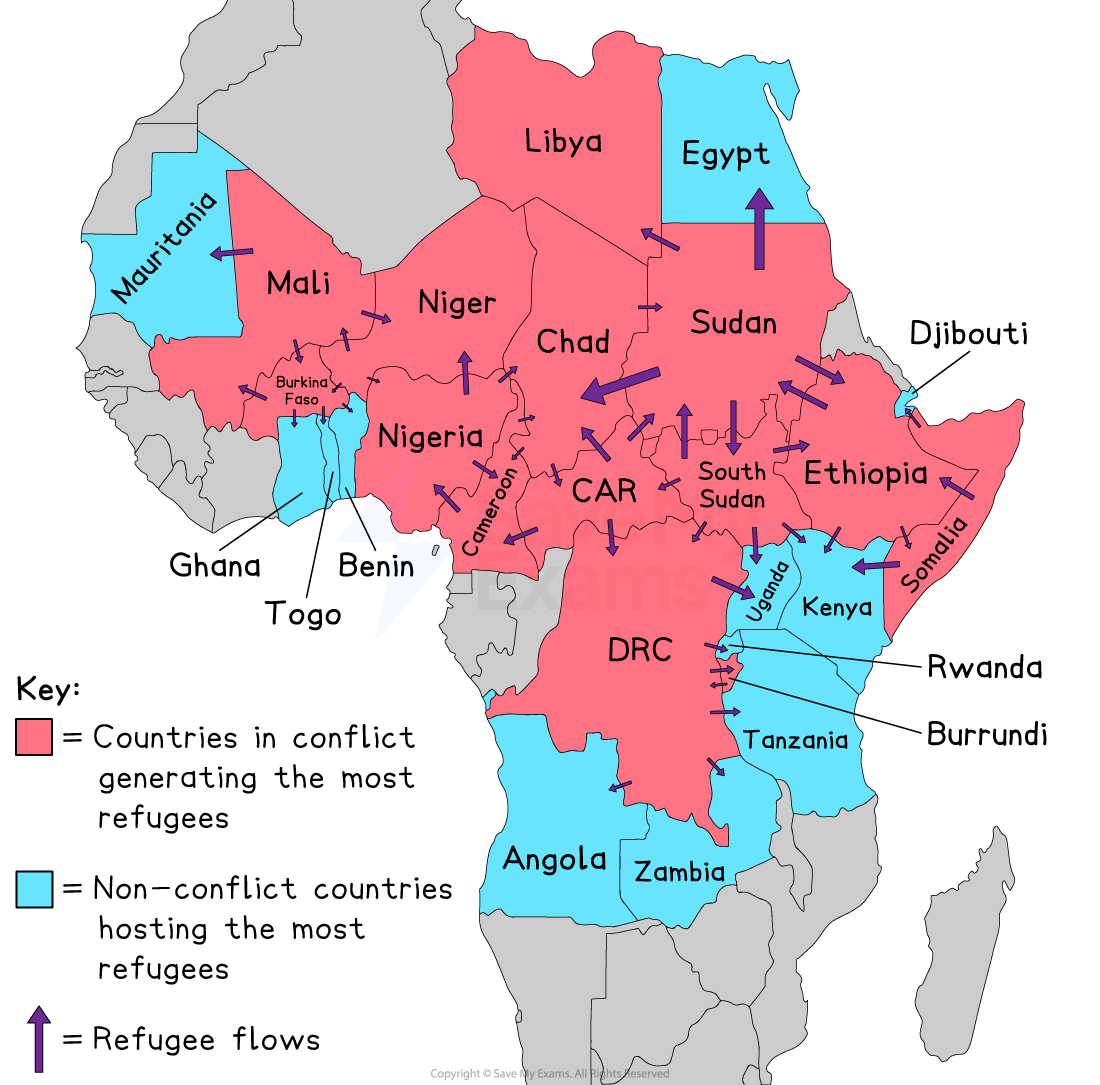
Conflict in Sudan
Sudan experienced more than a decade of political instability, extreme violence and rising poverty
These conditions created an environment highly vulnerable to conflict
In 2023, war broke out between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF)
The conflict has contributed to one of the world’s largest humanitarian crises
Regional Impact
The Sudan conflict affected multiple neighbouring states across Central Africa
Many of these states already face poverty and internal conflict
As a result, they are unable to cope with large numbers of displaced people.
The region is further destabilised by the presence of armed groups such as Wagner, the Lord’s Resistance Army, and M23
Role of regional and global organisations
African Union (AU) | United Nations and International Criminal Court |
|---|---|
|
|
Regionalism, human rights and the environment
Human Rights
Universalism with regard to human rights can be at odds with regional understandings of human rights
Cultural relativists would argue that human rights are not universal and that the cultural values should be considered
Several regions drafted their own documents outlining human rights
These regional declarations reinforce many of the rights outlined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)
They also provide slightly different interpretations of the rights human beings should be granted based on regional values
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR) | The African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights |
|---|---|
|
|
The ASEAN Human Rights Declaration | The Cairo Declaration on Human Rights in Islam |
|
|
Regional organisations argue that the protection and enforcement of human rights is best done at a regional level rather than an international level
They claim they have a better understanding of the regional context of human rights
States sovereignty is always an obstacle but states are more likely to cooperate with regional organisations to enforce human rights
The protection and enforcement at the regional level faces the same obstacles as that global governance
State sovereignty and limitations as to what can actually be done beyond diplomacy and suggestions
The environment
Many argue that international cooperation to address environmental issues, including climate change, is the only way forward
Regional cooperation also has its place, as different regions may have unique environmental challenges
Case Study
The Arctic Region
The Arctic Council fosters environmental cooperation between the Arctic states
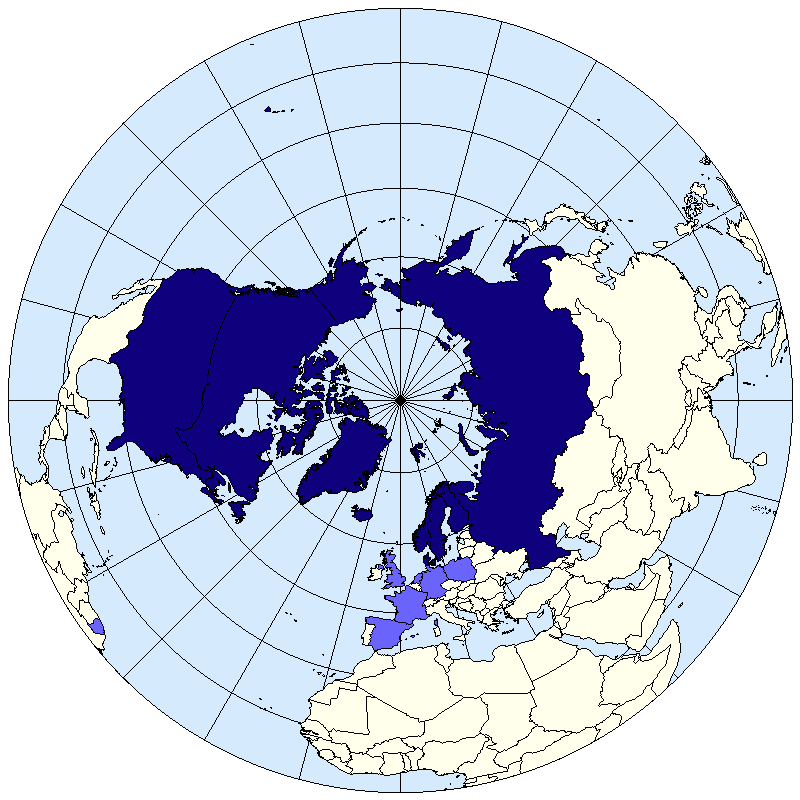
The Council has attempted to address environmental concerns in the region
Producing research papers outlining the impact of climate change on the region to better inform the global community and suggest plans of actions that need to be taken
Monitoring levels of air pollution over a 20-year period
Influencing international agreements and international law
Making agreements between states in areas such as protecting biodiversity and science-based research
Working in consultation with indigenous communities living in the region
Success of the Arctic Council
Their scientific research and data is widely distributed and used by multiple actors to attempt to change damaging environmental practices
The growth of non-member observer states demonstrate a recognition that the Arctic region reflects wider global environment concerns

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
