Ecosystems: Tundra (WJEC Eduqas GCSE Geography B): Revision Note
Exam code: C112
Specification Link
This page covers part of 3.2.2 and 3.2.3 of the WJEC Eduqas GCSE B specification
3.2.2 - How are ecosystems damaged by human activity?
How tundra have been damaged by human activity.
How processes within the ecosystem have been affected
The effects of the damage at the local scale, to include the effect on biodiversity, and at the global scale
3.2.3 - Why and how are ecosystems managed in a sustainable way?
The reasons for conservation and management.
The ways in which tundra have been managed
Strategies for sustainable management.
Human activity in the tundra
How human activity has damaged the tundra
Cold environments, such as the tundra, are fragile and easily damaged
They are mainly undisturbed, undeveloped, and usually uninhabited
They are considered important and worthwhile areas to protect because:
They provide niche habitats for organisms, which protect biodiversity
Scientists can research plants and animals in their natural habitats
Comparing natural ecosystems to managed ecosystems is useful
They are the last remaining areas that were unaltered by human activity
The biome has low biodiversity
Human impacts are increasing
The main threats to the biome are:
Resource exploitation
Infrastructure and development
Pollution
Fishing
Tourism
Resource Exploitation (Mineral/Energy Extraction)
Valuable reserves like oil, gas, gold, silver, iron ore, and copper are found beneath the tundra
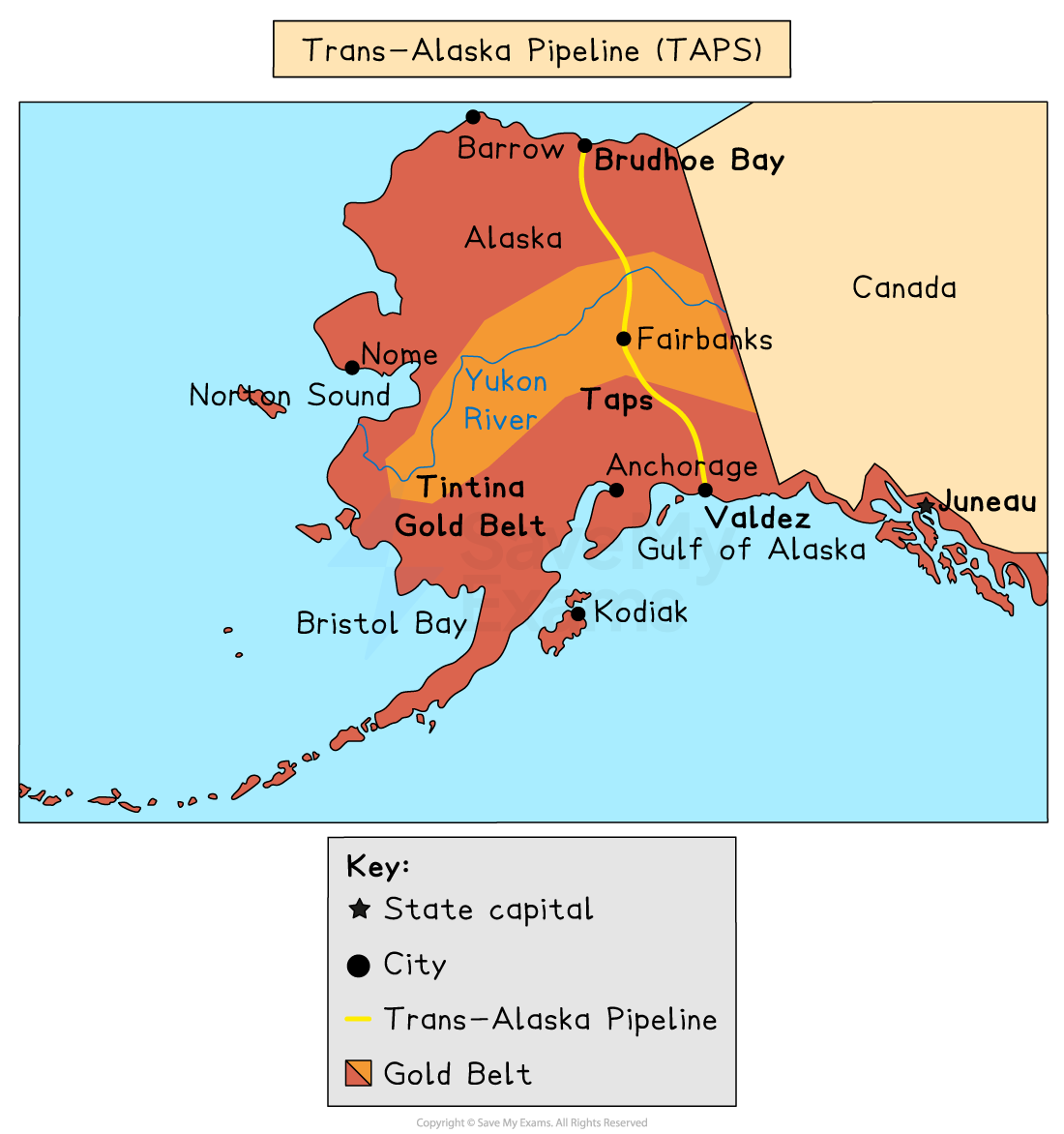
Activities like drilling and mining, such as the extraction of oil and gas near Prudhoe Bay, Alaska, exploit the tundra
Russia has also exploited large parts of the tundra for minerals
Pipelines such as the Trans-Alaska pipeline impact migration paths
Infrastructure and development
Heat generated by infrastructure, such as terminal buildings, worker homes, and transport associated with oil fields, causes environmental damage
The development of settlements and industry leads to the use of vehicles in these fragile areas, which can damage plant cover
If plants are damaged, they take a very long time to regrow, if at all
Pollution
Increased human activity leads to an increase in waste, including sewage
This leads to land, water and air pollution
Oil spills, such as the Exxon Valdez, have caused major environmental catastrophes
Mineral and energy mining can also cause ground and water pollution
Fishing
Overfishing has led to the depletion of fish stocks in cold coastal waters
Salmon, crab and pollock are fished in the waters around Alaska
Tourism
Growing adventure tourism increases pressure on these environments
Over 2 million tourists visit Alaska each year
The impact of human activity on ecosystem processes
Nutrient cycle
The nutrient cycle in the tundra is slow due to the low temperatures
The soil has low nutrient levels and is acidic because the organic matter decomposes very slowly
This means that the nutrients needed for plant growth, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are not available to the plants
When plants are damaged, for example, by vehicles, they take a long time to regrow or may not regrow at all
This affects the addition of nutrients to the soil
Habitat and food supply loss can affect the populations of animals such as reindeer
These animals add nutrients through their waste
If populations decrease, the amount of nutrients added to the soil decreases
Gas exchange
The layer of permafrost holds large amounts of methane and carbon
When the permafrost melts, both methane and carbon dioxide are released
This adds to the enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming, which has a global impact
Water cycle
The construction of settlements and industry increases the impermeable surfaces in the biome
Melting of the permafrost increases flooding
The impact of human activity on biodiversity
Human activities often damage the permafrost layer, which is vital for the tundra ecosystem
In the summer, the tundra has more plant cover
This helps surface plants absorb heat from the sun and keeps the permafrost below from thawing
Permafrost gives water and nutrients to plants
Damage to permafrost causes it to melt, which leads to flooding and halts plant growth
When it melts, the permafrost releases trapped greenhouse gases like methane
This increases global warming and alters the climate in cold environments, threatening plants and animals that rely on the delicate balance within the biome
Animal species in the tundra are highly specialised, which means that it is difficult for them to adapt to any changes
Changes which impact one species will have a significant impact on other species in the food web
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are asked to explain the impacts of a change in a biome in the exam it is essential to build cause - effect - consequence in your answer. For example, oil pipelines heat the ground - the permafrost melts - this leads to waterlogging - the vegetation is destroyed.
Management of tundra
The reasons for conservation and management
For the tundra to survive, there needs to be some sustainable management because the tundra ecosystems are:
Biodiversity hotspots for specialised species (e.g. polar bears, Arctic foxes, migratory birds)
Important for scientific research, especially climate change studies
Wilderness areas that are mostly untouched and extremely fragile
Slow to recover—vehicle tracks can last 30+ years
Carbon stores in permafrost help regulate the climate
Home to Indigenous communities with unique traditional cultures
Sustainable management:
Makes sure an environment can recover quickly from any use
Prevents damage to the environment
Helps local people get benefits from their environment
Helps local people understand the benefits
Ways in which the tundra has been managed
Basic management strategies include:
Using geothermal power where available
Having conservation zones to protect the tundra fauna and flora
Protecting the environment from pollution
Promoting ecotourism
Use of technology
Strategies for sustainable management in the tundra
How global actions can protect:
Placing animals on the Endangered Species List
In 2008, polar bears were added to the list
The Convention on Biological Diversity (1992) covers biodiversity in all biomes
The Paris Agreement (2015) aims to limit global warming and climate change
If successful, this would reduce permafrost melt
Government role:
Regulation of development is needed to prevent damage to the environment; e.g., mineral and energy mining can cause ground and water pollution and logging activities destroy habitats
Environmental protection laws can be put in place, such as the 1964 Wilderness Act, which designates wilderness areas but also protects them from future development
Large parts of Alaska have protection laws in place
The USA invests in environmental science initiatives like NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) to safeguard marine habitats and fisheries, and to assess the sustainability of any activities
Establishing conservation zones
Use of technology
Roads are constructed on 1-2 metre thick gravel pads
This stops heat from the vehicles from transferring to the soil beneath, reducing permafrost melt
The use of geothermal energy reduces the use of fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions
Building houses and other constructions on stilts to prevent heat from the building melting the permafrost
Raised pipelines, including the Trans-Alaskan pipeline
Conservation groups:
Conservation groups have less power than governments, but they can put pressure on governments to protect cold environments at risk or damaged
Groups such as Greenpeace and the World Wildlife Fund for Nature (WWF) encourage sustainable management and pressure governments to prevent any actions that would cause damage
They collect data and information independent of governments and monitor the reliability of other data
Create petitions, lobby and campaign for change
Report on issues and release findings to the public and governments, which spreads awareness on issues and boosts donations
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Sustainability is a key concept in management questions. Ensure you demonstrate a full understanding beyond a simple definition. You need to show in your answers that you understand how strategies increase sustainability. For example, raising pipelines and houses reduces the amount of permafrost melt, which then reduces methane emissions and habitat loss.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
