Water management (WJEC Eduqas GCSE Geography B): Revision Note
Exam code: C112
Specification link
This page covers section 3.3.3 of the WJEC Eduqas GCSE specification.
3.3.2 - What are the challenges of managing water supplies?
Ways in which an imbalance of supply and demand can be met within one country at a local scale.
The international issues facing future water management across national boundaries.
Case Study: Water management in Spain
The average precipitation in south-east Spain is approximately 365mm a year
Most precipitation occurs in winter
The area is one of the driest in Europe
Agriculture uses 80% of the water available
147,000 hectares of land require irrigation
Regular droughts mean the supply of water is further reduced
There is a water deficit as demand exceeds supply
Tourism increases the problem:
Water parks and golf courses use significant quantities of water
An average tourist uses between 450-800 litres per day
An average Spaniard uses 127 litres per day
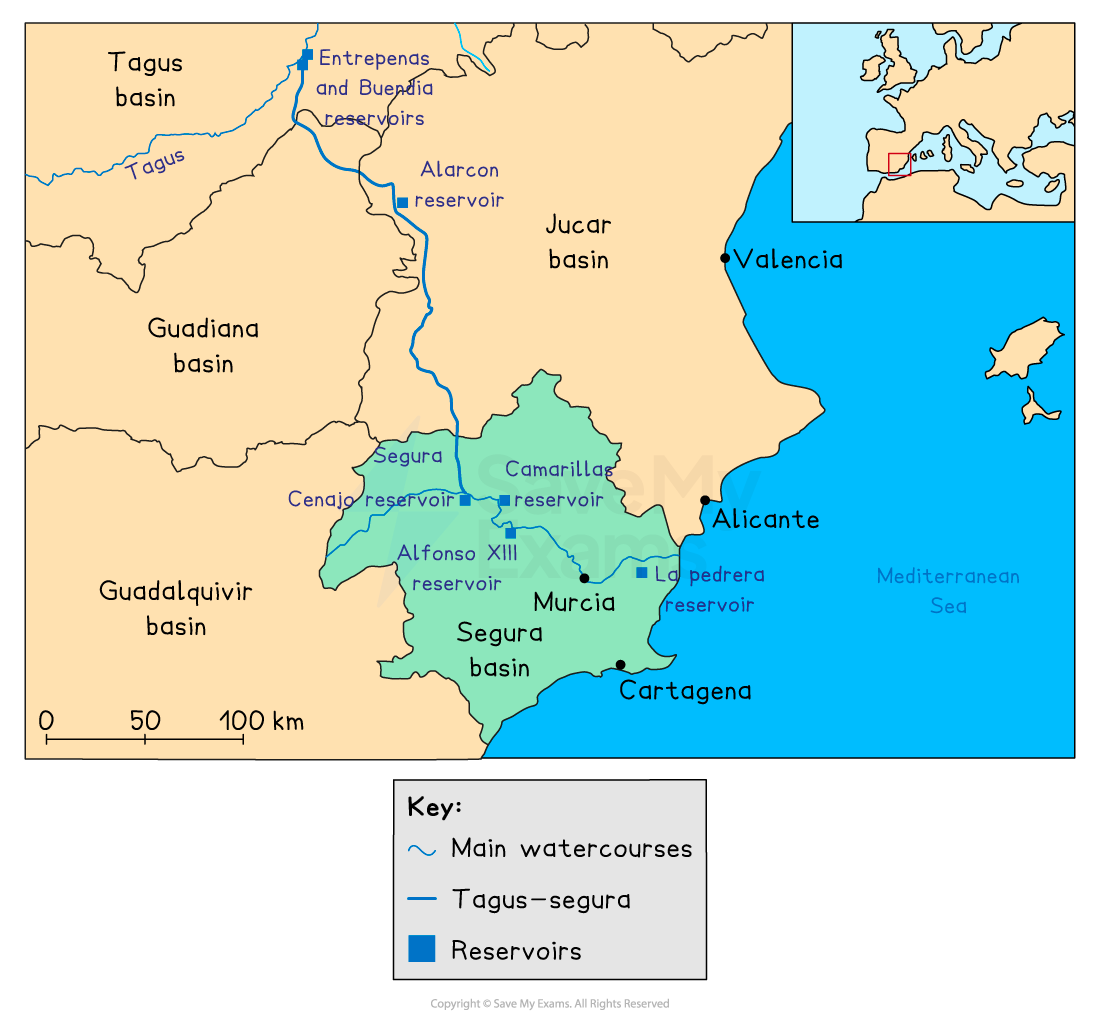
Tagus-Segura Project
Completed in 1978
60% of the water flowing into the Tagus is transferred
A 286-km pipeline which connects for Spanish river basins Tagus, Jucar, Segura and Guadiana
The aim was to supply Alicante, Murcia and Cartagena in the south-east to reduce the water deficit
Issues
Much of the water transferred went to tourists and leisure users, not to small-scale farmers
Water consumption in the south-east increased due to an increase in supply
It is estimated that 15% of the transferred water is being illegally used by leisure users, such as golf courses
Large commercial farms are benefiting more than small-scale farmers
Ebro project
A second water transfer project was proposed in 2001 to transfer water from the River Ebro
This project was abandoned due to:
The failure and issues with the Tagus-Segura project
The cost
The threat to the Ebro delta is that the scheme would have disrupted sediment flow to the delta
Future of water management in Spain
Spain has now moved to utilising desalination plants to meet the demand for water
Two additional plants are being built to open in 2028 and 2029
The estimated cost is €467 million
Increased use of reclaimed water
About 62% of the water used in agriculture is reclaimed
Over 17% of water used in industrial processes is reclaimed
International water management issues
At least 60% of the world's water sources (rivers and aquifers) cross a boundary between countries
The actions in one country can have significant impacts on countries and regions downstream, including:
Over-abstraction
Construction of dams and reservoirs
Pollution (sewage, industrial and agricultural waste)
Mismanagement of water sources can cause conflict between neighbouring countries and regions
The construction of the dams on the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in Türkiye has significantly affected water flow into Syria and Iraq
During the filling of the Ilisu Dam in Türkiye in 2019, the water flow into Iraq decreased by 50%
The quality of the water was also affected
In Basra, people's health was severely affected with an increase in rashes, diarrhoea and vomiting
On the border between India and China, there have been clashes between communities due to concerns that China was reducing water flow into India

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
