The Montgomery Bus Boycott, 1955-1960 (Edexcel GCSE History): Revision Note
Exam code: 1HI0
Timeline
Summary
The refusal by a Black woman to give up her seat for a White passenger on a segregated bus sparked a protest that made headlines around the world. It also led to the Supreme Court ruling that segregation on buses, just like in education, broke the Constitution. The protests caused by the arrest of Rosa Parks in December 1955 saw Martin Luther King emerge as a leader of the civil rights movement, proved the effectiveness of peaceful direct action and led to Congress passing the Civil Rights Act in 1957.
Who was Rosa Parks?
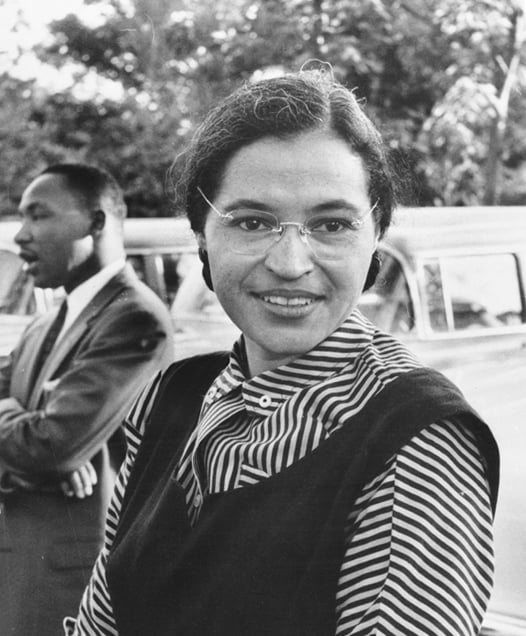

Rosa Parks was a Black woman who became an important figure in the civil rights struggle after being arrested for refusing to move seats on a segregated bus
Born in 1913, she joined the NAACP in 1943 and took part in several civil rights campaigns
At the time of her arrest, she was secretary of the NAACP chapter in Montgomery, Alabama
The significance of Rosa Parks
There was enormous publicity around her arrest
Her arrest triggered the protests
The protests led to the desegregation of buses
Rosa was a non-violent, hard-working, middle-aged woman
This made it very difficult for opponents of desegregation to attack or criticise her
She campaigned tirelessly, worked to get people to register to vote and became known as the “Mother of the modern-day Civil Rights Movement”
The Montgomery Improvement Association (MIA) & Martin Luther King
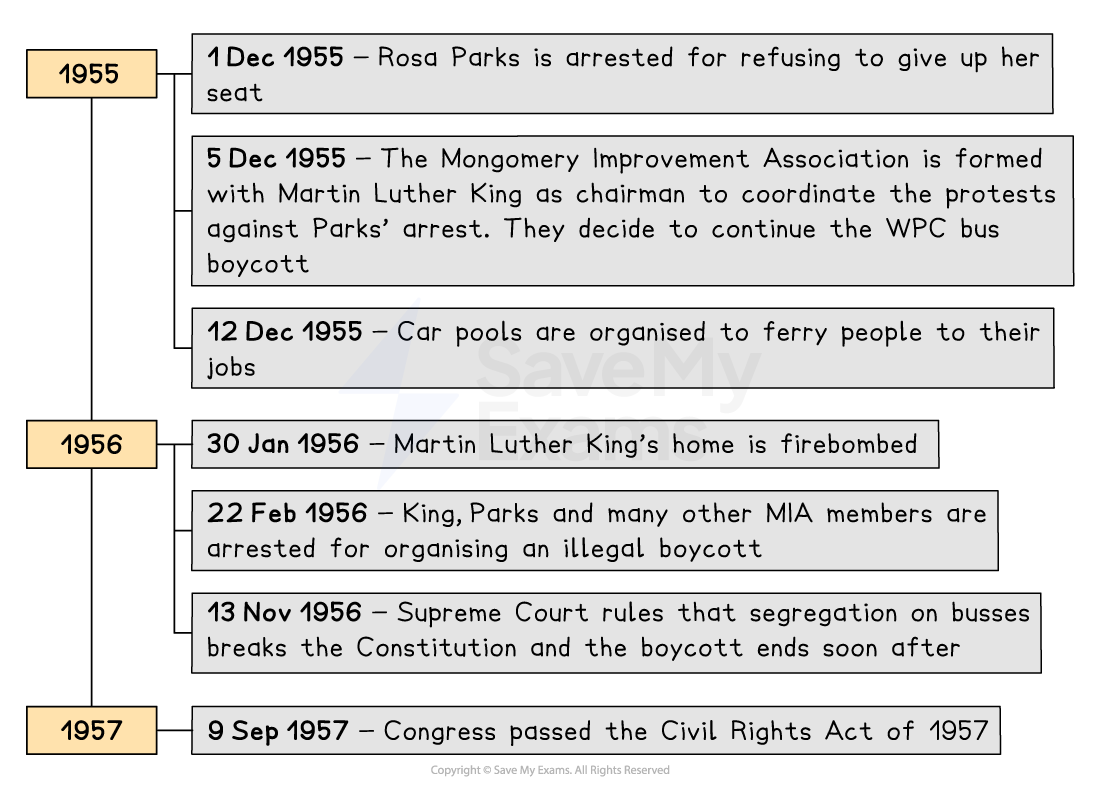
Civil rights activists met in Montgomery on 2 December to discuss their response to Parks’ arrest
They formed the Montgomery Improvement Association (MIA)
Martin Luther King was elected as the chairman
He was a pastor from Montgomery, Alabama
After meeting with the MIA on 8 December, the bus company still refused to desegregate, so Black passengers continued with the boycott
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Martin Luther King is also known as MLK or Doctor King. Any version is acceptable in your exam answers. Whilst there are many abbreviations in this course, it may help in your exam answers to shorten King’s name. When writing an answer, write “Martin Luther King (MLK)” once. This will allow you to write “MLK” throughout the rest of your answer.
Causes of the Montgomery Bus Boycott
The Montgomery Bus Company segregated its buses
The front rows were reserved for white people
Black people had to sit in the back rows
If the bus was full, Black Americans had to give up their seats for white people
There had been demands from the Women’s Political Council (WPC) for this to stop which were ignored by the bus company
On 1 December 1955, Rosa Parks refused to give up her seat for a White passenger
Rosa was arrested and fined $14
Her arrest triggered outrage, and the WPC launched a boycott of the Montgomery Bus Company
Events of the Montgomery Bus Boycott
On 5 December, 90% of the Black residents of Montgomery supported the boycott by refusing to use the buses
However, many Black people in Montgomery relied upon the bus to get to work, so alternatives had to be provided
The MIA made a deal with taxi companies to charge each passenger the same amount as individual bus tickets
This was eventually declared illegal
On 12 December, a carpool of over 300 vehicles was organised by MIA to ferry people to the city centre
The boycott showed no signs of stopping in 1956, so opponents of desegregation increased the intimidation of its leaders
On 30 January 1956, Martin Luther King’s home was firebombed with his wife and daughter narrowly avoiding injury
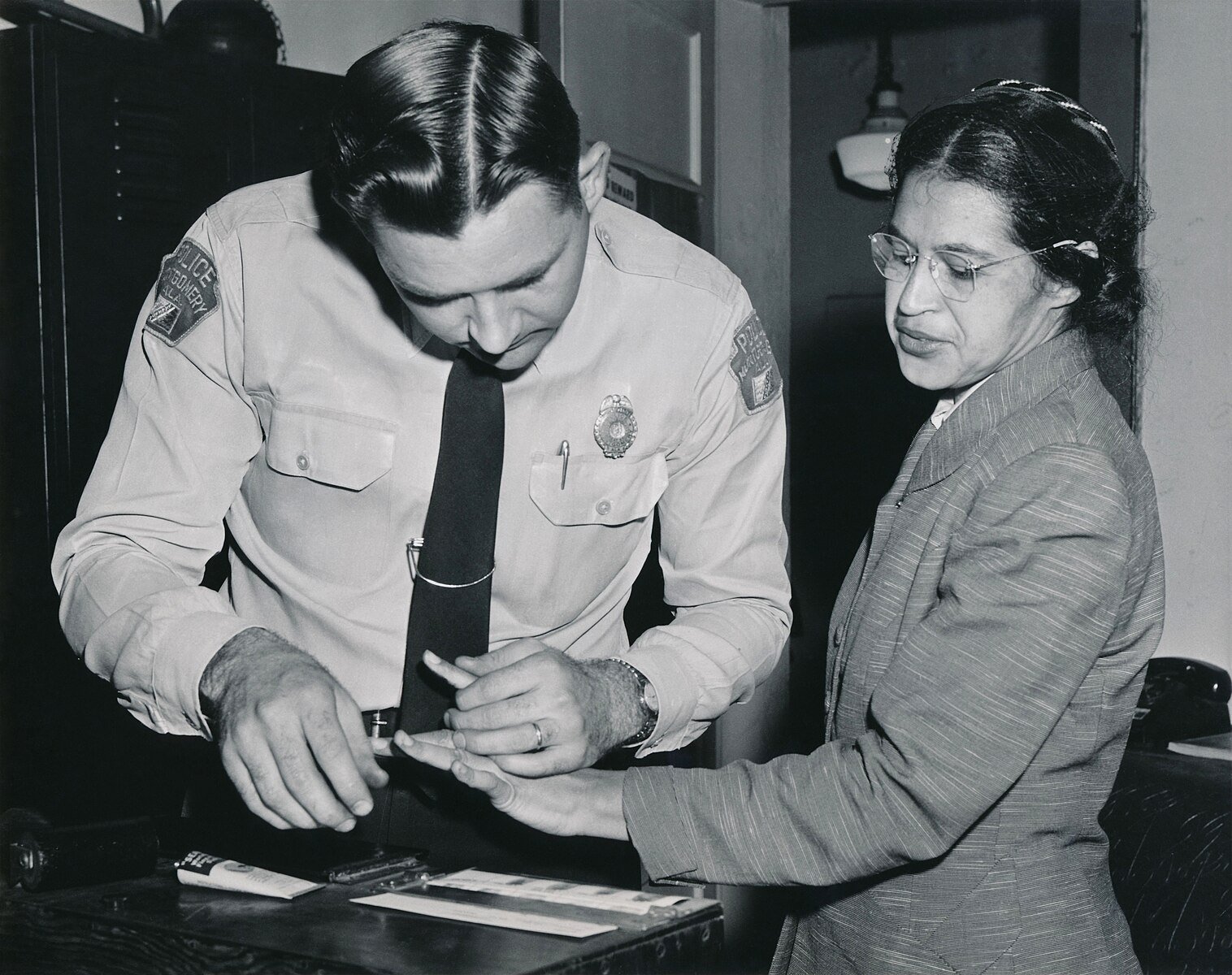
On 22nd February 90 members of the MIA, including Parks and King, were arrested and found guilty of organising an illegal boycott
Parks having her fingerprints taken after arrest for illegal boycott:

As the boycott continued, the MIA went to court to argue that segregation on buses went against the Constitution
On 5 June, a federal district court agreed and ruled that bus segregation, just like segregation in schools, was unconstitutional
The bus company appealed the decision and it went to the Supreme Court
When the Supreme Court reached its verdict on 13 November 1956
It upheld the federal district court’s decision
The bus company was ordered to desegregate
On 20 December 1956, the MIA called an end to the boycott
After 340 days, the boycott had succeeded
Martin Luther King, Rosa Parks and others travelled on a desegregated bus
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Creating flashcards of the causes and consequences of events such as the Montgomery Bus Boycott is a great way to help prepare for answering questions on why they are significant.
Why did the Montgomery Bus Boycott succeed?
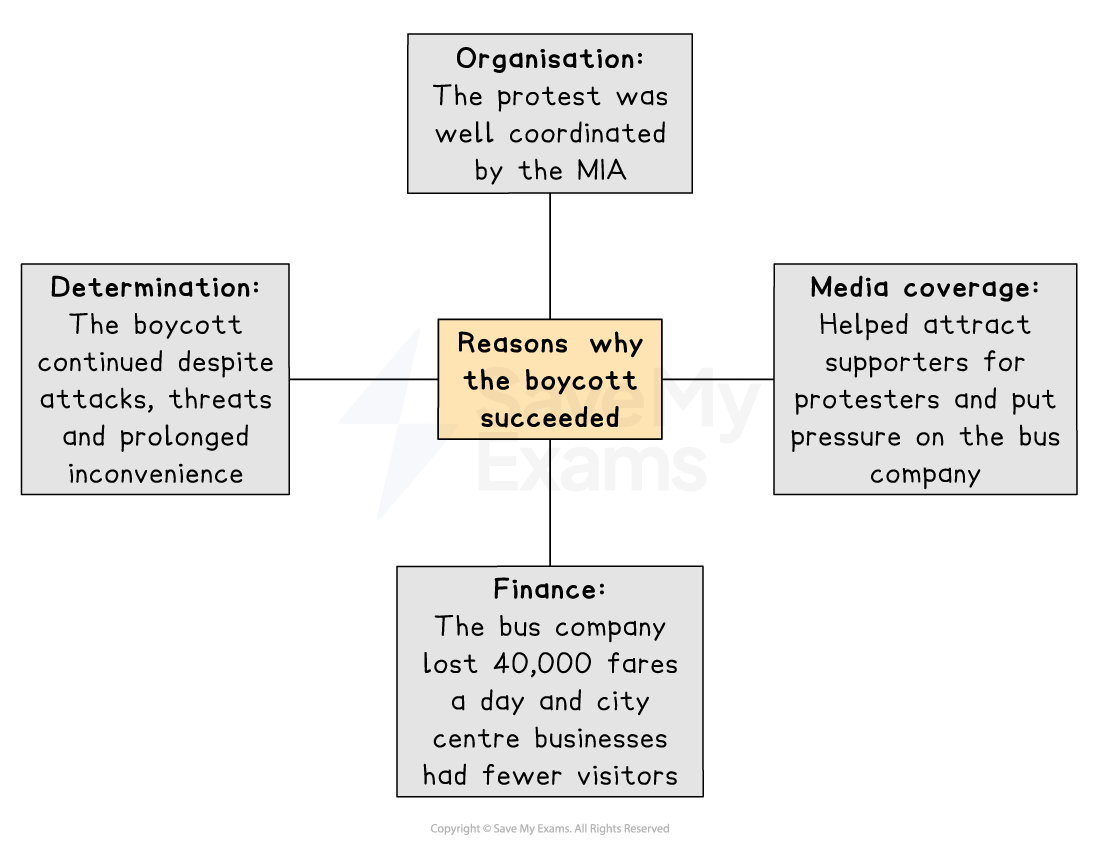
There are several reasons why the Montgomery Bus Boycott was a success
Impacts of the Montgomery Bus Boycott
The Montgomery Bus Boycott saw Martin Luther King emerge as a leader of the Civil Rights movement
The boycott proved that non-violent direct action was an effective way to bring about change
It also proved that Black Americans were determined and organised

The victories in Montgomery and Brown v. Topeka led to Congress passing the Civil Rights Act in 1957
This was the first Civil Rights Act in 82 years and reflected how attitudes and opinions in American society had changed
Many White Americans were still against it
It was also criticised by some Black Americans for not going far enough


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
