Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
The Accounting Process (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Accounting): Revision Note
Exam code: 0452 & 0985
The accounting process
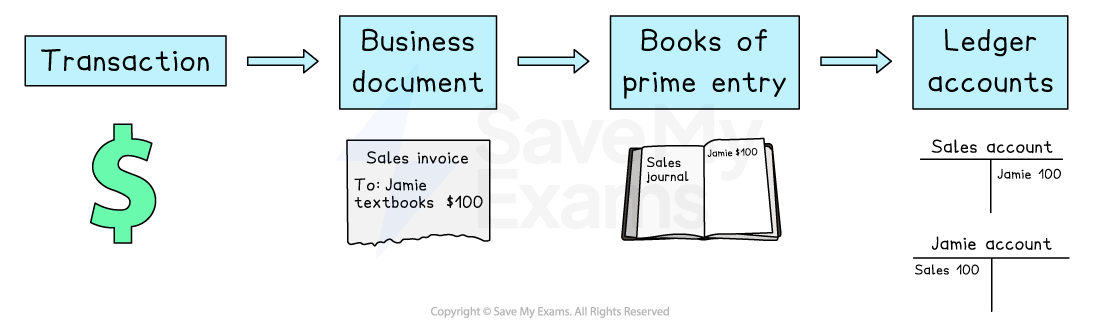
What is the accounting process?
Stage 1: Transaction
A transaction takes place
Examples include:
The sale or purchase of goods, a service or an asset
Withdrawing or depositing cash
Paying an expense or receiving income
Stage 2: Business document
A business document is issued or received
This is a record of the transaction
Stage 3: Book of prime entry
The amount is entered into a book of prime entry
This collates the different types of transactions
Stage 4: Ledger account
The entries from the books of prime entry are entered into the ledger accounts
These are part of the double-entry accounting system
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The aim of the accounting process is to have the information in the ledger accounts so that financial statements can be produced at the end of the accounting period.
Purpose of business documents
What are business documents?
Business documents are used to keep records of all transactions
They are used as sources of information
The amounts are then entered into the books of prime entry
They can be used to check potential errors
What business documents do I need to know?
Invoices
Debit notes
Credit notes
Statements of account
Cheques
Cheque counterfoils
Receipts
Paying-in slips
Bank statements
Petty cash vouchers
Are business documents produced and recorded manually or digitally?
Business documents can be produced and recorded either manually or digitally
They can be produced and recorded manually by:
physical receipts and invoices
paper-based bank statements and statements of account
cheques
They can be produced and recorded digitally by:
electronic receipts and invoices
electronic bank statements and statements of account
Purpose of books of prime entry
What are books of prime entry?
Books of prime entry are used to record the details of a transaction
Older terminology for these books includes
Subsidiary books
Books of original entry
Daybooks
Information is taken from the business documents and entered into the books of prime entry
The details are then transferred from the books of prime entry to the ledger accounts
The seven books of prime entry are:
Sales journal
Purchases journal
Sales returns journal
Purchases returns journal
Cash book
Petty cash book
General journal
What are the advantages of using books of prime entry?
Books of prime entry are another stage which can be used to check for errors
They can help in the preparation of control accounts to check the accuracy of the ledger accounts
Each book of prime entry collects the same type of transaction
The books allow managers to see the totals for different types of transactions easily
Therefore, there are fewer entries in some of the ledger accounts
Bigger businesses may have multiple book-keepers
Different book-keepers can be responsible for different books of prime entry without any risk of work being duplicated or missed
What are the benefits and limitations of using manual or digital methods for entering transactions into books of prime entry?
The books of prime entry can be updated manually or digitally
Manually means the transactions are entered into physical books
Digitally means the transactions are entered into spreadsheets or accounting software
Benefits | Limitations | |
|---|---|---|
Manual entry |
|
|
Digital entry |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
