Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
The Double Entry System (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Accounting): Revision Note
Exam code: 0452 & 0985
The double entry system
What is the double entry system?
The double entry system is used by book-keepers
The double entry system is used to improve the accuracy of financial statements
The double entry system is closely linked to the accounting equation
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
The equation is always balanced
Each transaction causes both sides of the equation to:
increase
or decrease
or remain the same
Each transaction is entered into two accounts
One is called a debit entry
One is called a credit entry
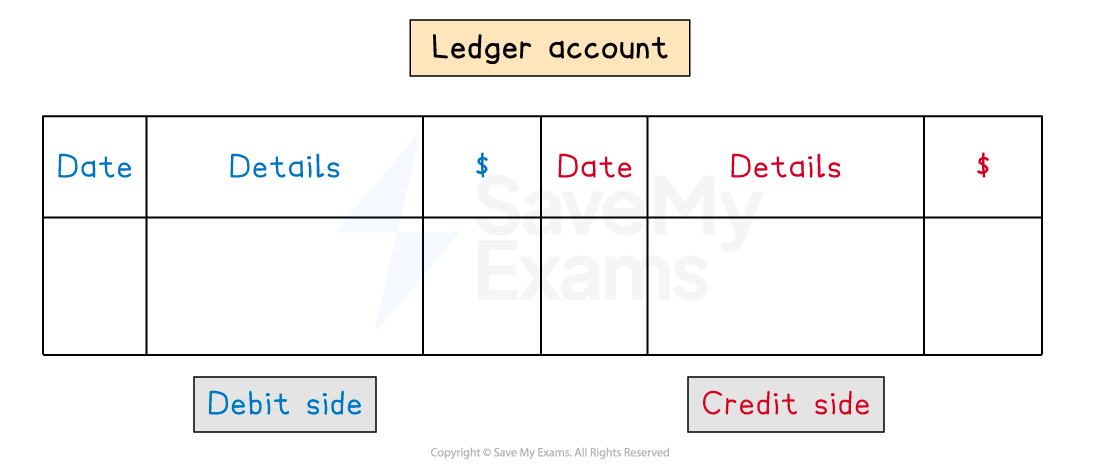
What is the layout of a ledger account?
Each account will be split into two sides
The debit entries appear on the left
This side is sometimes labelled as Dr
The credit entries appear on the right
This side is sometimes labelled as Cr
When you make an entry you need to include:
The date of the transaction
The details of the transaction
This is normally the name of the other account involved
The value of the transaction
What are the advantages of maintaining double entry records?
It is straightforward to prepare financial statements
It can help give an accurate calculation of the profit or loss
It reduces the possibility of fraud
It gives easy access to information for the bank or other lenders
Debits & credits
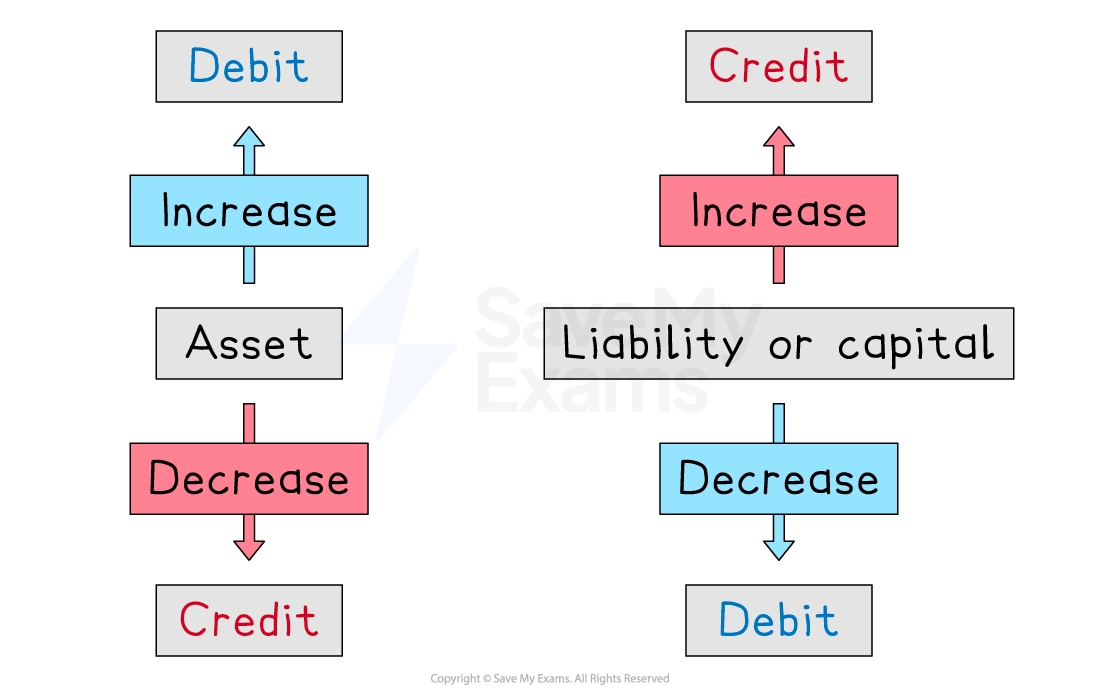
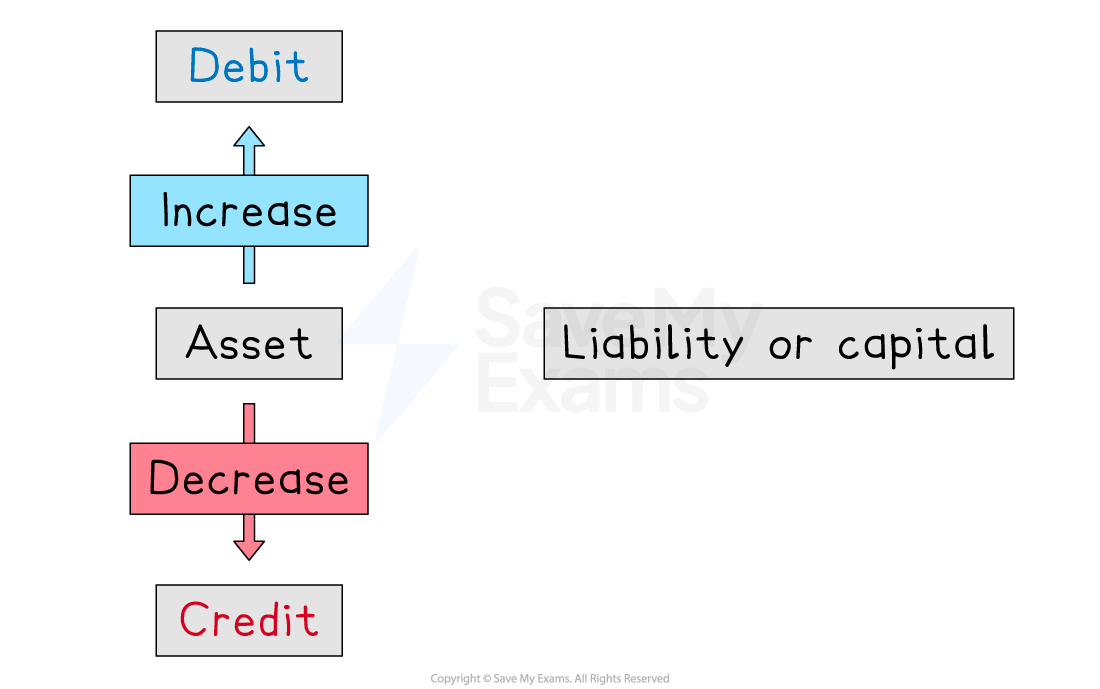
What is a debit entry?
A debit entry is used to:
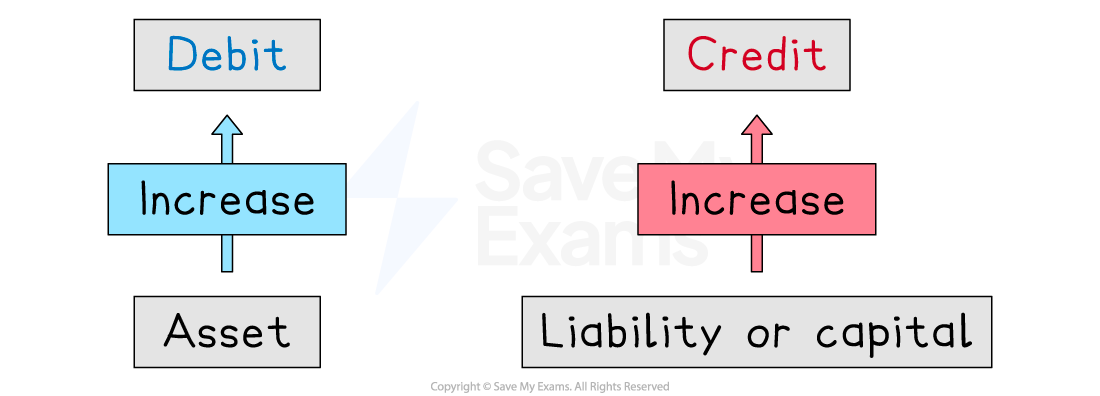
increase the value of an asset
The left-hand side of the accounting equation increases
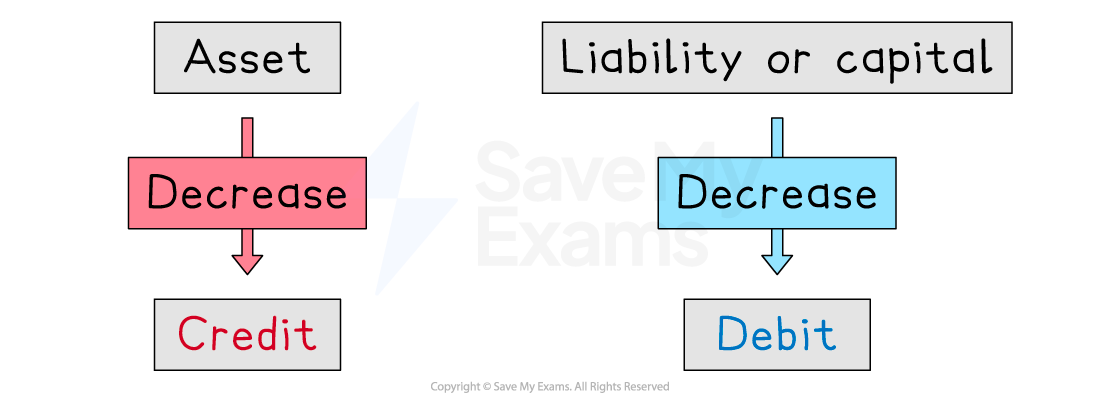
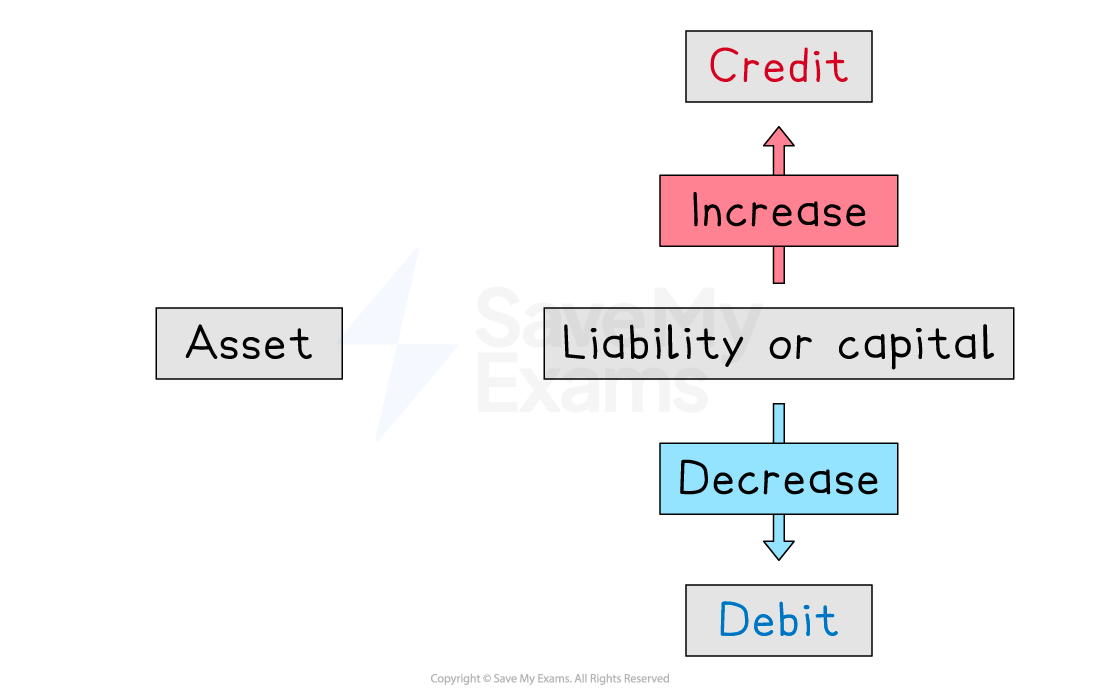
decrease the value of a liability or the capital
The right-hand side of the accounting equation decreases
What is a credit entry?
A credit entry is used to:
increase the value of a liability or the capital
The right-hand side of the accounting equation increases
decrease the value of an asset
The left-hand side of the accounting equation decreases
Which accounts should I debit?
Debit an asset account when its value is increasing
You receive cash
Debit the cash account
A customer buys goods on credit
Debit their trade receivables account
Debit a liability account when its value is decreasing
You make a repayment on a bank loan
Debit the bank loan account
You pay an invoice to a credit supplier
Debit their trade payables account
Debit other accounts when the transaction decreases the capital
You take assets from the business for personal use
Debit the drawings account
You pay an expense which decreases the profit
Debit the relevant expense account
Such as purchases, rent paid, discount allowed, etc
Which accounts should I credit?
Credit a liability account when its value is increasing
You take out a bank loan
Credit the bank loan account
You buy goods on credit from a supplier
Credit their trade payables account
Credit an asset account when its value is decreasing
You pay rent by bank transfer
Credit the bank account
A credit customer pays their invoice
Credit their trade receivables account
Credit other accounts when the transaction increases the capital
You put more personal assets (such as money) into the business
Credit the capital account
You receive income which increases the profit
Credit the relevant income account
Such as sales, rent received, discount received, etc
How do I enter the transactions into the accounts using the double-entry system?
STEP 1
Identify the accounts involved in the transactionOne is usually cash, bank, trade receivables or trade payables
STEP 2
Identify whether each account affects the assets, liabilities or capitalUsually this is cash, trade receivables or trade payables
STEP 3
Determine whether the value of each account is increasing or decreasingSTEP 4
Debit or credit the accountDebit the account if:
It is an asset account and its value is increasing
It is a liability or the capital account and its value is decreasing
Credit the account if:
It is an asset account and its value is decreasing
It is a liability or the capital account and its value is increasing
Examples where assets increase and liabilities or capital increase
Transaction | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
Credit sale to a customer | Trade receivables
| Sales
|
The business takes out a bank loan | Bank
| Bank loan
|
The business receives money for rent from a tenant | Bank
| Rent received
|
The owner deposits some of their personal money into the business bank account | Bank
| Capital
|
Examples where assets decrease and liabilities or capital decrease
Transaction | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
The owner takes money out of the business bank account for personal use | Drawings
| Bank
|
The business pays cash for an electricity bill | Electricity
| Cash
|
The business makes a cash payment to a credit supplier | Trade payables
| Cash
|
Examples where assets increase and decrease
Transaction | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
The business receives a cash payment from a credit customer | Cash
| Trade receivables
|
The business withdraws cash from the business bank account | Cash
| Bank
|
The business deposits cash into the business bank account | Bank
| Cash
|
Examples where liabilities or capital increase and decrease
Transaction | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
The business purchases goods on credit from a supplier | Purchases
| Trade payables
|
Worked Example
Hina is a sole trader.
Complete the table below to show the accounts that Hina should debit and credit for each of the following transactions.
Transaction | Account to be debited | Account to be credited |
Hina sells goods on credit to Priya | ||
Hina receives a cash payment from Priya | ||
Hina pays an electricity bill by cheque | ||
Hina buys goods on credit from Dida | ||
Hina repays some of a bank loan by bank transfer | ||
Hina takes ownership of a company vehicle for her own use | ||
Hina puts some of her own money into the business bank account |
Answer:
Transaction | Account to be debited | Account to be credited |
Hina sells goods on credit to Priya | Priya
| Sales
|
Hina receives a cash payment from Priya | Cash
| Priya
|
Hina pays an electricity bill by bank transfer | Electricity
| Bank
|
Hina buys goods on credit from Dida | Purchases
| Dida
|
Hina repays some of a bank loan by bank transfer | Bank loan
| Bank
|
Hina takes ownership of a company vehicle for her own use | Drawings
| Vehicles
|
Hina puts some of her own money into the business bank account | Bank
| Capital
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
To remember which side of an account to record a transaction, you can use the acronym DEAD CLIC.
The transaction is on the debit side for expense, asset, and drawings accounts if the account is increasing.
The transaction is on the credit side for liability, income, and capital accounts if the account is increasing.
If the account is decreasing then the transaction is recorded on the opposite side!
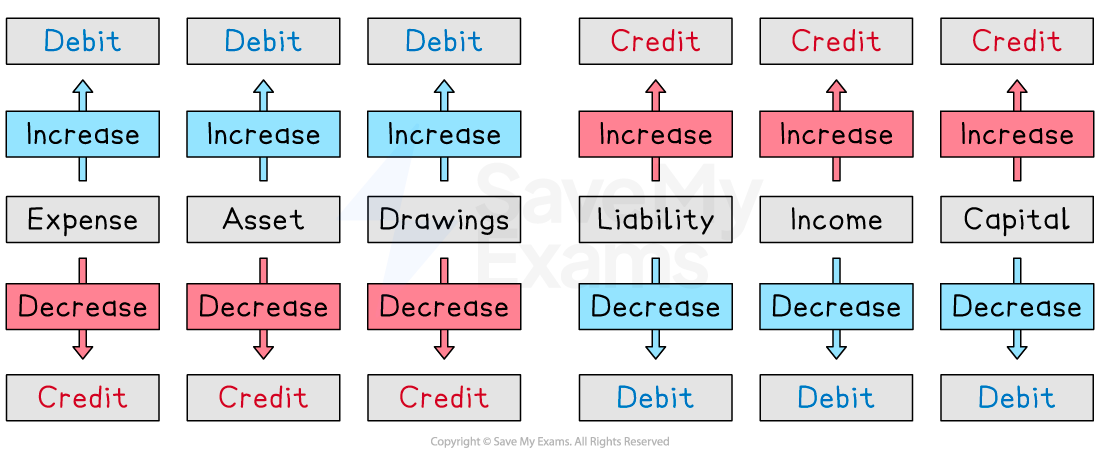
Another set of acronyms are:
DIADL: Debits Increase Assets or Decrease Liabilities
CILDA: Credits Increase Liabilities or Decrease Assets
However, try to remember the connection to the accounting equation.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
