The Gametes (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
Haploid & diploid cells
Haploid and diploid cells play key roles in reproduction
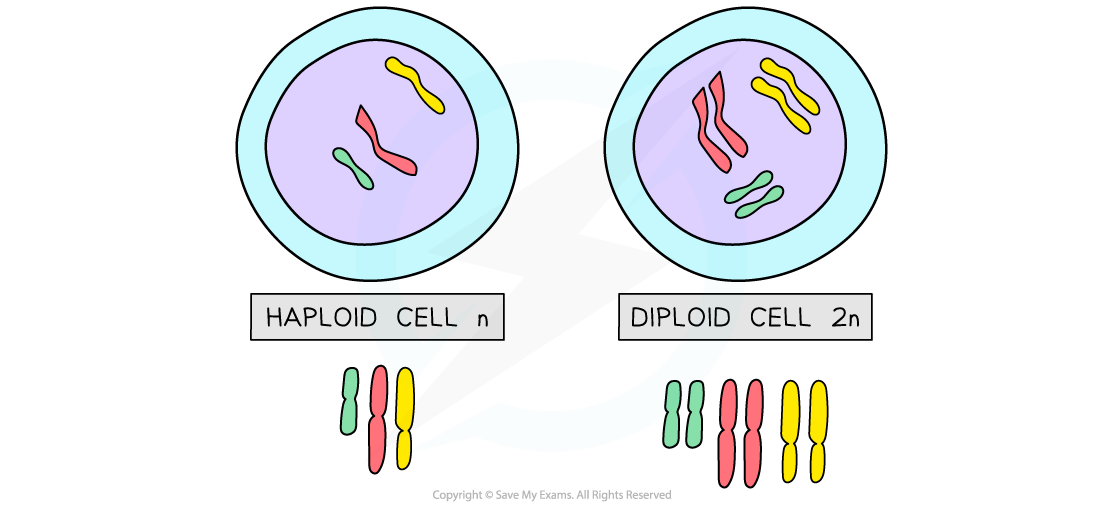
A diploid cell is a cell that contains two complete sets of chromosomes (2n)
These chromosomes contain the DNA necessary for protein synthesis and cell function
Nearly all cells in the human body are diploid with 23 pairs (46) of chromosomes in their nucleus
Haploid cells contain one complete set of chromosomes (n)
They have half the number of chromosomes compared to diploid cells
Humans have haploid cells that contain 23 chromosomes in their nucleus (no pairs)
These haploid cells are called gametes, and they are involved in sexual reproduction
Gamete production in plants & animals
Gametes are sex cells
They contain half the number of chromosomes compared to non-gametes (body cells)
Gamete production in plants
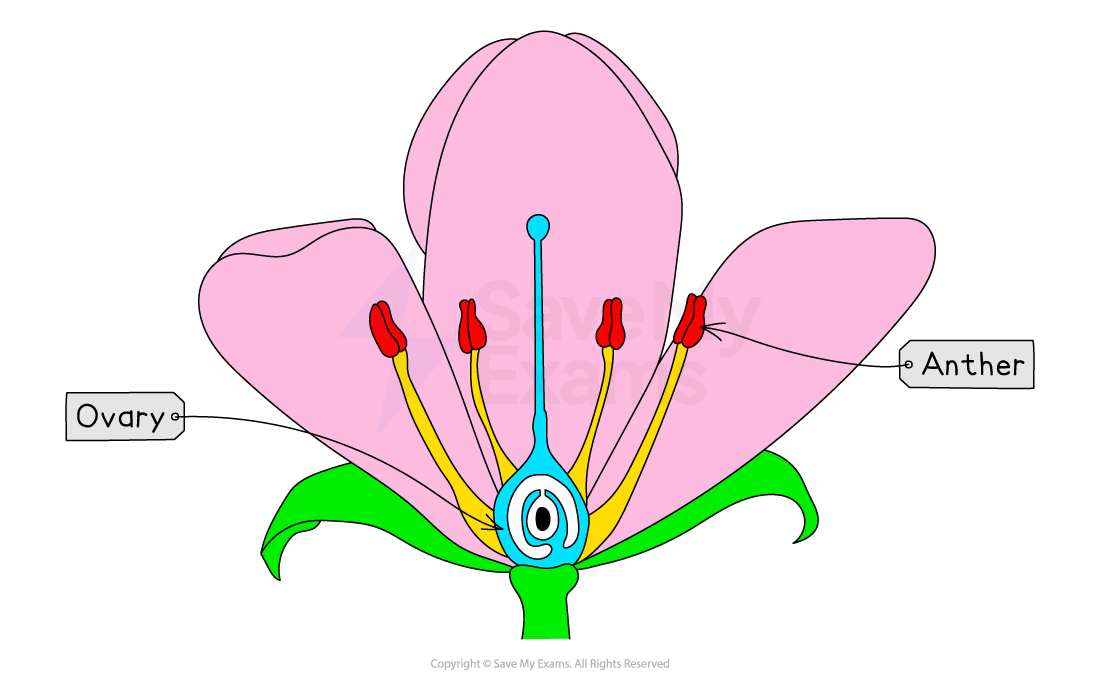
In flowering plants:
Male gametes are in pollen grains, produced in the anthers
Female gametes are in the ovules, found inside the ovary
Gamete production in animals
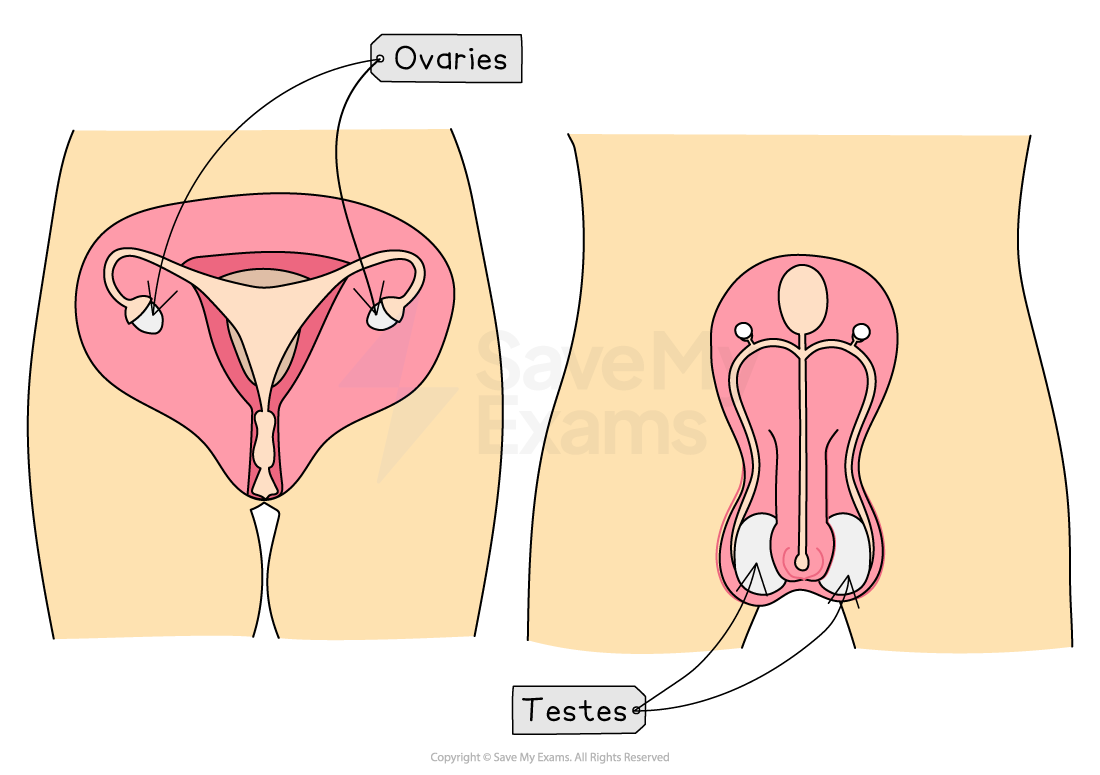
In humans (animals):
Male gametes (sperm cells) are produced in the testes, located in the scrotum
Female gametes (egg cells or ova) are produced in the ovaries, located in the lower abdomen
The structure of mammalian gametes
Mammalian gametes have adaptations to improve the chances of successful fertilisation and embryo development
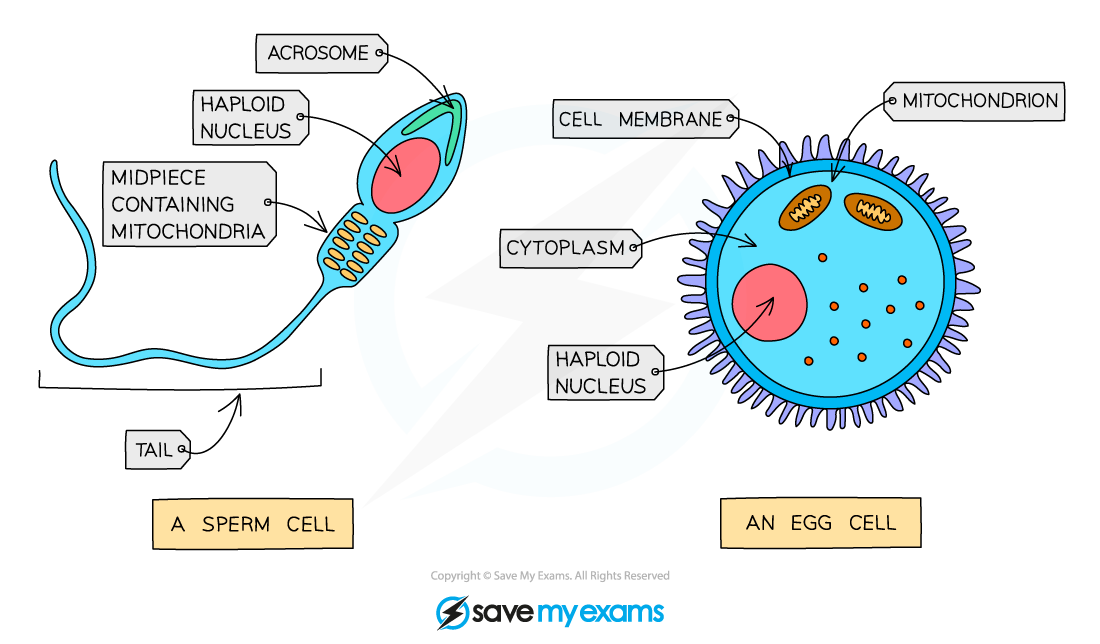
Sperm cells
Sperm cells are male gametes in mammals
They are highly specialised for their role in reproduction
To carry the DNA of the male to the egg cell (the ovum) of the female
Sperm cells have
a tail to propel them towards the egg
many mitochondria to provide energy for this movement
Egg cells
Egg cells (ova = plural, ovum = singular) are female gametes in mammals
They are also highly specialised for their role in reproduction
To be fertilised by a single sperm and to develop into an embryo
Egg cells have energy stores within the cytoplasm to support early embryo development

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
