Mutations (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
The definition of mutation
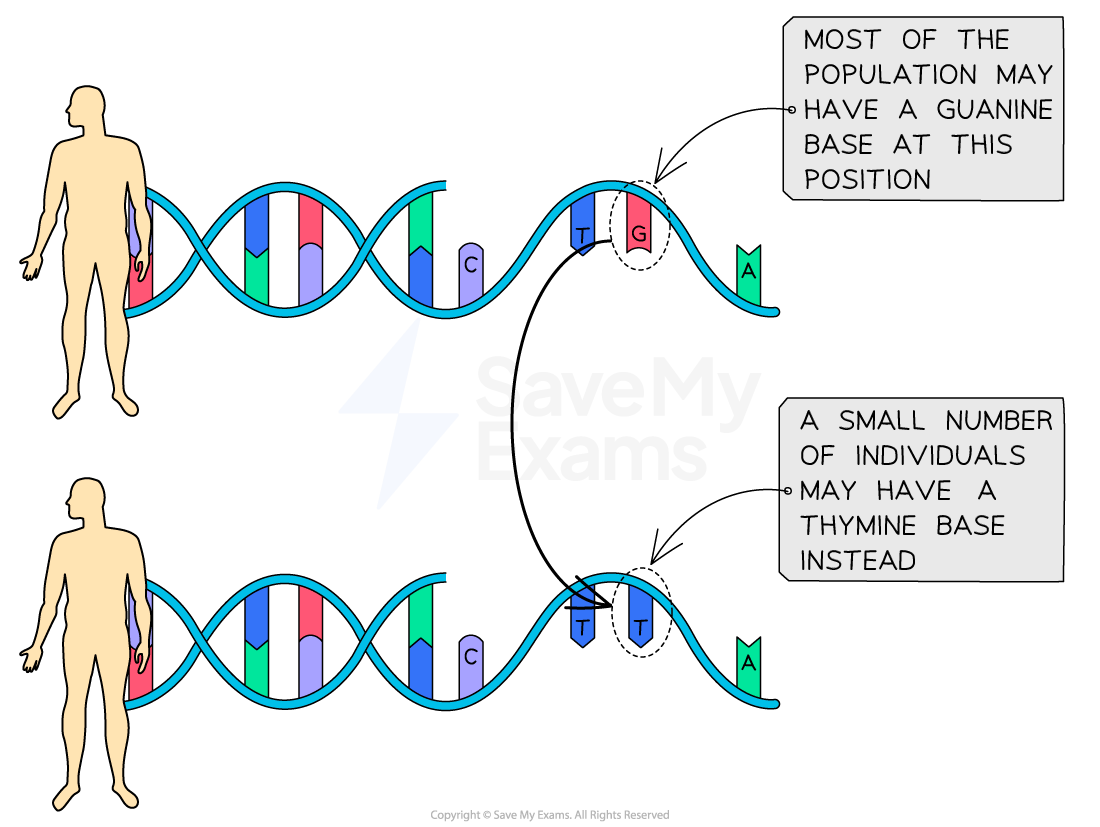
A mutation is a random change to the genetic material
Mutations are said to be random because they occur spontaneously, meaning that they do not need to be triggered by external factors in the environment
While mutations occur randomly, environmental factors, such as radiation and some chemicals, can increase the rate at which they occur
New alleles may arise due to mutation, and these alleles may affect the features of organisms
Mutation is the only source of new alleles, though alleles may be recombined in different ways by other processes
Mutations may be:
neutral: these have no impact on survival
advantageous: these increase the chances of survival
disadvantageous: these decrease the chances of survival
New alleles & variation
The new alleles produced by mutation can result in some plants and animals becoming better adapted to their environment
This occurs when advantageous mutations increase survival chances
Different mutations will occur in different individuals, introducing variation into a population
Variation within a population makes it possible for a population to evolve, or change, over time in response to changing environmental conditions
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful with the language that you use when describing the ideas discussed here. Remember that:
mutations occur at random, not in direct response to changes in the environment
when random mutations result in a survival advantage, they allow a population as a whole to respond to a changing environment

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
