Excess nitrates (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
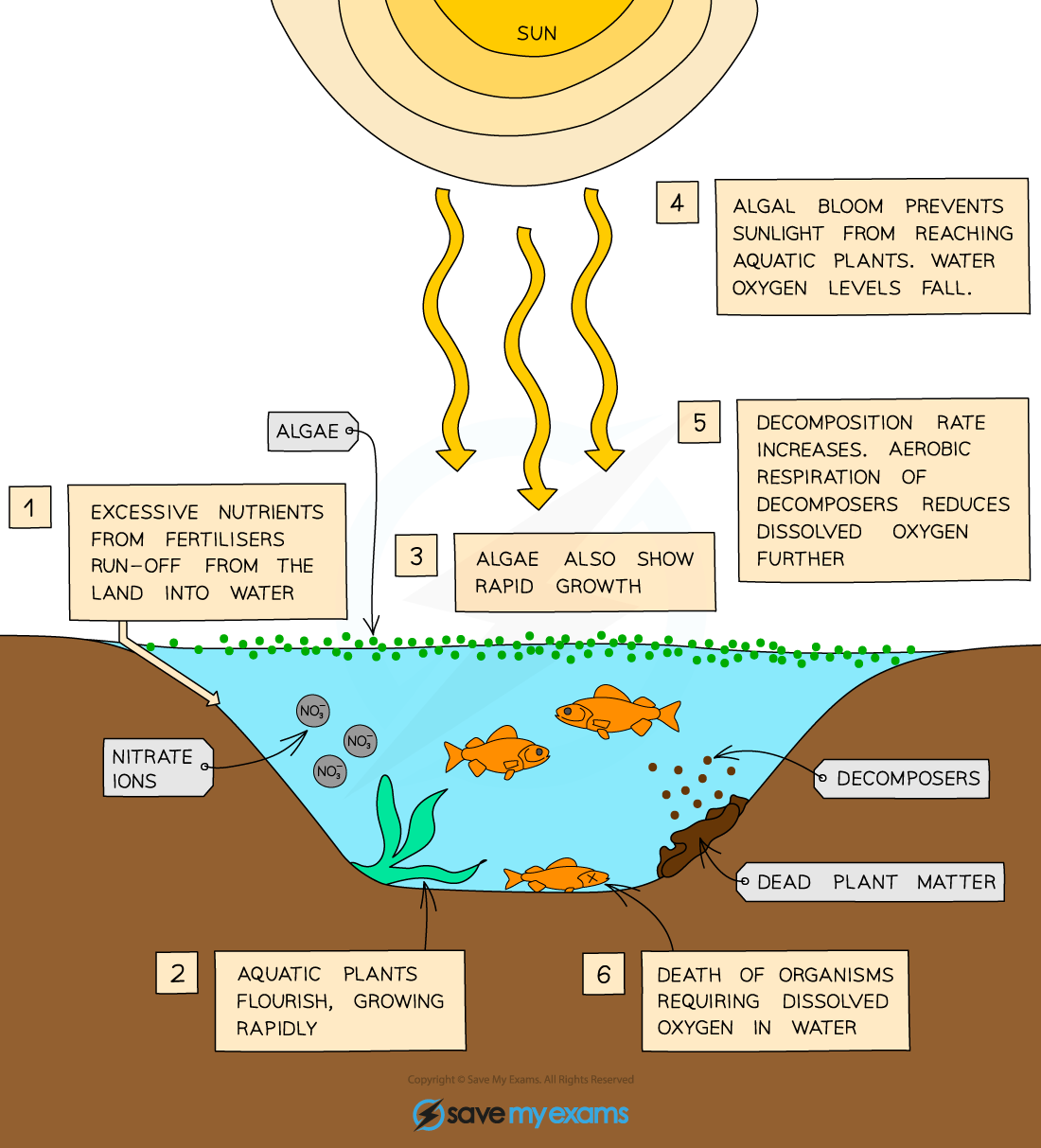
Algal blooms
Fertilisers can leach into water bodies such as lakes and streams, adding extra, unwanted nitrates
Leaching is the process by which soluble substances, e.g. nitrates, are washed out of the soil by rainwater
The following events can occur as a result:
Fertilisers provide nitrates to aquatic plants
There is overgrowth of aquatic plants and algae at the water surface; algae overgrowth is known as an algal bloom
Light is blocked, and aquatic plants below the surface die
dead plant matter becomes food for decomposers, e.g. bacteria and fungi, which increase in number
The increased respiration of these organisms uses up oxygen in the water, reducing dissolved oxygen levels
The water no longer contains enough oxygen to support other organisms, so many aquatic organisms die
Genetically modified crops
Overusing fertilisers raises costs for farmers and leads to environmental problems, such as leaching and algal blooms
Genetically modified (GM) crops can be used to reduce the use of fertilisers
GM crops are crop plants in which the DNA has been deliberately altered using genetic engineering
GM crops can reduce fertiliser use as follows:
Low-phosphate-tolerant rice can continue growing despite phosphate-poor soil, reducing the need for phosphate fertilisers
Nitrogen-efficient wheat and rice varieties can use nitrates from the soil more efficiently, allowing them to survive when nitrate levels are low and decreasing the need for nitrate fertilisers

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
