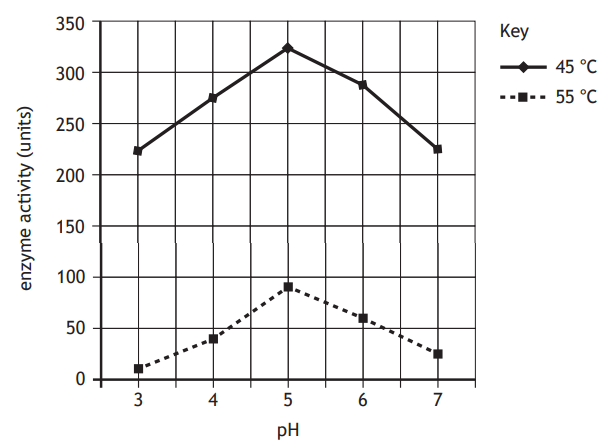
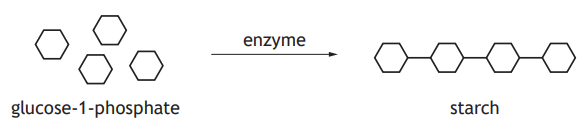
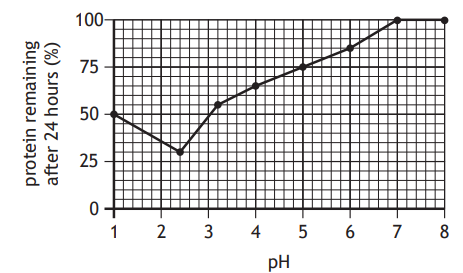
Lipase is an enzyme that speeds up the breakdown of fats, producing an acid that decreases the pH.
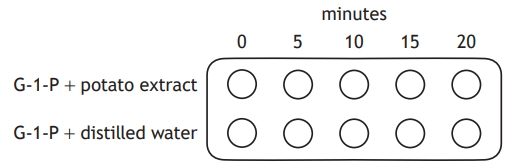
Three test tubes were set up to investigate the action of lipase on fat in milk.
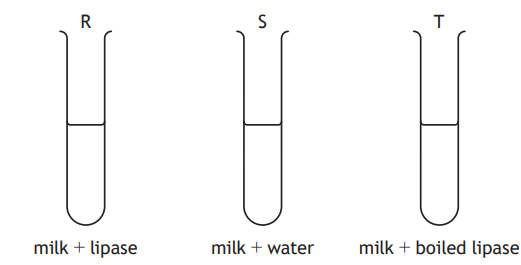
The pH of each test tube was recorded at the start of the experiment and then again 20 minutes later.
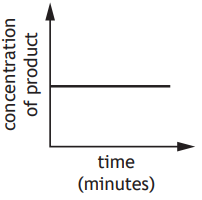
In which of the test tube(s) would the pH stay the same?
R only
T only
R and T
S and T
Was this exam question helpful?