Bit-Mapped Graphics (SQA National 5 Computing Science): Revision Note
Exam code: X816 75
Bit-mapped graphics
What is a bit-mapped graphic?
A bit-mapped graphic is an image that is made up of small squares called pixels (picture elements)
Each pixel represents one tiny part of the image and is stored as a binary value (a pattern of 1s and 0s) in the computer’s memory
The collection of all these pixel values forms the complete image
This method of storage is sometimes described as storing the image as an array of pixels
How is it represented in memory?
Each pixel’s binary value identifies the colour of that pixel
The more bits used to store each pixel, the greater the number of colours that can be represented
The computer stores these binary values in a grid pattern that matches the layout of the image on screen
Resolution
Resolution refers to the number of pixels that make up the image
It is calculated using the width × height of the image in pixels
A higher resolution means more pixels are stored, which gives more detail but increases the file size
Colour depth
Colour depth is the number of bits used per pixel
This determines how many different colours each pixel can represent
For example:
1-bit → 2 colours (black and white)
4-bit → 16 colours
8-bit → 256 colours
24-bit → 16,777,216 colours (True Colour)
The number of colours available can be calculated using 2ⁿ, where n is the colour depth in bits

Factors affecting file size
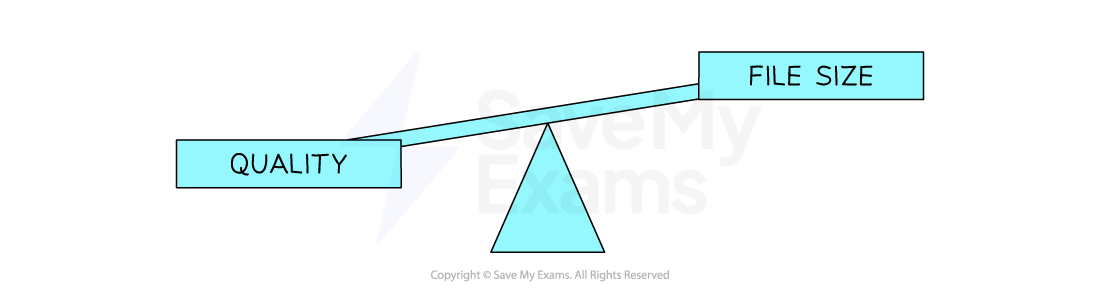
The file size of a bit-mapped image depends on:
Resolution – more pixels increase the amount of data stored
Colour depth – more bits per pixel mean more data is needed for each pixel
As either resolution or colour depth increases, so does the file size
A balance must be found between image quality and the amount of storage space required
Common bit-mapped file formats
Different bit-mapped file types are used depending on the required features:
JPEG – uses compression to reduce file size, suitable for photographs
PNG – supports transparency, often used for logos or web graphics
GIF – supports simple animation and a limited colour palette
Worked Example
A digital camera captures a photograph of a garden. This image is stored on the memory card using the bit-mapped method of representation.
Describe how this bit-mapped graphic is represented in the camera system's memory
[2]
Answer
Represented as an array or grid of tiny dots known as pixels [1 mark]
Each pixel is stored as a binary value (or bits) in memory [1 mark]

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
