SQL Manipulation (SQA National 5 Computing Science): Revision Note
Exam code: X816 75
SQL manipulation
What is SQL manipulation?
SQL provides commands to add, change, and remove records from a database table
These are known as data manipulation commands
They are used when you need to maintain or correct data in a database
Adding/changing data
Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Adds new data to a database table | INSERT INTO users (name, age) |
| Edit data in a database table | UPDATE users |
Examples
Table: Employees
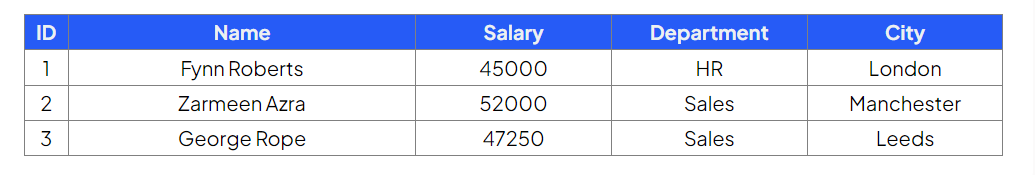
Insert a new employee into the Employees table with the 'Name', 'Salary', 'Department' and 'City' fields
Command:
INSERT INTO Employees (Name, Salary, Department, City)
VALUES ('George Rope', 47250, 'Sales', 'Leeds');
Output:
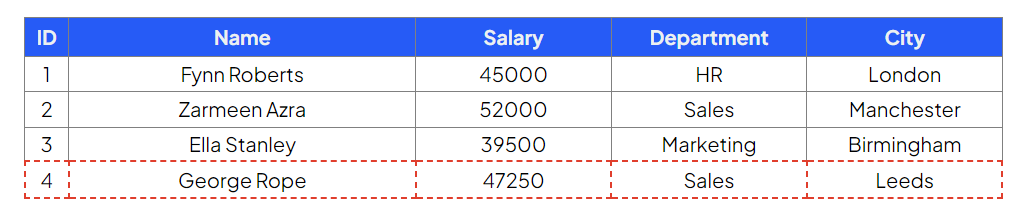
Table: Employees
Update employee ID 3 to a salary of 47500 and city to London
Command:
UPDATE Employees
SET Salary = 47500, City = 'London'
WHERE ID=3;
Output
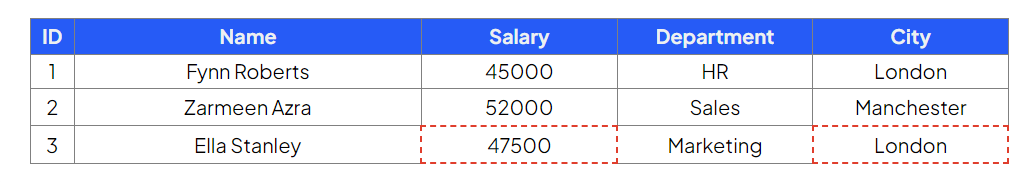
Deleting data
Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Removes data from a database table | DELETE FROM users DELETE FROM users |
Example
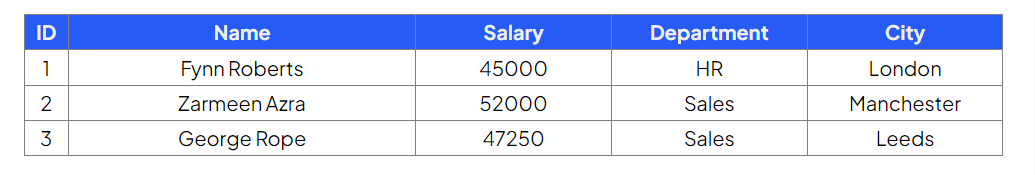
Table: Employees
ID | Name | Salary | Department | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Fynn Roberts | 45000 | HR | London |
2 | Zarmeen Azra | 52000 | Sales | Manchester |
3 | Ella Stanley | 39500 | Marketing | Birmingham |
4 | George Rope | 47250 | Sales | Leeds |
Delete all records from the Employees table whose department is 'Marketing'
Command:
|
Output:
ID | Name | Salary | Department | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Fynn Roberts | 45000 | HR | London |
2 | Zarmeen Azra | 52000 | Sales | Manchester |
3 | George Rope | 47250 | Sales | Leeds |
Summary
SQL command | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Add a new record |
|
| Modify existing data |
|
| Remove a record |
|
Worked Example
Scenario: The Restaurant Employee Database
A local restaurant uses a single database table, Employee, to store staff records.
The table structure and a small sample of data are shown below. Note that fullTime stores a Boolean value (where the absence of the '✓' in the sample data implies they are part-time, or equivalent to FALSE):
Attribute Name | Key | Type |
|---|---|---|
| PK | Number |
| Text | |
| Text | |
| Date | |
| Boolean | |
| Text |
(i) Adding a Record
A new employee, Leo Sanchez, is hired as a server. He is part-time (False) and starts on 10/05/2026. He is assigned employee ID 555777 and contact number 07700123456
Write a single SQL statement that will add this new employee's details to the Employee table
[2]
(ii) Modifying a Record
Employee Rayyan Patel (ID 259631) has recently changed their contact number to 07778589500 and has been promoted to Manager
Write a single SQL statement that will update Rayyan Patel's record to reflect both the new contact number and the new jobTitle
[2]
(iii) Removing Records
The restaurant decides to remove all part-time servers from the database. Part-time employees are identified where the fullTime field is FALSE
Write an efficient SQL statement to delete all records where the employee is a server AND is part-time
[2]
Answer
(i)
INSERT INTO Employee (empID, empName, jobTitle, startDate, fullTime, contactNum) [1 mark]
VALUES (555777, 'Leo Sanchez', 'Server', '10/05/2026', FALSE, '07700123456'); [1 mark]
(ii)
UPDATE Employee SET contactNum = '07778589500', jobTitle = 'Manager' [1 mark]
WHERE empID = 259631; [1 mark]
(iii)
DELETE FROM Employee [1 mark]
WHERE jobTitle = 'Server' AND fullTime = FALSE; [1 mark]

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
