SQL SELECT Operations (SQA National 5 Computing Science): Revision Note
Exam code: X816 75
SQL select
What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a language used to create, update, delete and retrieve data from a database
Students are expected to use SELECT statements to query and organise data
The following examples all use a single database table named Customers and its contents can be seen below:
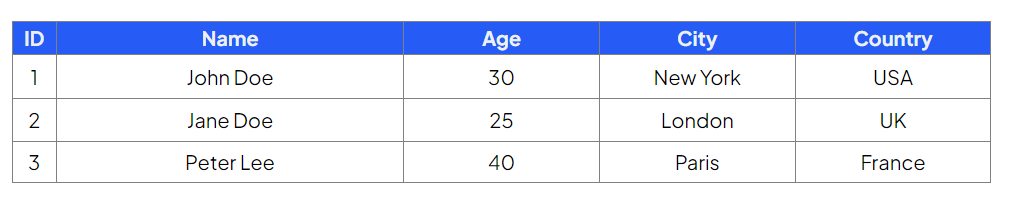
SELECT statement
The SELECT command is used to retrieve data from one or more database tables
Example
SELECT * FROM Customers;
This retrieves all records and all fields from the table Customers
Examiner Tips and Tricks
'*' is used to select all columns in a table, also known as a wildcard
FROM clause
The FROM clause specifies which table the data will be selected from
Example
SELECT ID, Name, Age FROM Customers;
This retrieves only the
ID,NameandAgefields from the Customers table

WHERE clause
The WHERE clause filters results based on a condition
Conditions can use comparison operators such as =, <, >, and logical operators such as AND and OR
Examples
SELECT ID, Name, Age FROM Customers
WHERE Age > 25;
Retrieves all customers older than 25

SELECT * FROM Customers
WHERE City = 'London' AND Age < 30;
Retrieves customers who live in London and are under 30
SELECT * FROM Customers
WHERE City = 'London' OR City = 'Paris';
Retrieves customers who live in either London or Paris
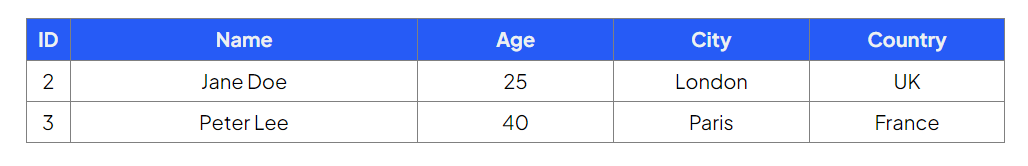
ORDER BY clause
The ORDER BY clause is used to sort the output of a query in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order
At this level, you can order by up to two fields
Examples
SELECT Name, City FROM Customers
ORDER BY City;
Orders customers by City in ascending order (A–Z)
SELECT Name, City FROM Customers
ORDER BY City DESC, Name ASC;
Orders customers by City in descending order, and then by Name in ascending order
Summary
SQL keyword | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
SELECT | Choose which fields to retrieve |
|
FROM | Choose which table to retrieve from |
|
WHERE | Filter data using conditions |
|
AND / OR | Combine multiple conditions |
|
ORDER BY | Sort the results (max two fields) |
|
Worked Example
Scenario: The Global Dino Record Database
The DinoDiscoveries group has consolidated all their fossil findings into a single, comprehensive database table called DinoRecord.
The table structure includes the following attributes:
Attribute Name | Type | Key | Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text | ||
| Number | Range: >= 0.1 and <= 50 | |
| Text | Restricted choice: Carnivore, Herbivorous, Omnivore | |
| Text | ||
| Text | Restricted choice: Cretaceous, Jurassic, Triassic | |
| Number | PK |
Write an SQL select statement that will display the dinosaur's name (dinoName), its diet, and the period it lived in, for all dinosaurs that were Herbivorous (plant-eaters) AND lived during the Jurassic period
The resulting list must be sorted alphabetically by dinoName.
[4]
Answer
SELECT dinoName, diet, period FROM DinoRecord
WHERE diet = 'Herbivorous' AND period = 'Jurassic' ORDER BY dinoName ASC;
SELECT dinoName, diet, period[1 mark]FROM DinoRecord[1 mark]WHERE diet = 'Herbivorous' AND period = 'Jurassic'[1 mark]ORDER BY dinoName ASC;[1 mark]

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
