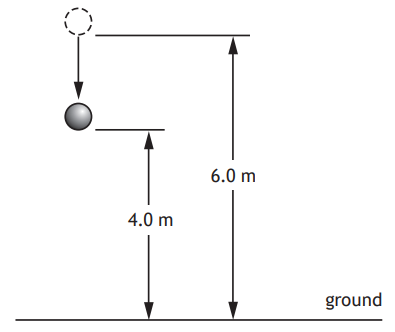
A block is pushed 3.0 m up a slope by a constant force of 6.0 N.
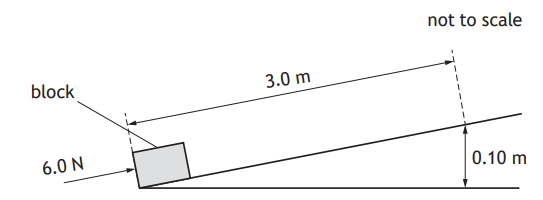
The force of friction between the block and the slope is 2.0 N.
The mass of the block is 1.5 kg.
The work done by the pushing force in moving the block 3.0 m up the slope is
1.5 J
6.0 J
12 J
18 J
24 J
Was this exam question helpful?