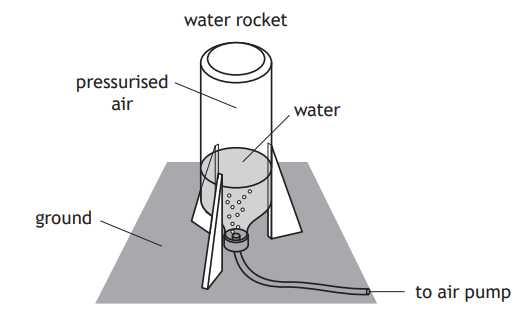
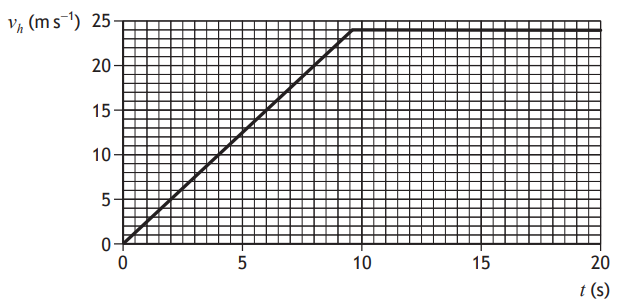
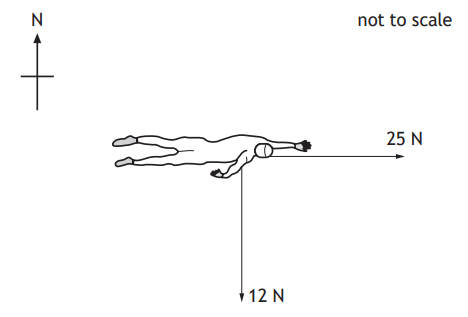
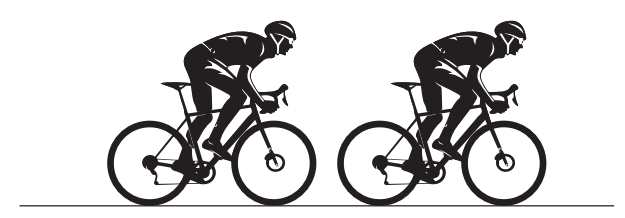
During a cycle race, a cyclist rides behind their team‑mate along a straight, flat section of road.
(i) The cyclist and bike have a combined mass of 74 kg.
The cyclist produces a forward force of 54 N.
The total frictional force acting on the cyclist and bike is 22 N.
Determine the acceleration of the cyclist and bike.
[4]
(ii) Explain, in terms of the forces acting on the cyclist, the advantage of cycling behind a team‑mate.
[1]
Was this exam question helpful?