The minimum energy required to melt 3.5 kg of ice at its melting point into water at the same temperature is
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X857 75
The minimum energy required to melt 3.5 kg of ice at its melting point into water at the same temperature is
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Two substances X and Y are both solid at 20 °C.
The substances have the same mass and are supplied with the same amount of energy per second.
The graph shows how the temperature of each substance varies with time.
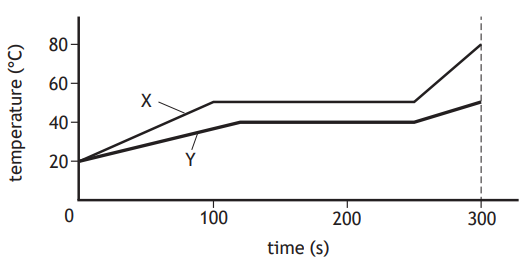
A student uses information from the graph to make the following statements:
I The specific heat capacity of the solid substance X is greater than that of the solid substance Y.
II Substance X changes state at a higher temperature than substance Y.
III The specific latent heat of fusion of substance X is greater than that of substance Y.
Which of these statements is/are correct?
I only
I and II only
III only
II and III only
I, II and III
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Heat from the Sun melts 1.6 kg of ice in 40 minutes.
The minimum heat energy required to change 1.6 kg of ice at 0 °C into water at 0 °C is:
6.7 103 J
1.3 104 J
2.1 105 J
5.3 105 J
3.6 106 J
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A solid substance is placed in an insulated container and heated.
The graph shows how the temperature T of the substance varies with time t.
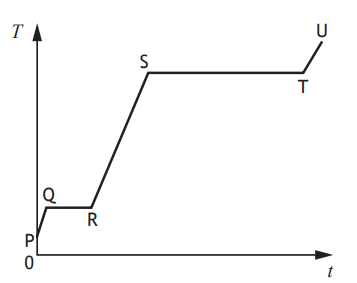
To calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of the substance a student would use the time from section
PQ
QR
RS
ST
TU
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A solid substance is placed in an insulated container and heated.
The graph shows how the temperature T of the substance varies with time t.
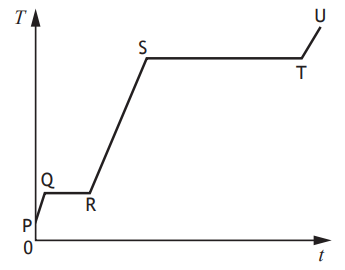
To determine the specific latent heat of vaporisation of the substance, a student would use the time from section
PQ
QR
RS
ST
TU
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Bottles used for feeding babies require sterilising before use.
For one design of bottle, a microwave oven is used to heat water in the bottle. This produces steam, which sterilises the bottle.
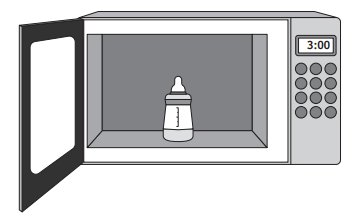
To sterilise the bottle, 0.020 kg of water is placed in the base of the bottle, before being heated in the microwave oven.
The initial temperature of the water is 6.3 °C.
During heating, 0.014 kg of water is changed to steam.
Calculate the energy required to change 0.014 kg of water at its boiling point to steam.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A block of wax is initially in the solid state.
The block of wax is then heated.
The graph shows how the temperature of the wax changes with time.
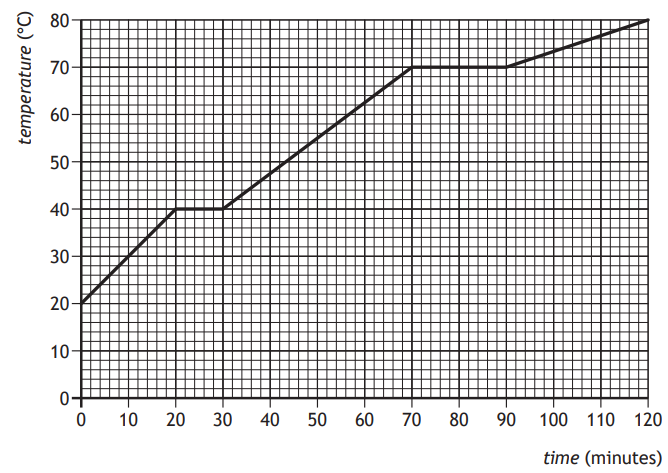
The melting point of the wax is
0 °C
20 °C
40 °C
70 °C
80 °C
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student carries out a experiment, using the apparatus shown, to determine a value for the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water.
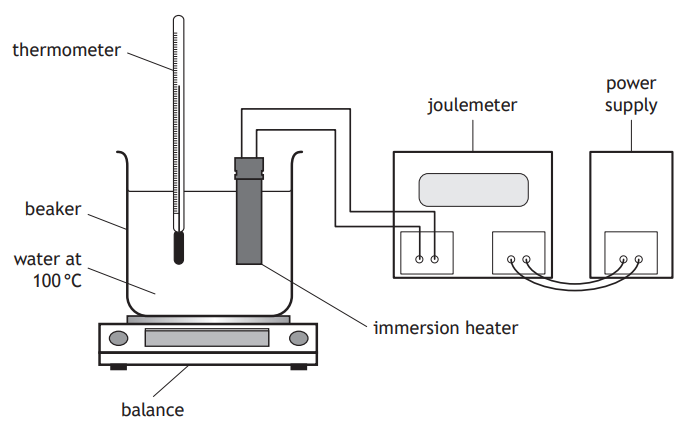
Describe how this apparatus would be used to determine a value for the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water.
Your description must include:
measurements made
any necessary calculations
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?