Read the passage and answer the questions that follow.
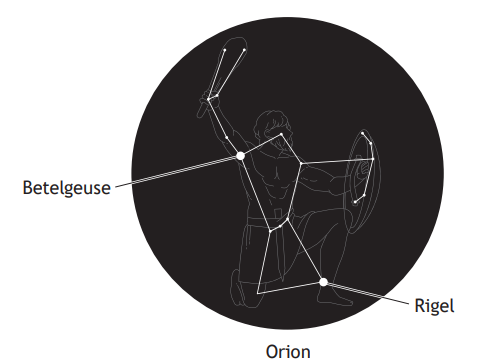
Making plans for Rigel
Betelgeuse might be regularly mentioned in the news but there are other supergiants in the night sky. One of these is Rigel, a blue supergiant star that makes up the ‘left foot’ of the constellation of Orion. It is approximately 8 million years old and is one of the brightest stars in our night sky.
Blue supergiants, such as Rigel, are short‑lived and are destined to explode as a supernova. Even though Rigel is 860 light‑years from Earth, the supernova will be clear to see. Astronomers believe that it will be as bright as a half‑moon and will be visible in the sky during the day. However, the light show will only last a few months before it fades.
When it explodes, Rigel will throw debris into space at approximately 5% of the speed of light. Intense waves of radiation, including X‑rays and gamma rays, will be radiated into space. The core of the star will collapse into an extremely dense ball of nuclear matter called a neutron star.
It is not possible to predict exactly when Rigel will explode and there is the possibility that it has already happened, it just hasn’t been detected yet! The best estimate scientists have is that it will take place within the next million years, or so.
(i) Calculate the distance, in metres, from Rigel to Earth.
[3]
(ii) Determine the approximate speed of the debris that will be ejected from the star during the supernova explosion.
[1]
(iii) Calculate the time it would take for this debris to reach Earth.
[3]
1018 m.