The diagram shows the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing wavelength.
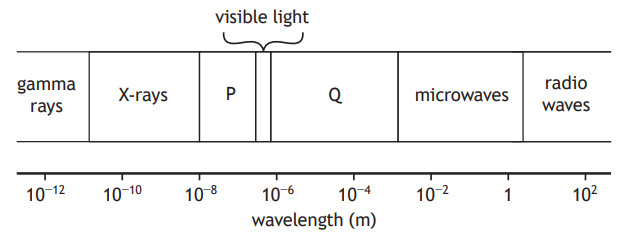
The names of two parts of the spectrum P and Q have been omitted.
State the names of parts P and Q.
P:
Q:
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X857 75
The diagram shows the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing wavelength.

The names of two parts of the spectrum P and Q have been omitted.
State the names of parts P and Q.
P:
Q:
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A student draws a diagram to show the bands of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing wavelength.
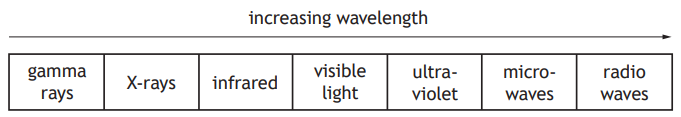
The diagram is not correct.
Which two bands of the electromagnetic spectrum are in the wrong position?
gamma rays and radio waves
X‑rays and microwaves
infrared and ultraviolet
visible light and microwaves
X-rays and visible light
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
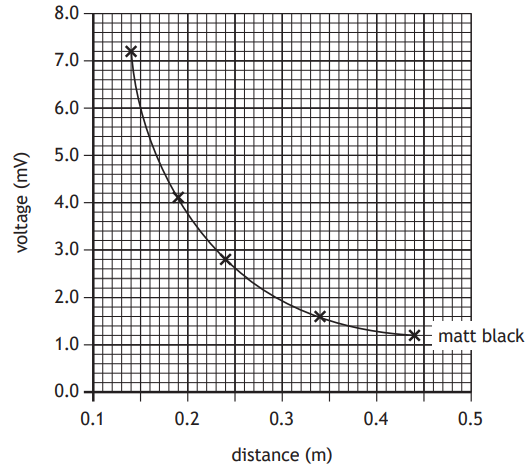
A student uses a Leslie’s cube and thermopile to investigate the amount of infrared radiation emitted by different surfaces of the cube.
A Leslie’s cube is a hollow metal cube. Four sides of the cube have different finishes: matt white, matt black, shiny silver, and shiny black.
Darker surfaces emit more infrared radiation than lighter surfaces. Matt surfaces emit more infrared radiation than shiny surfaces.
A thermopile is a device that produces a voltage proportional to the amount of infrared radiation detected.
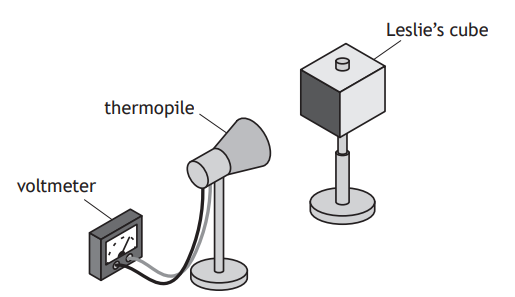
The student fills the cube with hot water and measures the amount of infrared radiation at different distances from the cube, using the thermopile.
The student produces a graph of their results for the matt black side.
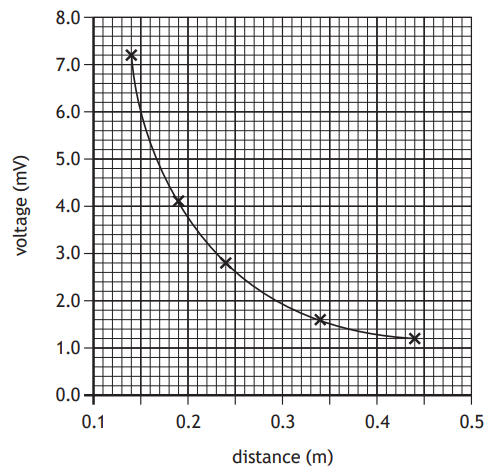
(i) State a conclusion that can be made about how the distance from a Leslie’s cube affects the amount of infrared radiation detected by the thermopile.
[1]
(ii) The experiment is repeated using the shiny silver side.
On the graph below, draw a line to show how the voltage produced by the thermopile varies with distance for the shiny silver side.
[2]
How did you do?
A solar shower consists of a heavy‑duty plastic bag, with a matt black surface and a shiny silver surface, connected to a hose and shower head. The bag uses infrared radiation from the Sun to heat water for a shower, when camping.
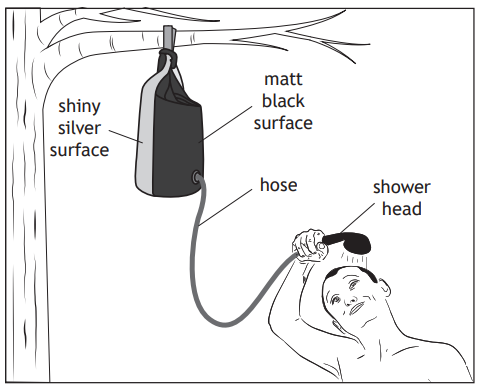
Using your knowledge of physics, comment on how the solar shower works.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A lifeboat crew is made up of local volunteers. When there is an emergency they have to get to the lifeboat quickly.
The lifeboat crew members are alerted to an emergency using a pager.
Text messages are sent to the pager using radio waves.

The radio waves have a frequency of 153 MHz.
Calculate the wavelength of the radio waves.
When the pager receives a message it beeps loudly and a light on the pager flashes.
A crew member holding the pager observes the beeps and the flashes happening at the same time.
A second crew member, who is 100 m away from the pager, also observes the beeps and the flashes.
Explain why the second crew member does not observe the beeps and the flashes happening at the same time.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Infrared and gamma rays are both members of a family of waves.
State the name given to this family of waves.
How did you do?
State how the frequency of infrared compares to the frequency of gamma rays.
How did you do?
Some examples of sources and detectors of waves in this family are shown.
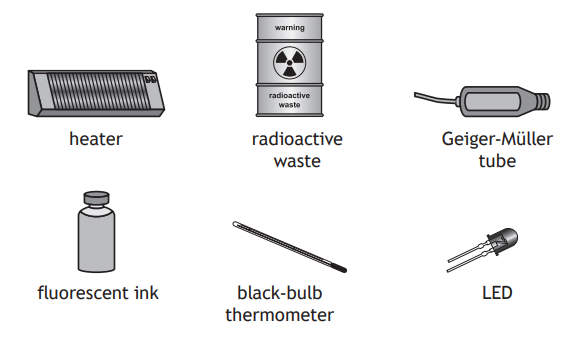
(i) From the examples shown, identify
(A) the detector of infrared
[1]
(B) the source of gamma rays.
[1]
(ii) Suggest one application for the waves that are detected using fluorescent ink.
[1]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The letters X, Y, and Z represent missing words or phrases from the following passage.
Infrared has a .... X .... wavelength than visible light.
Infrared diffracts ....Y.... than visible light.
The speed of infrared is .... Z .... visible light.
Which row in the table shows the missing words or phrases?
X | Y | Z | |
A | longer | less | the same as |
B | shorter | less | slower than |
C | longer | more | the same as |
D | shorter | more | faster than |
E | longer | more | faster than |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The diagram shows part of the electromagnetic spectrum arranged in order of increasing wavelength.
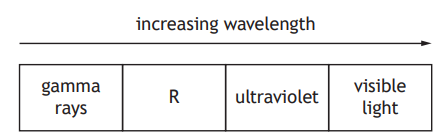
Which row in the table identifies radiation R and describes its frequency?
Radiation R | Frequency of radiation R | |
A | X-rays | higher frequency than visible light |
B | microwaves | lower frequency than visible light |
C | X-rays | lower frequency than visible light |
D | infrared | lower frequency than visible light |
E | microwaves | higher frequency than visible light |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A rain sensor is attached to the glass windscreen of a vehicle to automatically control the windscreen wipers.
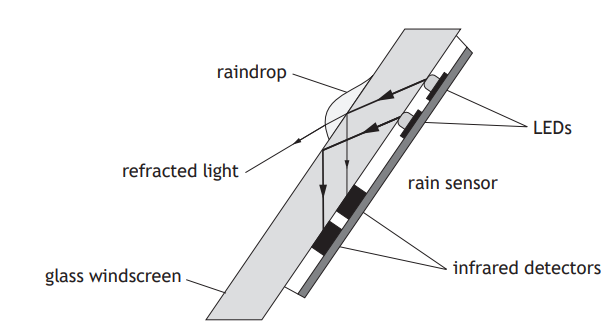
Infrared light is emitted from LEDs and is received by infrared detectors.
State a suitable detector of infrared radiation for this rain sensor.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?