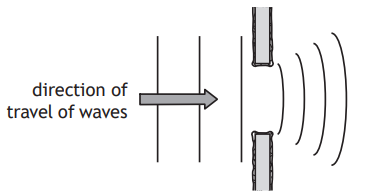
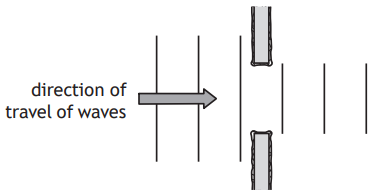
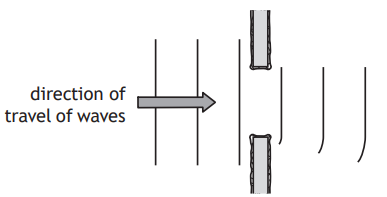
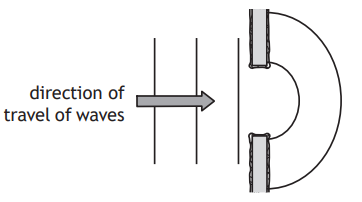
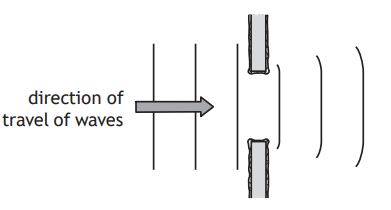
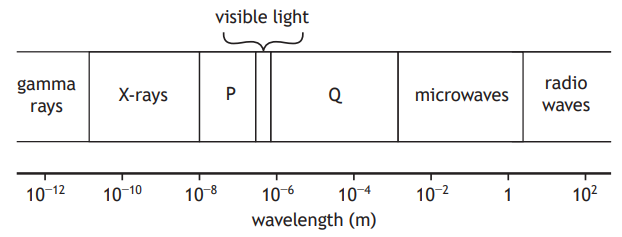
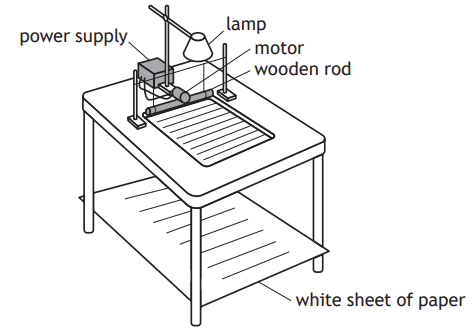
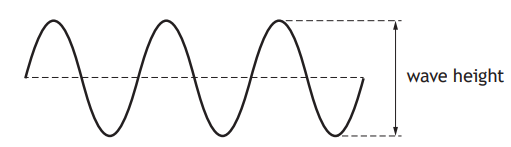
A student sets up a ripple tank. A ripple tank is a shallow tank of water used to demonstrate wave properties.
The wooden rod moves in and out of the water to generate water waves.
The pattern of the water waves is projected onto a white sheet of paper below the tank.
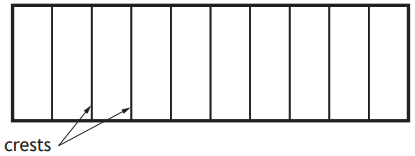
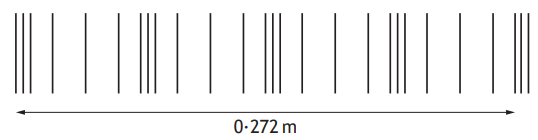
The wave pattern appears on the paper as a series of bright and dark lines. The dark lines correspond to the wave crests.
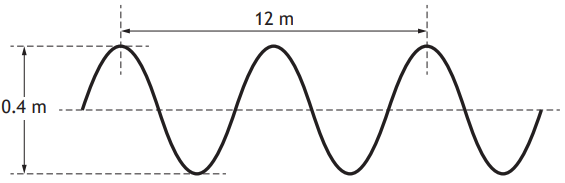
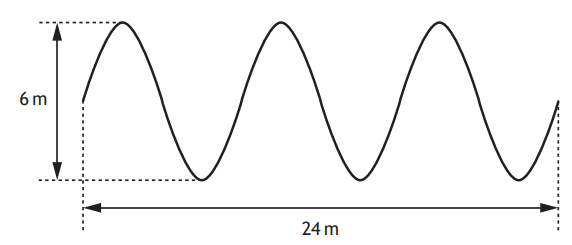
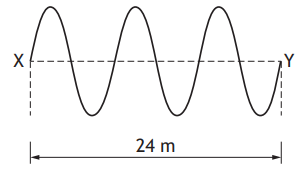
The student determines that there are six complete waves in 0.12 m.
(i) Determine the wavelength of the waves.
[1]
(ii) The six complete waves are produced in a time of 0.40 s.
Show that the frequency of the waves is 15 Hz.
[2]
(iii) Calculate the speed of the waves.
[3]