The Structure of RNA (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
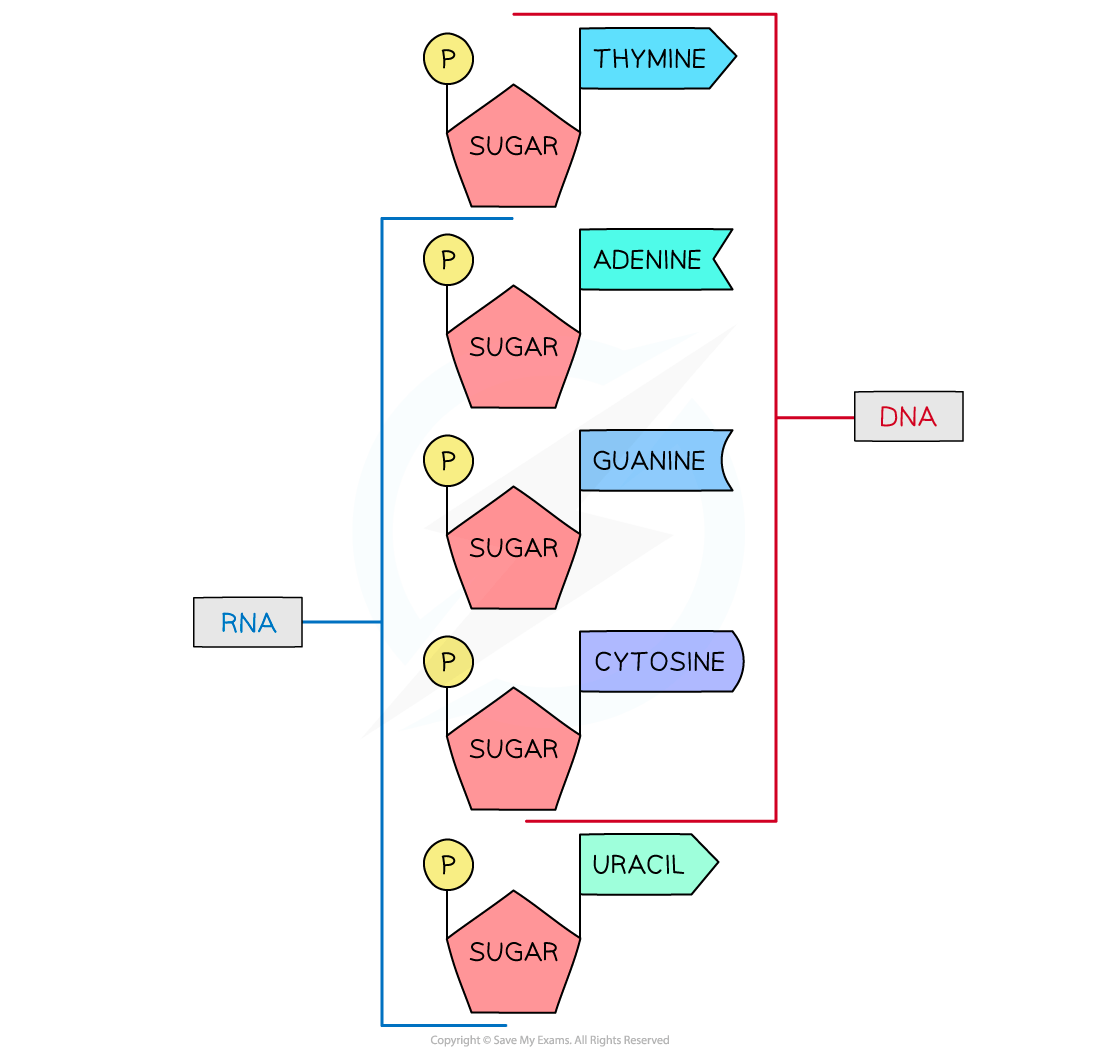
RNA structure
Like DNA:
The nucleic acid RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a polynucleotide
It is made up of many nucleotides linked together in a long chain
RNA nucleotides contain the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G) and cytosine (C)
Unlike DNA:
RNA nucleotides never contain the nitrogenous base thymine (T)
In place of this they contain the nitrogenous base uracil (U)
RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar ribose (instead of deoxyribose)
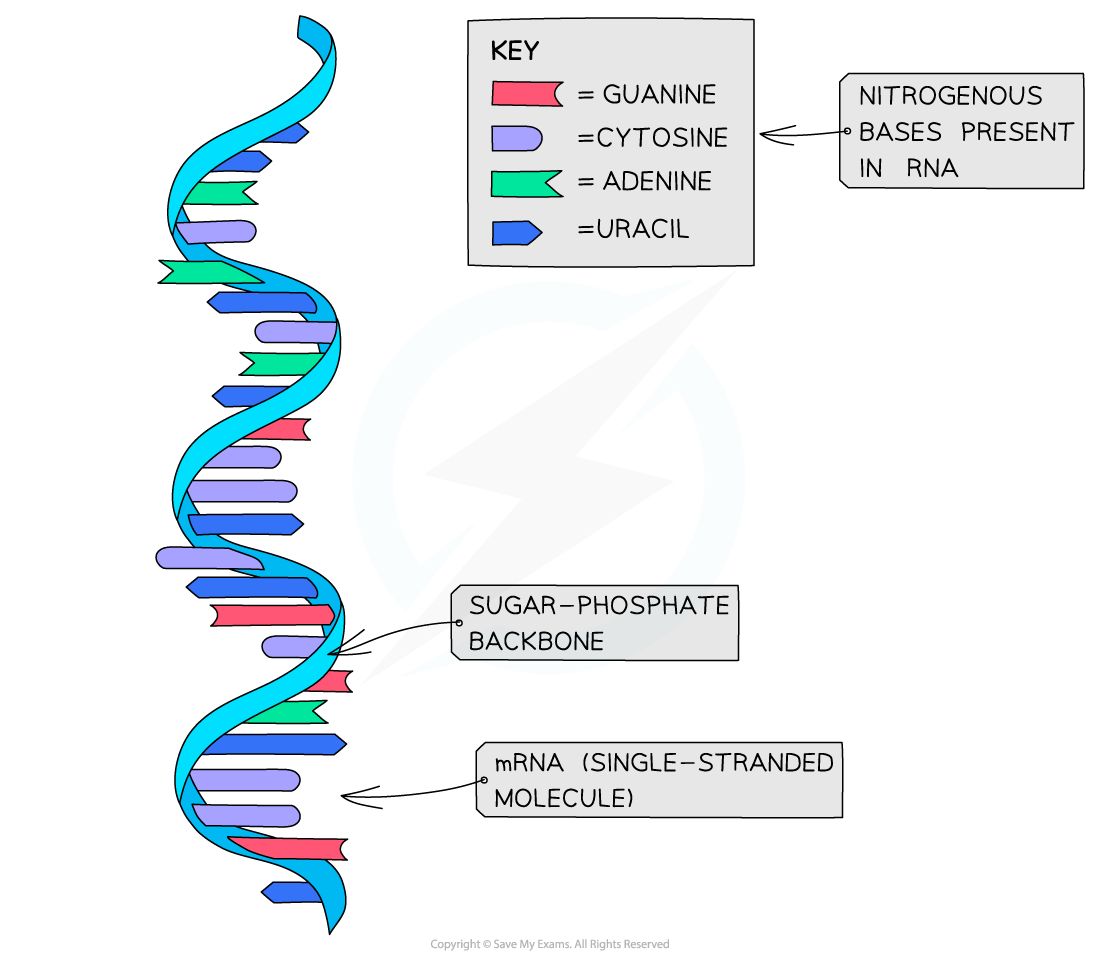
RNA molecules are only made up of one polynucleotide strand (they are single-stranded)
Each RNA polynucleotide strand is made up of alternating ribose sugars and phosphate groups linked together
The nitrogenous bases of each nucleotide projecting out sideways from the single-stranded RNA molecule
Properties | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
Pentose sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
Bases | Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) | Adenine (A) Uracil (U) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) |
Number of strands | Double-stranded (double helix) | Single-stranded |
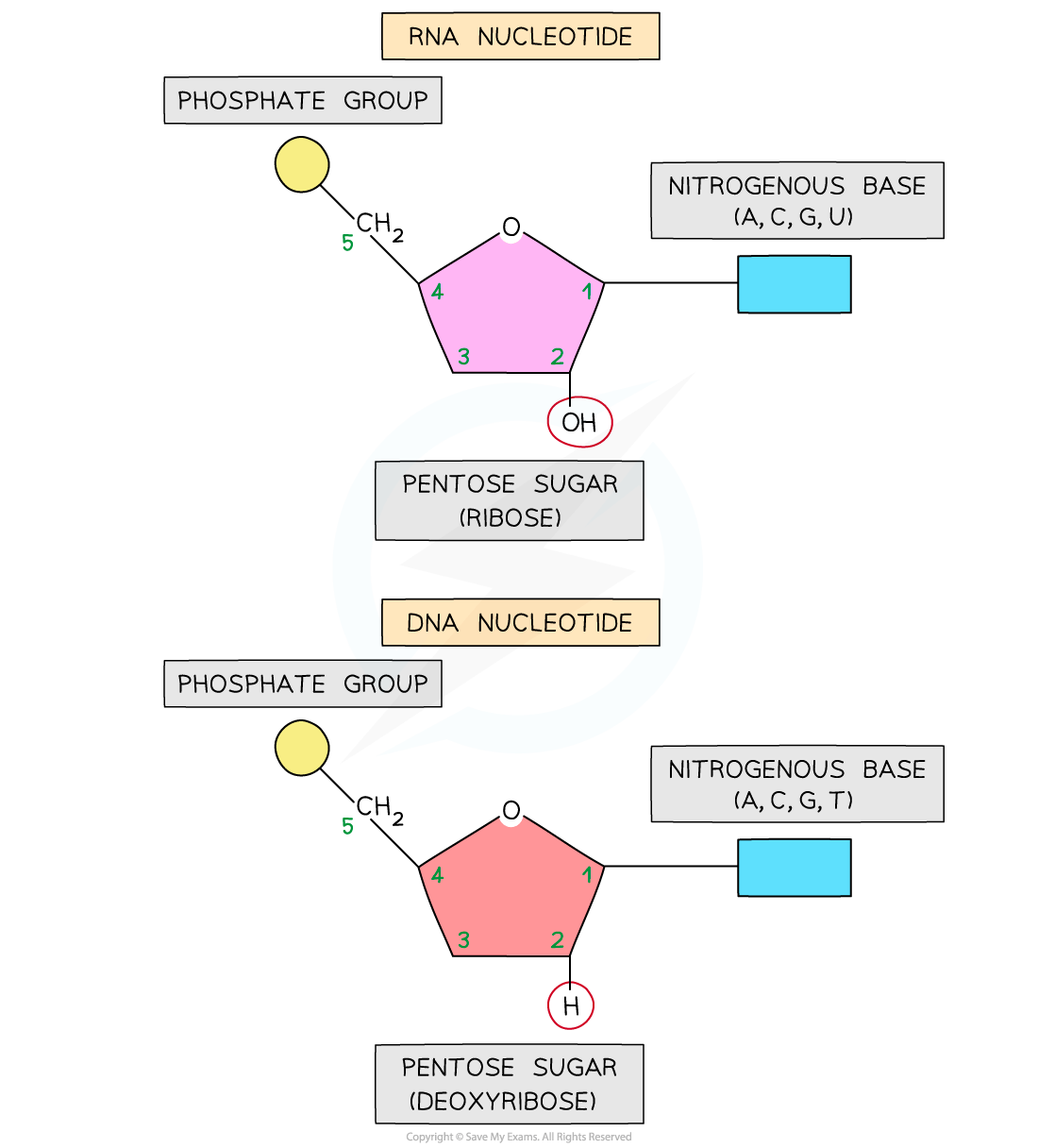
The sugar-phosphate bonds (between different nucleotides in the same strand) are covalent bonds known as phosphodiester bonds
These bonds form what is known as the sugar-phosphate backbone of the RNA polynucleotide strand
The phosphodiester bonds link the 5-carbon of one ribose sugar molecule to the phosphate group from the same nucleotide, which is itself linked by another phosphodiester bond to the 3-carbon of the ribose sugar molecule of the next nucleotide in the strand
An example of an RNA molecule is messenger RNA (mRNA)
mRNA is the transcript copy of a gene that encodes a specific polypeptide
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to know the difference between DNA and RNA molecules (bases, number of strands, pentose sugar present).

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
