The Universal Genetic Code (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
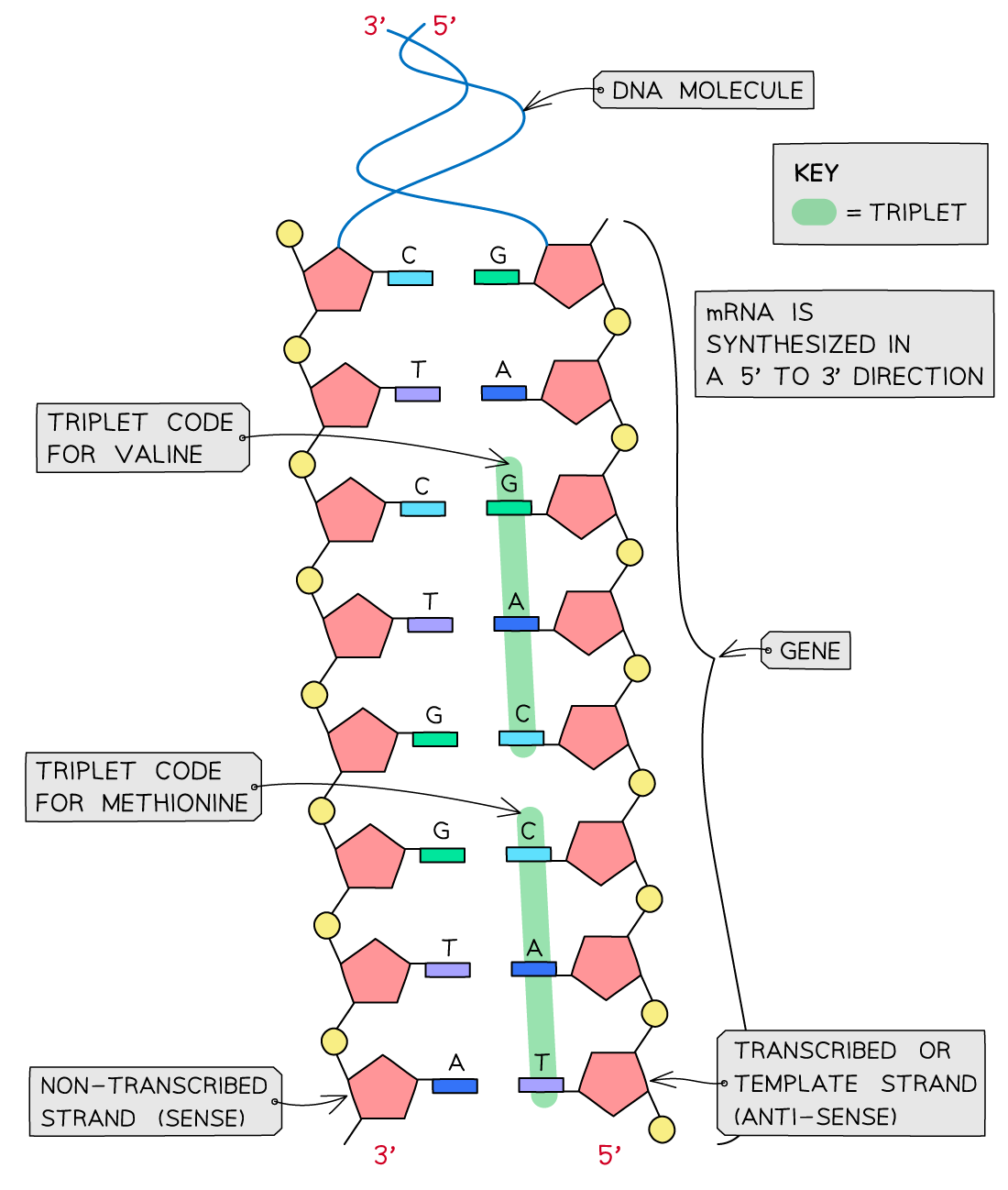
The universal genetic code
A gene is a sequence of nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule that codes for the production of a specific sequence of amino acids
These amino acids in turn make up a specific polypeptide (protein)
The DNA nucleotide base code found within a gene is a three-letter, or triplet, code
Each sequence of three bases (in other words each triplet of bases) codes for one amino acid
There are 20 different amino acids that cells use to make up different proteins
For example:
CAG codes for the amino acid valine
TTC codes for the amino acid lysine
GAC codes for the amino acid leucine
CCG codes for the amino acid glycine
Some of these triplets of bases code for start and stop signals
These signals tell the cell where individual genes start and stop
This ensures the cell:
Reads the DNA correctly (the code is non-overlapping)
Can produce the correct sequences of amino acids (and therefore the correct protein molecules) that it requires to function properly
The genetic code is universal, meaning that almost every organism uses the same code
This means that the same triplets code for the same amino acids in all living things
This means that genetic information is transferable between species

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
