Basic Questions of Resource Allocation (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9708
What to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce?
As resources are scarce, every economy faces the fundamental economic problem
This forces all societies to make decisions about how limited resources should be allocated
These decisions can be summarised by three key economic questions
The three fundamental economic questions
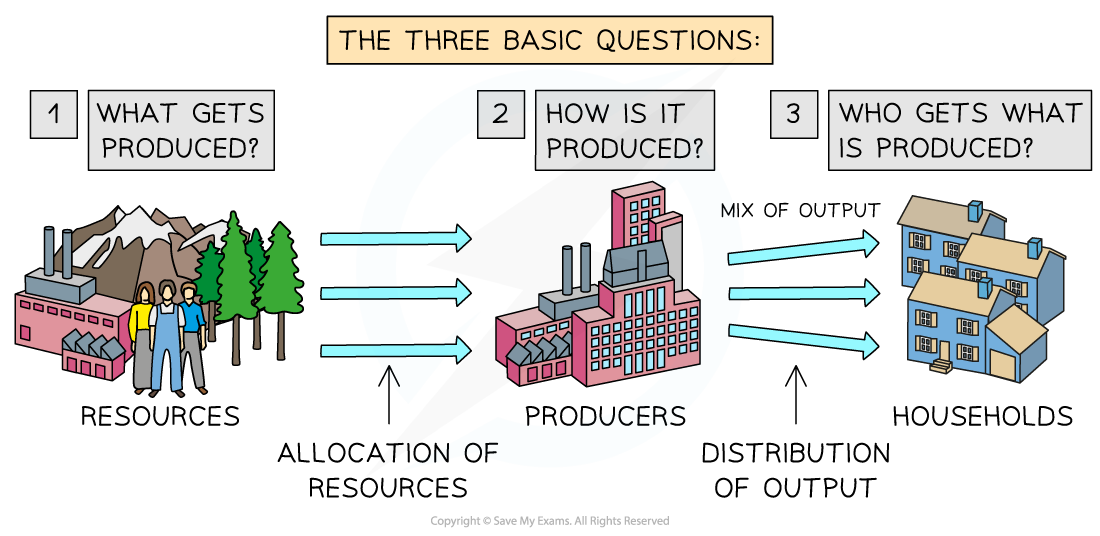
What to produce?
No economy has enough resources to produce everything people want. As a result, decisions must be made about which goods and services to produce and in what quantities
For example, governments and firms must choose between producing:
Consumer goods and services (such as food, clothing and transport) to raise living standards, or
Capital and defence goods (such as military equipment) to improve national security
Different priorities explain why some countries devote a much larger proportion of their resources to defence spending than others
These choices always involve opportunity cost, as producing more of one type of good means producing less of another
How to produce?
This question focuses on how resources are combined and used in the production process
Firms aim to use resources as efficiently as possible so that output is maximised from the available inputs
Decisions about production methods may involve choosing between:
labour-intensive or capital-intensive techniques
traditional or more advanced technology
Although firms often aim to minimise costs, production decisions are not always based purely on economic efficiency.
Ethical and environmental considerations may also influence how goods are produced. For example, the use of very low-paid labour may reduce costs but raise moral concerns
In agriculture, output can be increased through more intensive farming methods or by making better use of natural resources, such as using underground water supplies to grow crops in dry regions
For whom to produce?
This question concerns how output is distributed among the population
Governments must decide whether goods and services should be shared relatively equally or whether income and wealth gaps are acceptable
Some economies use policies such as taxation and welfare payments to redistribute income and reduce inequality
Others allow market forces and inheritance to play a larger role, which can result in significant gaps between rich and poor
Income and wealth inequality is a major issue in many developing and emerging economies, where economic growth has not benefited all groups equally
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should see all three questions as connected, as they are all caused by scarcity
Resources are limited so every economy must decide what goods to produce, how to use resources efficiently, and who will receive the output

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
