Market Equilibrium & Disequilibrium (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Economics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9708
Price determination in markets
A market is any place or process that brings buyers and sellers together to exchange goods and services
This exchange can happen in a physical location (such as a food market in Jakarta) or through a virtual platform (such as Alibaba or Amazon)

Roles of buyers and sellers
In any market, both buyers and sellers play essential roles
In an efficient market, sellers respond to what buyers want, and buyers choose between competing sellers
This interaction helps determine prices and quantities
Buyers
Also known as consumers or demanders
Their choices and preferences determine demand for goods and services
They help to set prices by signalling how much they are willing to pay
For example, a buyer in Mexico City searching for the best price on mobile phones influences how firms set prices to compete
Sellers
Also known as producers or suppliers
They aim to supply goods or services in order to make a profit
They decide what to produce, how much and at what price based on costs and expected demand
For example, a coconut farmer in the Philippines choosing whether to sell to local markets or export to Singapore
Market equilibrium
Equilibrium occurs in a market when demand = supply
At this point, the price is called the equilibrium or market-clearing price
This is the price at which sellers are clearing (selling) their stock at an acceptable rate
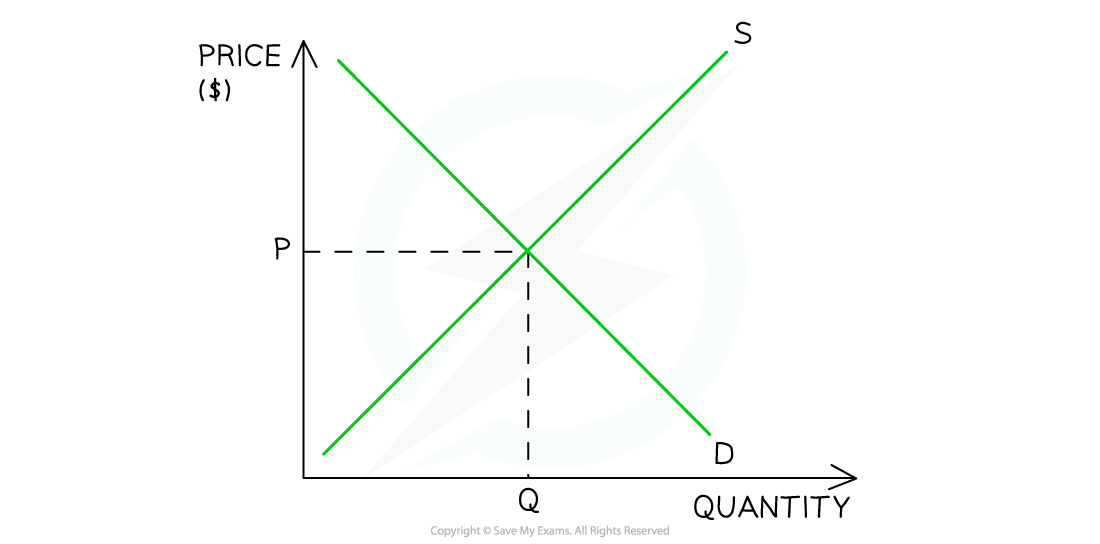
Diagram analysis
Any price above or below P creates disequilibrium in this market
Disequilibrium occurs whenever there is excess demand or excess supply in a market
Market disequilibrium
Disequilibrium occurs when demand is not equal to supply
If demand > supply, the market is facing excess demand
If demand < supply, the market is facing excess supply
1. Disequilibrium: excess demand
Excess demand occurs when the demand is greater than the supply
It can occur when prices are too low or when demand is so high that supply cannot keep up with it
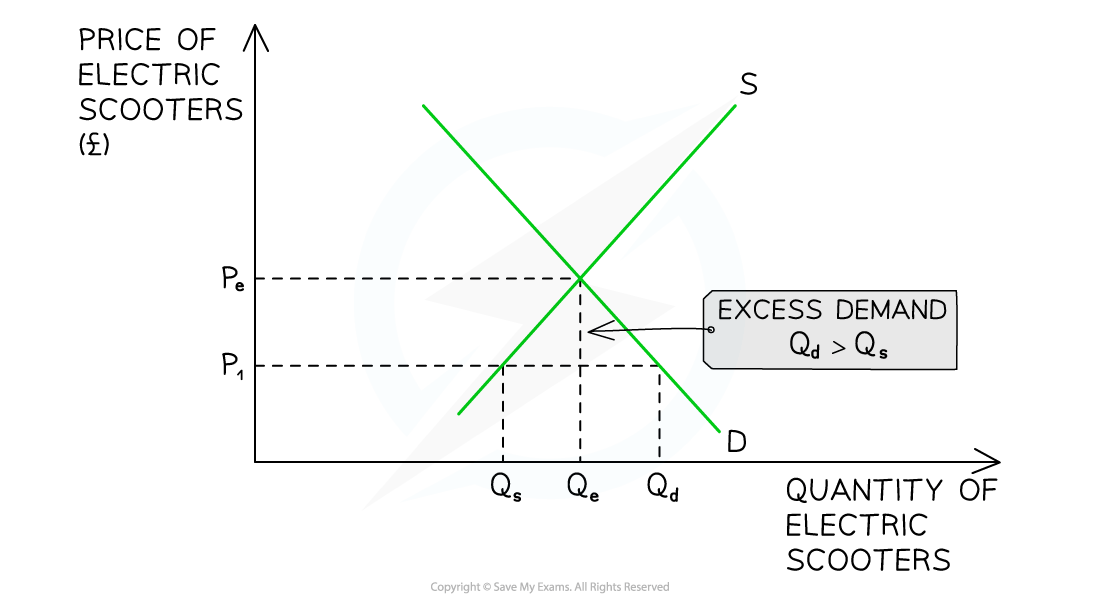
Diagram analysis
At a price of P1, the quantity demanded of electric scooters (Qd) is greater than the quantity supplied (Qs)
There is a shortage (excess demand) in the market equivalent to QsQd
Market response
This market is in disequilibrium
Sellers are frustrated that products are selling so quickly at a price that is obviously too low
Some buyers are frustrated as they will not be able to purchase the product
Sellers realise they can increase prices and generate more revenue and profits
Sellers gradually raise prices
This causes a contraction in QD as some buyers no longer desire the good/service at a higher price
This causes an extension in QS as other sellers are more incentivised to supply at higher prices
In time, the market will have cleared the excess demand and arrive at a position of equilibrium, PeQe
Different markets take different lengths of time to resolve disequilibrium
E.g., retail clothing can do so in a few days. Whereas the housing market may take several months or even years
2. Disequilibrium: excess supply
Excess supply occurs when the supply is greater than the demand
It can occur when prices are too high or when demand falls unexpectedly
During the later stages of the pandemic, the market for face masks was in disequilibrium
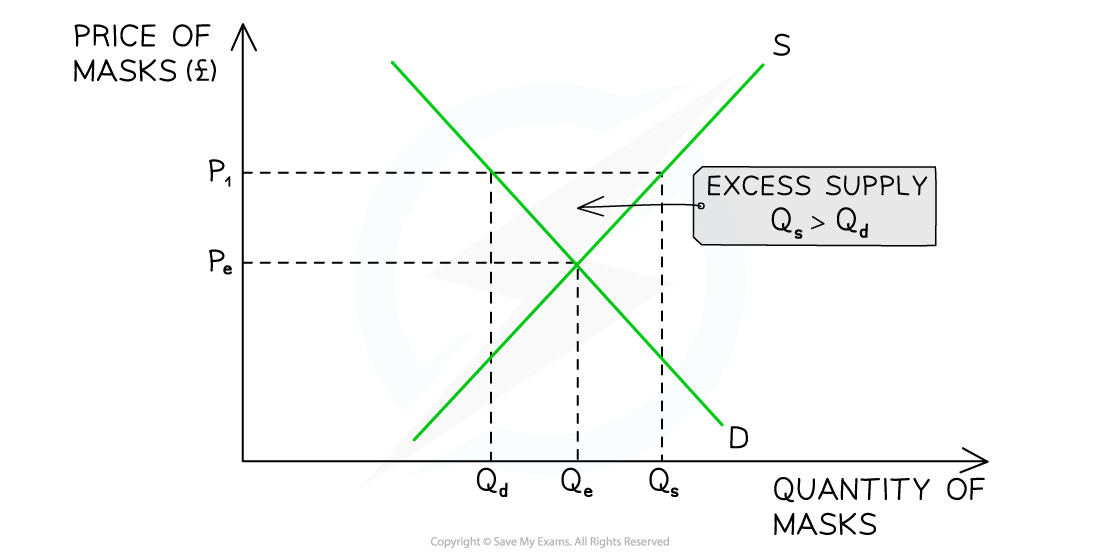
Diagram analysis
At a price of P1, the quantity supplied of face masks (Qs) is greater than the quantity demanded (Qd)
There is a surplus in the market (excess supply) equivalent to QdQs
Market response
This market is in disequilibrium
Sellers are frustrated that the masks are not selling and that the price is obviously too high
Some buyers are frustrated, as they want to purchase the masks but are not willing to pay the high price
Sellers will gradually lower prices in order to generate more revenue
This causes a contraction in QS as some sellers no longer desire to supply masks
This causes an extension in QD as buyers are more willing to purchase masks at lower prices
In time, the market will have cleared the excess supply and arrive at a position of equilibrium, PeQe
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should memorise the rule that shortages arise when the price is below equilibrium, whereas surpluses arise when the price is above the equilibrium

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
