Kruskal's Algorithm (Edexcel A Level Further Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9FM0
Kruskal's algorithm
What is Kruskal's algorithm?
In a situation that can be modelled by a network, Kruskal’s algorithm is a mathematical tool that can be used to connect all of the vertices in a way that reduces costs, materials or time by finding the minimum spanning tree (MST).
Why do we use Kruskal’s algorithm?
Kruskal’s algorithm is a series of steps that when followed will produce the minimum spanning tree for a network
Finding the minimum spanning tree is useful in a lot of practical applications as it connects all of the vertices in the most efficient way possible
The number of edges in a minimum spanning tree will always be one less than the number of vertices in the graph
A minimum spanning tree cannot contain any cycles.
What are the steps of Kruskal’s algorithm?
STEP 1
Sort the edges in terms of increasing weightSTEP 2
Select the edge of least weightIf there is more than one edge of the same weight, either may be used
STEP 3
Select the next edge of least weight that has not already been chosenReject it if it forms a cycle with the other selected edges
Otherwise, add it to your tree
STEP 4
Repeat STEP 3 until all of the vertices in the graph are connected
If there are n nodes then there will be n - 1 edges in the minimum spanning tree
STEP 5
List the edges in the minimum spanning tree in the order they were added
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Draw out the edges included in the minimum spanning tree as you go along as it will make it easier to spot potential cycles
When using any of the algorithms for finding the minimum spanning tree, make sure that you state the order in which the edges are selected to get full marks for working!
In Kruskal's algorithm, the edges are sorted into increasing weight first
there are algorithms for that too !
Worked Example
Consider the network below.
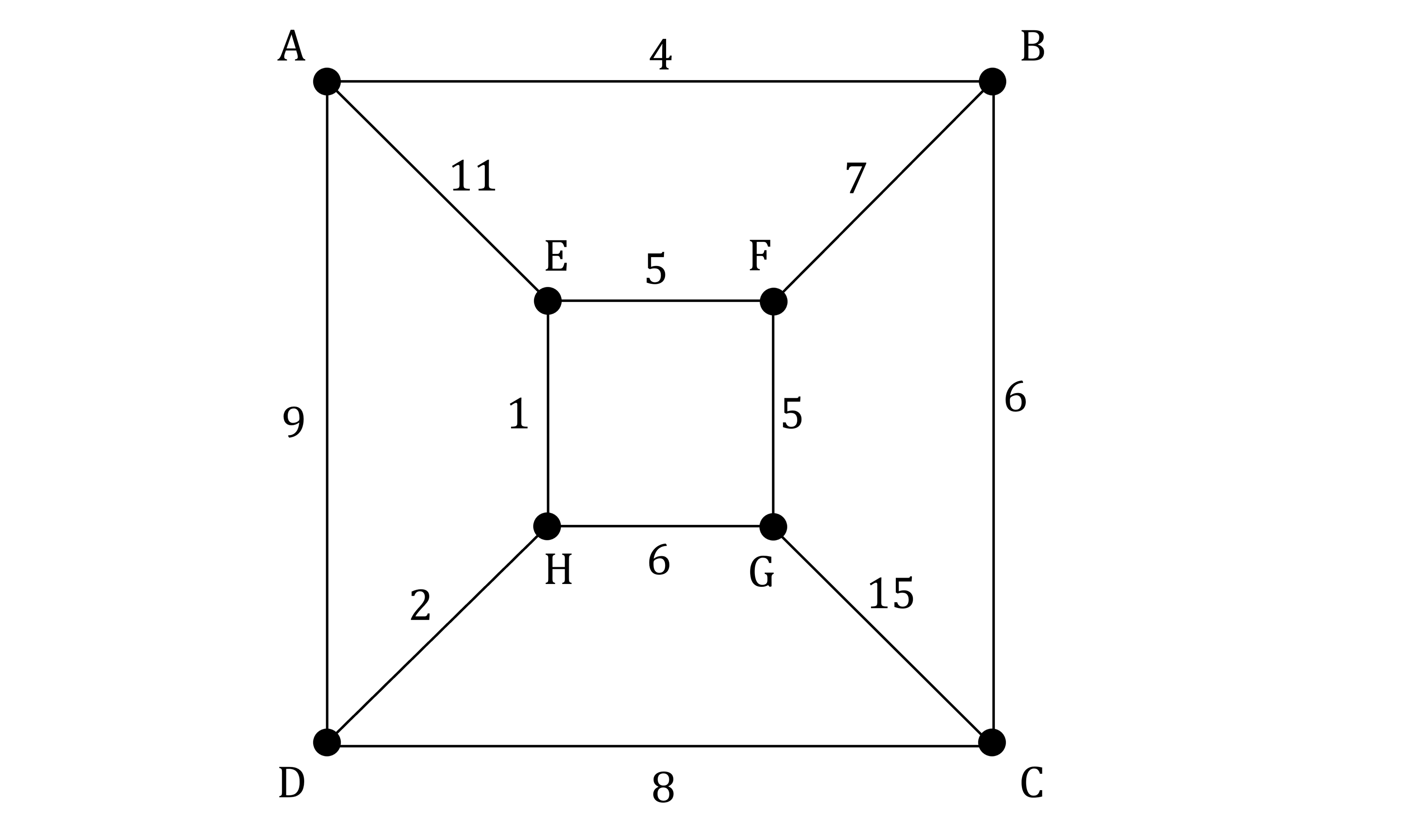
a) Use Kruskal’s algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree. Show each step of the algorithm clearly.
STEP 1
List the edges in order of increasing weight
EH (1)
DH (2)
AB (4)
EF (5)
FG (5)
GH (6)
BC (6)
BF (7)
CD (8)
AD (9)
AE (11)
CG (15)
STEP 2
Add the edge of least weight (EH)
STEP 3
Add the next edge of least weight (DH)
STEP 4
Repeat Step 3
Repeat adding the next edge of least weight each time provided it does not create a cycle until all vertices are connectedAdd AB
Add EF
Add FG
Reject GH as it forms a cycle
Add BC
Add BF

Edges are added in the order: EH (1), DH (2), AB (4), EF (5), FG (5), reject GH, BC (6), BF (7)
b) State the total weight of the minimum spanning tree.
Add up the weights of the edges in the minimum spanning tree
1 + 2 + 4 + 5 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 30
Total weight = 30

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
