Functionalism (AQA A Level Sociology): Revision Note
Exam code: 7192
Functionalism
Functionalism is a consensus theory that seeks to explain why the structure of modern societies tends to remain relatively stable, orderly, and well-organised
Social structure refers to the way society is organised economically, politically, and socially
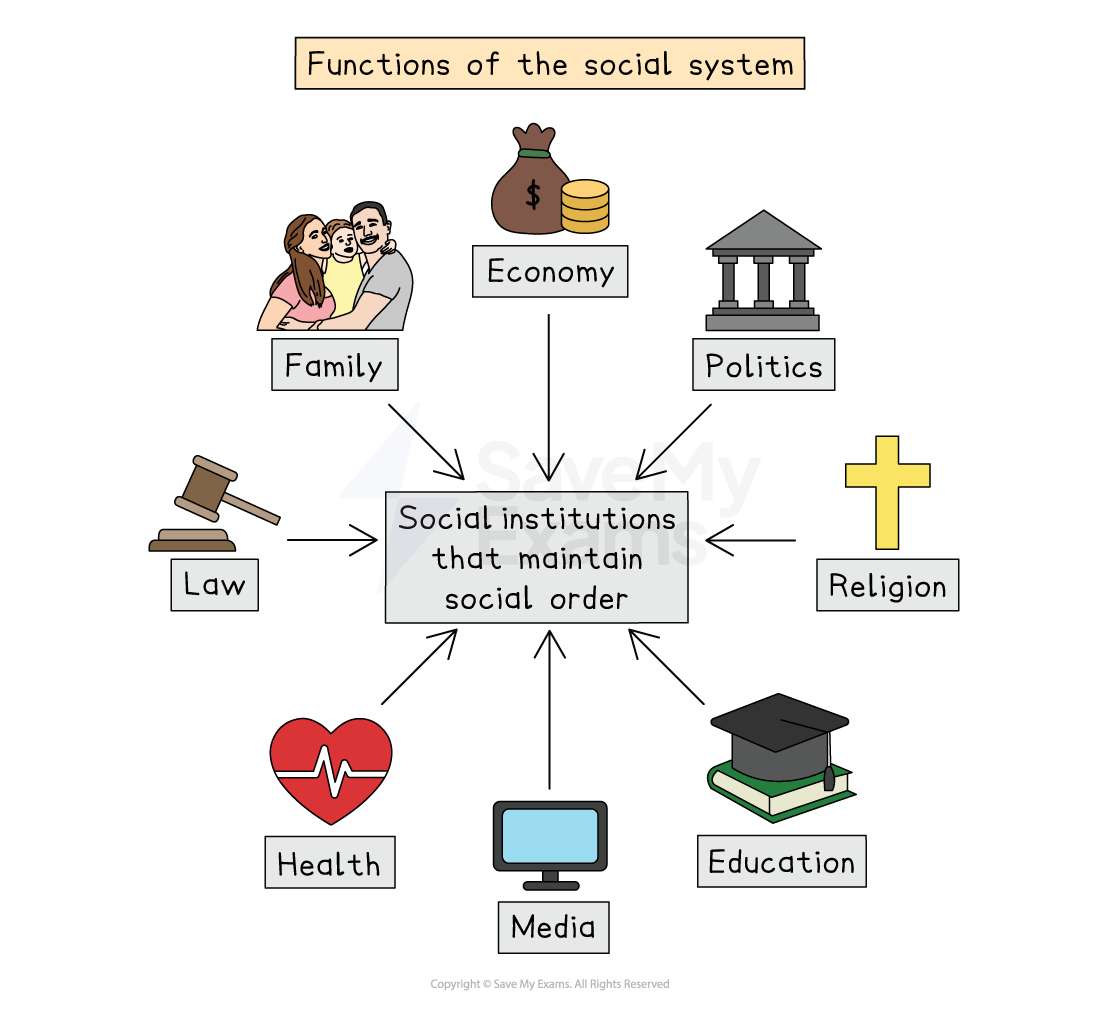
Society as a social system
Society is viewed as a system made up of interdependent social institutions (e.g., the family, education, and law)
They work together to maintain social order and meet the needs of its members
They meet society's needs by carrying out functions that guarantee its survival
This is often explained using the biological analogy
Just like the organs in the human body, each has a function that keeps the body alive and healthy; social institutions each perform vital roles that keep society functioning smoothly
Functionalism focuses on the positive functions that social institutions perform rather than the negative aspects
The functions of the social system
Functionalists argue that social institutions perform three main functions to maintain consensus, cooperation, and social order:
Value consensus
Individuals are socialised into sharing common values, norms, and beliefs
This agreement on what’s right and wrong creates social unity and reduces conflict
E.g., the education system teaches shared values like punctuality, respect, and hard work, helping people cooperate in public life
Social integration
A shared culture and common identity help individuals feel part of something bigger than themselves
This sense of belonging leads to solidarity and a stable society
E.g., national events like the King's Coronation bring people together, reinforcing a sense of national identity and unity
Specialised division of labour
Society is organised so that people take on specific roles and jobs
This ensures that all necessary tasks are carried out for society to function
E.g., education prepares individuals for different positions in the workplace
Evaluation of functionalism
Strengths
Highlights the importance of social order
It shows how institutions like education and the family work together to maintain cohesion and prevent chaos
Criticisms
Overlooks dysfunction
It tends to ignore the negative aspects of institutions; e.g., the family is not always positive—issues like domestic abuse can cause serious harm
Assumes harmony and consensus
It wrongly assumes that everyone in society benefits equally
Critics argue it fails to recognise inequalities in power, class, gender, and race
Neglects individual agency
Functionalism sees individuals as shaped by society, but interactionist theorists argue that individuals also shape society through their choices and actions

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
