Parking at an airport is controlled by computers.
No paper tickets are issued.
Here is an image of the control system at the exit.

The control system uses sensors, a camera and a database.
The barrier lifts if the parking fee has been paid.
Describe what the system does when the exit sensor is activated by a car driving towards it.
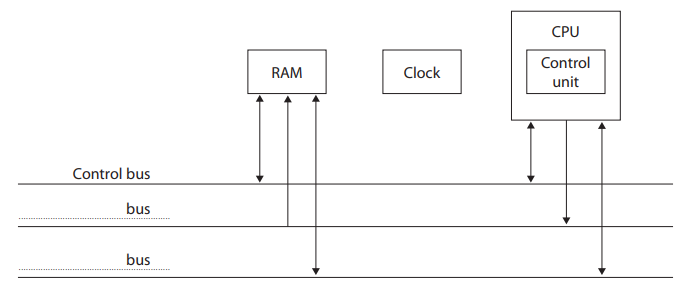
The components of a computer carry out the fetch‑decode‑execute cycle.
Complete the diagram with:
• the names of two buses
• a directional connection from the clock to the correct component.
Was this exam question helpful?