Current & Voltage Relationships (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Current & Voltage Relationships
Resistance is defined as the opposition to current:
Resistance occurs because the free electrons flowing in the circuit (current) collide with the metal ions in the wire which slows them down or resists their flow
The higher the resistance of a circuit, the lower the current
This means that good conductors have a low resistance and insulators have a high resistance
The symbol for resistance is R
It is measured in ohms (Ω)
Ω is the Greek capital letter ‘Omega’
The resistance of a circuit can be increased by adding resistors (or variable resistors) to it
Every electrical component has a resistance, even wires
In exam questions, the resistance of the wires and batteries are assumed to be negligible
Diagram Showing How Resistance Affects Current
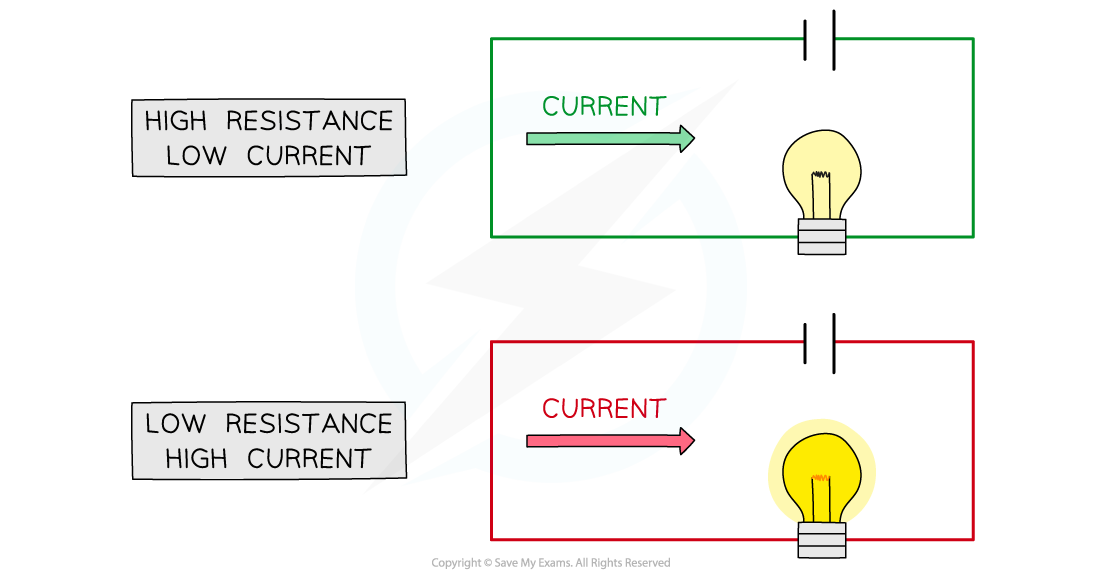
When a circuit has a high resistance, a lower current will flow, and vice versa
Current,
, voltage,V, and resistance, R, all affect one another
For a fixed resistance, current is directly proportional to voltage
If voltage doubles, current doubles
For a fixed voltage, current is inversely proportional to resistance
If resistance doubles, current halves
These relationships are described using the following equation
Where:
= current measured in amps (A)
V = voltage measured in volts (V)
R = resistance measured in ohms (Ω)
This equation is sometimes called the resistance equation or Ohm's law
Equation Triangle for Current, Voltage and Resistance
Students taking the Higher Tier exam paper will need to be able to rearrange this equation
The equation triangle can help with rearranging the equation if you need support
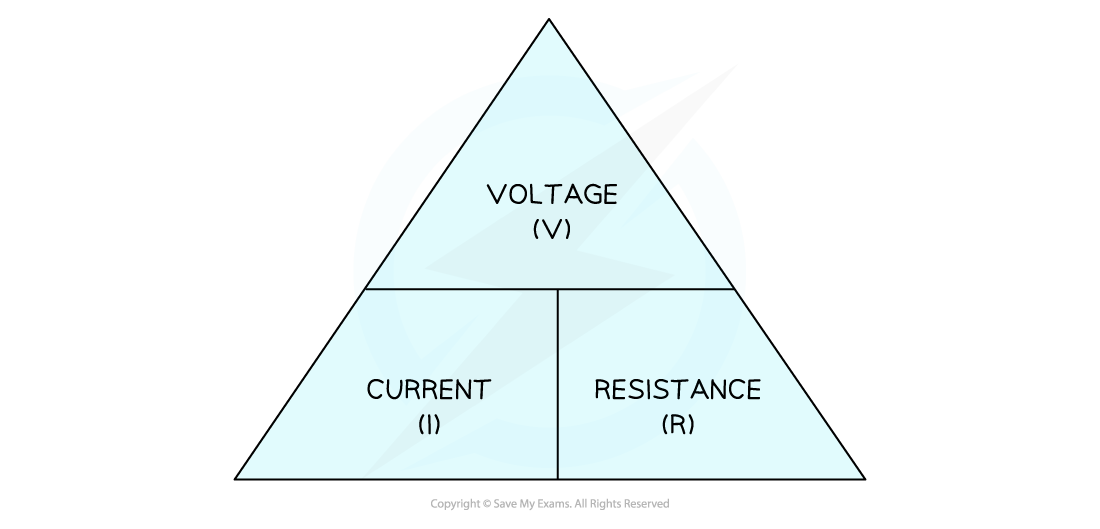
Cover up the variable you need to calculate, and the triangle shows you how the equation is arranged
To use an equation triangle:
Cover the variable to need to calculate
The remaining variables are positioned correctly for that equation
Multiplication across the base of the triangle
Division of the top of the triangle by the bottom
For example:
To calculate voltage,
To calculate resistance,
Examiner Tips and Tricks
For students taking the Foundation Tier exam paper, the equations will be given to you in the exam in the form that you will need to use them.
Worked Example
Calculate the current through a resistor of resistance 10 Ω if there is a voltage of 3 V across it.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Resistance, R = 10 Ω
Voltage, V = 3 V
Step 2: Write the equation relating resistance, potential difference and current
Step 3: Substitute in the values

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
