Development of New Energy Resources (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Environmental Management): Revision Note
Exam code: 0680
Hydrogen as an energy source
Why hydrogen can be used as an energy source
Hydrogen is a fuel that burns easily, releasing large amounts of energy
When hydrogen burns, it produces water vapour instead of carbon dioxide, so it can be a low-carbon energy source
Blue hydrogen fuel
Blue hydrogen—hydrogen fuel made from natural gas
Natural gas is reacted with steam in a process called steam methane reforming
This produces hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is captured and stored using carbon capture and storage (CCS)
Hydrogen can then be used as a clean fuel for vehicles, heating or electricity generation
Green hydrogen fuel
Green hydrogen—hydrogen fuel made using renewable energy
Electricity from solar, wind or hydropower is used for electrolysis
Electrolysis is the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity
Produces no carbon emissions during production
Hydrogen can be stored and used when needed, helping balance renewable energy supply
Ground source heat pumps
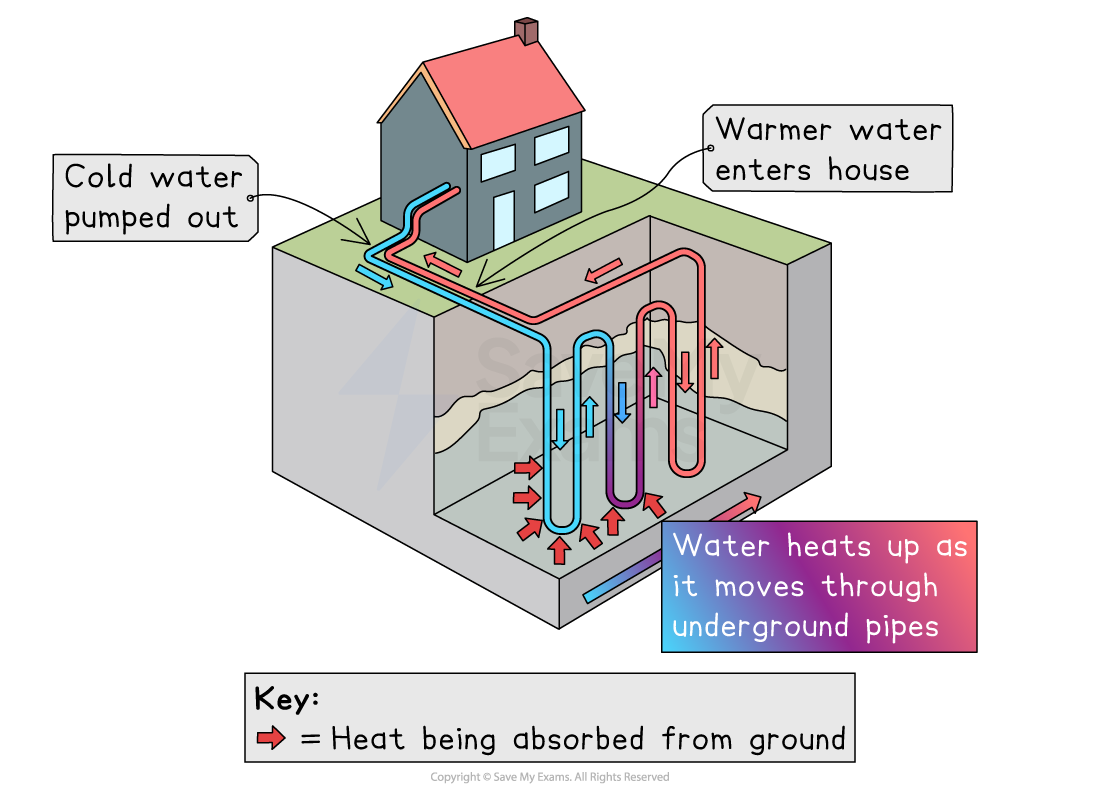
Ground source heat pumps: transfer of heat from the ground for heating
Pipes are buried underground, where the temperature stays fairly constant
A liquid (water mixed with antifreeze) flows through the pipes
The liquid absorbs heat from the ground
The pump transfers this heat into a building’s heating system
Provides low-carbon heating for homes, schools and offices
Works well in places with enough outdoor space for underground pipes
Examiner Tips and Tricks
For heat pumps, always include the phrase 'transfer of heat'. Examiners look for this because heat pumps move heat rather than create it. Missing this wording can lose marks.
Air source heat pumps
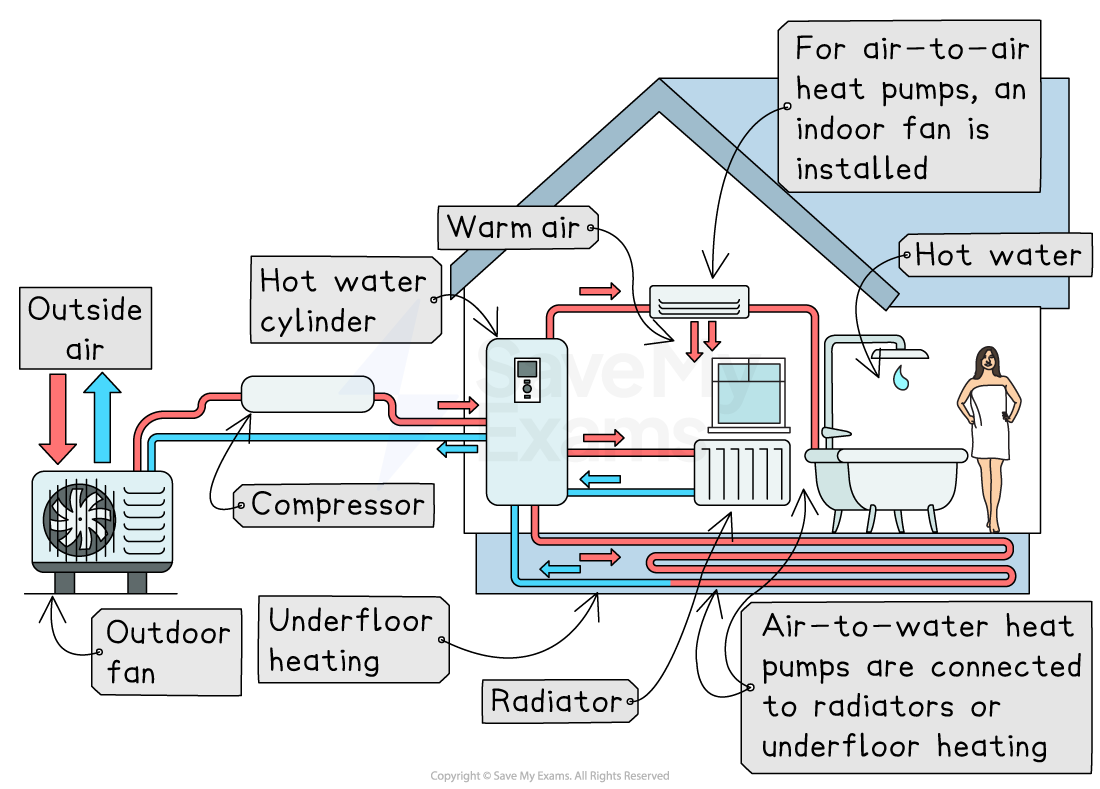
Air source heat pumps: transfer of heat from the air for heating
A fan draws in outside air, even on cold days
A refrigerant fluid absorbs heat from the air
A compressor then compresses the air, increasing its temperature
The heat is then transferred indoors
Can heat radiators, underfloor heating, or hot water
Easier to install than ground source systems because they stay above ground
More effective in mild climates where air temperatures stay higher

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
